Unit 3 Exam Level Questions
... A Increases the rate of the forward reaction only B Increases the rate of the reverse reaction only C Increases the rate of both the forward and reverse reactions D Changes the position of the equilibrium of the reaction 2. In which of the following systems will the equilibrium be unaffected by a ch ...
... A Increases the rate of the forward reaction only B Increases the rate of the reverse reaction only C Increases the rate of both the forward and reverse reactions D Changes the position of the equilibrium of the reaction 2. In which of the following systems will the equilibrium be unaffected by a ch ...
Reaction Stoichiometry
... Carbon reacts with steam to produce hydrogen and carbon monoxide. If 2.40 mol of carbon are exposed to 3.10 mol of steam, identify the limiting reactant. How many moles of each product are formed? What mass of each product is formed? ...
... Carbon reacts with steam to produce hydrogen and carbon monoxide. If 2.40 mol of carbon are exposed to 3.10 mol of steam, identify the limiting reactant. How many moles of each product are formed? What mass of each product is formed? ...
Unit 2 Chemical Reactions
... a) simplest type is when compound breaks into its component elements ____ H2O (l) ------> ____ H2 (g) + ____O2 (g) b) carbonates usually decompose into carbon dioxide plus the metal oxide when heated ___CaCO3 (s) ...
... a) simplest type is when compound breaks into its component elements ____ H2O (l) ------> ____ H2 (g) + ____O2 (g) b) carbonates usually decompose into carbon dioxide plus the metal oxide when heated ___CaCO3 (s) ...
Formulation - Good Hope School
... Complete and balance the half-equation below to show the reaction taking place at the cathode during electroplating. [1 mark] H2CrO4 + ___________ → _________________________________ ...
... Complete and balance the half-equation below to show the reaction taking place at the cathode during electroplating. [1 mark] H2CrO4 + ___________ → _________________________________ ...
General and Organic Chemistry Review Primer
... the number of protons and neutrons. Calculating an element’s mass number is complicated by the existence of isotopes, atoms of an element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Many naturally occurring elements exist as a mixture of isotopes. For example, carbon has three ...
... the number of protons and neutrons. Calculating an element’s mass number is complicated by the existence of isotopes, atoms of an element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Many naturally occurring elements exist as a mixture of isotopes. For example, carbon has three ...
Document
... Magnesium has to be heated before it will start to react with oxygen in the air, but once it starts reacting it produces lots of heat and a bright white light (another form of energy). When the reaction is over a white powdery substance has replaced the shiny, malleable metal. This white ...
... Magnesium has to be heated before it will start to react with oxygen in the air, but once it starts reacting it produces lots of heat and a bright white light (another form of energy). When the reaction is over a white powdery substance has replaced the shiny, malleable metal. This white ...
OCR_AS_Level_Chemistry_Unit_F321_Atoms
... o Most are insoluble in polar solvents, like water, because they do not interact with the dipoles in the solvent. Alcohols, however, can hydrogen bond to water molecules o Tend to dissolve in non-polar organic solvents, like cyclohexane, because the solvent can interact with the simple covalent subs ...
... o Most are insoluble in polar solvents, like water, because they do not interact with the dipoles in the solvent. Alcohols, however, can hydrogen bond to water molecules o Tend to dissolve in non-polar organic solvents, like cyclohexane, because the solvent can interact with the simple covalent subs ...
Name AP Chemistry Take Home Quiz – Due Thursday, 1/9/2014
... b. H+ acts as the oxidizing agent 2c. SO3 acts as the reducing agent d. MnO4 is oxidized e. SO32- is reduced 17. Equal volumes of 0.10-molar H3PO4 and 0.20-molar KOH are mixed. After equilibrium is established, the type of ion in solution in largest concentration, other than the K+ ion, is a. H2PO4¯ ...
... b. H+ acts as the oxidizing agent 2c. SO3 acts as the reducing agent d. MnO4 is oxidized e. SO32- is reduced 17. Equal volumes of 0.10-molar H3PO4 and 0.20-molar KOH are mixed. After equilibrium is established, the type of ion in solution in largest concentration, other than the K+ ion, is a. H2PO4¯ ...
Batteries are all over the place -- in our cars, our
... current to the battery at the right voltage, lead and lead dioxide form again on the plates so you can reuse the battery over and over. In a zinc-carbon battery, there is no easy way to reverse the reaction because there is no easy way to get hydrogen gas back into the electrolyte. Modern Battery Ch ...
... current to the battery at the right voltage, lead and lead dioxide form again on the plates so you can reuse the battery over and over. In a zinc-carbon battery, there is no easy way to reverse the reaction because there is no easy way to get hydrogen gas back into the electrolyte. Modern Battery Ch ...
Unit 8- The Mole
... 6. Reheat the crucible and salt for two minutes and then cool and record the mass again. 7. The final two masses should be within 0.02 g of one another. If they are not, repeat the last two ...
... 6. Reheat the crucible and salt for two minutes and then cool and record the mass again. 7. The final two masses should be within 0.02 g of one another. If they are not, repeat the last two ...
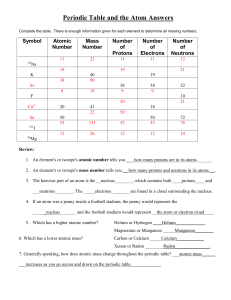
Periodic Table and the Atom Answers
... c) At a smaller volume the atoms will have less room to move around, so they will collide with the sides more often. d) The initial statement is false. Gas pressures do not increase when the volume is decreased. 6) What are the five assumptions we make about an ideal gas? ...
... c) At a smaller volume the atoms will have less room to move around, so they will collide with the sides more often. d) The initial statement is false. Gas pressures do not increase when the volume is decreased. 6) What are the five assumptions we make about an ideal gas? ...
Stoichiometry – Chapter 9
... 4. The fizz produced when some antacid tablets are dropped into water is created by the production of carbon dioxide during the reaction between sodium bicarbonate and citric acid. 3NaHCO3 + H 3C6 H 5O7 → 3CO 2 + 3H 2O + Na 3C6 H 5O7 Suppose 2.0 grams of sodium bicarbonate and 0.50 g of citric acid ...
... 4. The fizz produced when some antacid tablets are dropped into water is created by the production of carbon dioxide during the reaction between sodium bicarbonate and citric acid. 3NaHCO3 + H 3C6 H 5O7 → 3CO 2 + 3H 2O + Na 3C6 H 5O7 Suppose 2.0 grams of sodium bicarbonate and 0.50 g of citric acid ...
112- Unit I -Electrochem -pdf
... Determining the pH of a solution by measuring the Ecell: Here we will calculate the concentration of a single ionic species from the experimentally measured potential of a carefully designed cell. A Cu/H2 cell is used to measure the [H+] concentration. Voltage can be measured when the Cu electrode ...
... Determining the pH of a solution by measuring the Ecell: Here we will calculate the concentration of a single ionic species from the experimentally measured potential of a carefully designed cell. A Cu/H2 cell is used to measure the [H+] concentration. Voltage can be measured when the Cu electrode ...
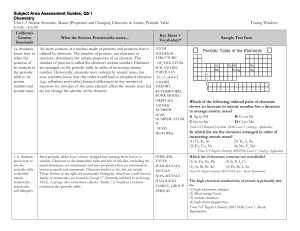
Subject Area Assessment Guides
... Group III) have three. Unfilled energy levels are also available for bonding. For example, Group 16, the chalcogens, has room for two more electrons; and Group 17, the halogens, has room for one more electron to fill its outermost energy level. To find the number of electrons available for bonding o ...
... Group III) have three. Unfilled energy levels are also available for bonding. For example, Group 16, the chalcogens, has room for two more electrons; and Group 17, the halogens, has room for one more electron to fill its outermost energy level. To find the number of electrons available for bonding o ...
physical setting chemistry
... discoveries important to science today. According to a legend, Hiero, the king of Syracuse, commanded Archimedes to find out if the royal crown was made of gold, only. The king suspected that the crown consisted of a mixture of gold, tin, and copper. Archimedes measured the mass of the crown and the ...
... discoveries important to science today. According to a legend, Hiero, the king of Syracuse, commanded Archimedes to find out if the royal crown was made of gold, only. The king suspected that the crown consisted of a mixture of gold, tin, and copper. Archimedes measured the mass of the crown and the ...
Solar Energy, Kit #1:
... requirements of humanity, maximizing its efficiency as a renewable energy source is essential. At this time, we use a significant fraction of this energy but we could learn to use it even more effectively in the future. Background: The process of photosynthesis involves the use of light energy to co ...
... requirements of humanity, maximizing its efficiency as a renewable energy source is essential. At this time, we use a significant fraction of this energy but we could learn to use it even more effectively in the future. Background: The process of photosynthesis involves the use of light energy to co ...
5. Stoichiometry - Sakshi Education
... • In O2F2 and OF2 oxygen oxidation states are +1 and +2 respectively. • Transition elements exhibit more than one oxidation state. • Osmium and Ruthenium show the highest oxidation state i.e. +8. • The oxidation state of any atom in its elementary state is zero. • Nitrogen exhibits large number of o ...
... • In O2F2 and OF2 oxygen oxidation states are +1 and +2 respectively. • Transition elements exhibit more than one oxidation state. • Osmium and Ruthenium show the highest oxidation state i.e. +8. • The oxidation state of any atom in its elementary state is zero. • Nitrogen exhibits large number of o ...
CHEMISTRY SEC 06 SYLLABUS
... noble gases and carbon dioxide. An experimental determination of the percentage composition by volume of nitrogen and oxygen in air. Air pollution - see Section 5.3(e). Handling techniques for preparation and collection of gases, including the use of the gas syringe. Principle of the extraction of o ...
... noble gases and carbon dioxide. An experimental determination of the percentage composition by volume of nitrogen and oxygen in air. Air pollution - see Section 5.3(e). Handling techniques for preparation and collection of gases, including the use of the gas syringe. Principle of the extraction of o ...
Chapter 8 - Inorganic carbon chemistry
... formed, which is mainly calcium silicate. More details of the extraction of iron and its conversion into steel are given in Chapter 9. Manufacture of cement and concrete Limestone (or chalk) is mixed with clay (or shale) in a heated rotary kiln, using coal or oil as the fuel (Figure 8.5). The materi ...
... formed, which is mainly calcium silicate. More details of the extraction of iron and its conversion into steel are given in Chapter 9. Manufacture of cement and concrete Limestone (or chalk) is mixed with clay (or shale) in a heated rotary kiln, using coal or oil as the fuel (Figure 8.5). The materi ...
reactions taking place within cells
... - Organic compounds thermodynamically unstable in the presence of oxygen CH4(l) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) (-)H But activation energies of the reactions with oxygen are high so organic compounds are kinetically stable at temperatures on earth If alkane and oxygen mixed first explosion will result ...
... - Organic compounds thermodynamically unstable in the presence of oxygen CH4(l) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) (-)H But activation energies of the reactions with oxygen are high so organic compounds are kinetically stable at temperatures on earth If alkane and oxygen mixed first explosion will result ...
English Medium
... 2. Explain the activity that you have conducted to show that the focal length of a lens depends on adjacent medium. 3. An object is placed on the principle axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Draw ray diagrams to show the formation of image in the following situations. i) Object is placed a ...
... 2. Explain the activity that you have conducted to show that the focal length of a lens depends on adjacent medium. 3. An object is placed on the principle axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. Draw ray diagrams to show the formation of image in the following situations. i) Object is placed a ...
Writing Net Ionic Equations
... sulfide. A typical reaction producing hydrogen sulfide gas is: FeS (s) + 2HCl (aq) → FeCl2 (aq) + H2S (g) NOTE: Be aware of reactions involving the formation of carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, ammonia and hydrogen sulfide gases on the AP exam. Over the years these reactions have appeared many, many ...
... sulfide. A typical reaction producing hydrogen sulfide gas is: FeS (s) + 2HCl (aq) → FeCl2 (aq) + H2S (g) NOTE: Be aware of reactions involving the formation of carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, ammonia and hydrogen sulfide gases on the AP exam. Over the years these reactions have appeared many, many ...
CHEMISTRY SEC 06 SYLLABUS
... noble gases and carbon dioxide. An experimental determination of the percentage composition by volume of nitrogen and oxygen in air. Air pollution - see Section 5.3(e). Handling techniques for preparation and collection of gases, including the use of the gas syringe. Principle of the extraction of o ...
... noble gases and carbon dioxide. An experimental determination of the percentage composition by volume of nitrogen and oxygen in air. Air pollution - see Section 5.3(e). Handling techniques for preparation and collection of gases, including the use of the gas syringe. Principle of the extraction of o ...
CHEMISTRY SEC 06 SYLLABUS
... noble gases and carbon dioxide. An experimental determination of the percentage composition by volume of nitrogen and oxygen in air. Air pollution - see Section 5.3(e). Handling techniques for preparation and collection of gases, including the use of the gas syringe. Principle of the extraction of o ...
... noble gases and carbon dioxide. An experimental determination of the percentage composition by volume of nitrogen and oxygen in air. Air pollution - see Section 5.3(e). Handling techniques for preparation and collection of gases, including the use of the gas syringe. Principle of the extraction of o ...
Artificial photosynthesis

Artificial photosynthesis is a chemical process that replicates the natural process of photosynthesis, a process that converts sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates and oxygen. The term is commonly used to refer to any scheme for capturing and storing the energy from sunlight in the chemical bonds of a fuel (a solar fuel). Photocatalytic water splitting converts water into Hydrogen Ions and oxygen, and is a main research area in artificial photosynthesis. Light-driven carbon dioxide reduction is another studied process, replicating natural carbon fixation.Research developed in this field encompasses design and assembly of devices (and their components) for the direct production of solar fuels, photoelectrochemistry and its application in fuel cells, and engineering of enzymes and photoautotrophic microorganisms for microbial biofuel and biohydrogen production from sunlight. Many, if not most, of the artificial approaches are bio-inspired, i.e., they rely on biomimetics.