Cephalic
... THE HEART is a hollow muscular organ that pumps blood into the large elastic arteries. It has four large chambers, seven great vessels, and four valves. Chambers of the heart and associated structures: I. Right Atrium – the superior chamber on the right side of the heart. It is separated from the r ...
... THE HEART is a hollow muscular organ that pumps blood into the large elastic arteries. It has four large chambers, seven great vessels, and four valves. Chambers of the heart and associated structures: I. Right Atrium – the superior chamber on the right side of the heart. It is separated from the r ...
Cardiovascular Quiz
... 13. The pulmonary trunk splits into right and left pulmonary arteries under the concavity of the _________ 14. Inflammation of the innermost lining of the heart is known as__________ 15. _________ are the structures through which the cusps of bicspid and tricuspid valves are anchored to the papillar ...
... 13. The pulmonary trunk splits into right and left pulmonary arteries under the concavity of the _________ 14. Inflammation of the innermost lining of the heart is known as__________ 15. _________ are the structures through which the cusps of bicspid and tricuspid valves are anchored to the papillar ...
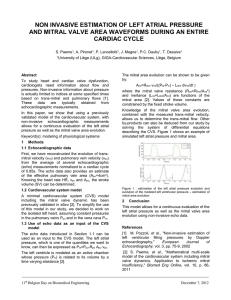
Simple method of assessment of right ventricular systolic function by
... systolic velocity of spectral tissue doppler sr' < 11 sm/s, fraction of RV area shortening in 4-chamber view < 40%, tricuspid annular peak systolic excursion < 19 mm). Conventional pulsed wave Doppler was also used for registration of motion of lateral border of tricuspid annulus (apical position of ...
... systolic velocity of spectral tissue doppler sr' < 11 sm/s, fraction of RV area shortening in 4-chamber view < 40%, tricuspid annular peak systolic excursion < 19 mm). Conventional pulsed wave Doppler was also used for registration of motion of lateral border of tricuspid annulus (apical position of ...
A Case of Left Atrial Sarcoma Presenting with Mitral Valve
... Case Report: 74 year-old woman with a distant history of coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction and percutaneous coronary intervention presented to the emergency department (ED) with several days of dry cough, malaise, shortness of breath, initially treated as community acquired pneumonia at ...
... Case Report: 74 year-old woman with a distant history of coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction and percutaneous coronary intervention presented to the emergency department (ED) with several days of dry cough, malaise, shortness of breath, initially treated as community acquired pneumonia at ...
Circulation
... – blood is pumped to the rest of the body, where it gives up oxygen and is carried back to the right atrium ...
... – blood is pumped to the rest of the body, where it gives up oxygen and is carried back to the right atrium ...
SSC – Perspectives On Medical Advances
... flow of blood through the aorta during surgery. Although the Potts/Smith shunt was technically easier to perform than the classical Blalock/Taussig operation it presented several postoperative complications including, excessive pulmonary blood flow, distortion of the pulmonary artery, and problems d ...
... flow of blood through the aorta during surgery. Although the Potts/Smith shunt was technically easier to perform than the classical Blalock/Taussig operation it presented several postoperative complications including, excessive pulmonary blood flow, distortion of the pulmonary artery, and problems d ...
Formation of the Cardiac Loop
... 2. Incorporation of sinus into Rt. atrium. 3. Sinuatrial node is formed. ...
... 2. Incorporation of sinus into Rt. atrium. 3. Sinuatrial node is formed. ...
519A ECG lvl 2 - WordPress.com
... The right atrium and right ventricle work as one unit to receive deoxygenated blood from the body and pump it to the lungs where it exchanges carbon dioxide for oxygen. The muscles in the right ventricle are relatively small because the pressure in the lungs is weak. The left atrium and left ventric ...
... The right atrium and right ventricle work as one unit to receive deoxygenated blood from the body and pump it to the lungs where it exchanges carbon dioxide for oxygen. The muscles in the right ventricle are relatively small because the pressure in the lungs is weak. The left atrium and left ventric ...
The physical examination of a child with cardio
... superior part of body(aa. Anonyma, Carotis, Subclavia sin.), About 10% of blood from right ventricle through pulmonary artery, gets in the not functioning lungs and through pulmonary veins is returning in the left atrium. The most part of blood from pulmonary artery, through arterial channel(Botallo ...
... superior part of body(aa. Anonyma, Carotis, Subclavia sin.), About 10% of blood from right ventricle through pulmonary artery, gets in the not functioning lungs and through pulmonary veins is returning in the left atrium. The most part of blood from pulmonary artery, through arterial channel(Botallo ...
Transposition of the Great Arteries Description and Epidemiology
... the incidence in siblings is no higher than that of the general population. Less than 10% of cases of TGA have associated to non-cardiac anomalies, which is less frequent than other CHD defects. As a result, genetic testing and family screening are not warranted for children with TGA. ...
... the incidence in siblings is no higher than that of the general population. Less than 10% of cases of TGA have associated to non-cardiac anomalies, which is less frequent than other CHD defects. As a result, genetic testing and family screening are not warranted for children with TGA. ...
Congenital Absence of Right Superior Vena Cava
... anomalous venous connections, orthotopic heart transplantation, and endomyocardial biopsies.1,2 Because the persistent left SVC receives the entire venous drainage of the head and thorax, an abnormally large coronary sinus might indicate an absent right SVC. Through a simple injection of agitated sa ...
... anomalous venous connections, orthotopic heart transplantation, and endomyocardial biopsies.1,2 Because the persistent left SVC receives the entire venous drainage of the head and thorax, an abnormally large coronary sinus might indicate an absent right SVC. Through a simple injection of agitated sa ...
Patent ductus arteriosus - British Heart Foundation
... Before a baby is born the arterial duct allows blood to go around their lungs. After the baby is born and the lungs fill with air, the arterial duct is no longer needed - it usually closes by itself within the first week after birth. Sometimes the duct fails to close by itself and remains open (pate ...
... Before a baby is born the arterial duct allows blood to go around their lungs. After the baby is born and the lungs fill with air, the arterial duct is no longer needed - it usually closes by itself within the first week after birth. Sometimes the duct fails to close by itself and remains open (pate ...
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS)
... right ventricular hypertrophy4 follows as seen in our case.Reduced end diastolic compliance hence leads to displacement of interventricular septum into left ventricular cavity. IPS is present from birth. Many patients are asymptomatic but severity of stenosis progresses with age . The murmur is disc ...
... right ventricular hypertrophy4 follows as seen in our case.Reduced end diastolic compliance hence leads to displacement of interventricular septum into left ventricular cavity. IPS is present from birth. Many patients are asymptomatic but severity of stenosis progresses with age . The murmur is disc ...
DEVELOPMENT OF THE HEART
... Vitelline veins drain blood from the yolk sac; their formation has associations with formation of the liver and the portal system. Umbilical veins bring oxygenated blood from the chorion (early placenta). There are two at the start. The right umbilical vein degenerates and disappears. The left umbil ...
... Vitelline veins drain blood from the yolk sac; their formation has associations with formation of the liver and the portal system. Umbilical veins bring oxygenated blood from the chorion (early placenta). There are two at the start. The right umbilical vein degenerates and disappears. The left umbil ...
European Respiratory Society Annual Congress 2012
... Medical Statistics, Informatics, and Intelligent Systems, Medical University of Vienna, Austria, 1090 . Body: PURPOSE: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is defined by a mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) ≥25mmHg. The disease can be further classified into pre- (pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, PCWP≤ ...
... Medical Statistics, Informatics, and Intelligent Systems, Medical University of Vienna, Austria, 1090 . Body: PURPOSE: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is defined by a mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) ≥25mmHg. The disease can be further classified into pre- (pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, PCWP≤ ...
Follow this link for more information.
... unable to take blood thinning medications. Since stroke is the third largest cause of death in atrial fibrillation pa tie nts, the new therapy is a potential life saver. Atrial Fibrillation affects an estimated three mi l lio n people. and patients with this condition are five times more likely to h ...
... unable to take blood thinning medications. Since stroke is the third largest cause of death in atrial fibrillation pa tie nts, the new therapy is a potential life saver. Atrial Fibrillation affects an estimated three mi l lio n people. and patients with this condition are five times more likely to h ...
Adult Congenital Heart Disease - STA HealthCare Communications
... Congenital heart disease (CHD) has an incidence of 0.8% in North America, which does not take into account bicuspid aortic valve (1 to 2% incidence) and mitral valve prolapse. This translates into a prevalence of 4 per 1,000 adults,1 compared to a prevalence of about 6% for ischemic heart disease2 i ...
... Congenital heart disease (CHD) has an incidence of 0.8% in North America, which does not take into account bicuspid aortic valve (1 to 2% incidence) and mitral valve prolapse. This translates into a prevalence of 4 per 1,000 adults,1 compared to a prevalence of about 6% for ischemic heart disease2 i ...
File
... Receives blood from superior and inferior vena cava and the coronary sinus Auricles on top of atria Help atria receive more blood ...
... Receives blood from superior and inferior vena cava and the coronary sinus Auricles on top of atria Help atria receive more blood ...
Sheep Heart Dissection
... The heart is a fist-sized muscle located to the left of the center of the chest. The heart contains four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. The lower chambers are called ventricles. Between each chamber, there are valves that prevent the backflow of blood. Blood is carried away from the ...
... The heart is a fist-sized muscle located to the left of the center of the chest. The heart contains four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. The lower chambers are called ventricles. Between each chamber, there are valves that prevent the backflow of blood. Blood is carried away from the ...
The heart is an extraordinary organ that has incredible endurance
... ventricles pumps blood through the heart Superior/inferior vena cava Right atrium Tricuspid valve Right ventricle Pulmonary valve Pulmonary artery ...
... ventricles pumps blood through the heart Superior/inferior vena cava Right atrium Tricuspid valve Right ventricle Pulmonary valve Pulmonary artery ...
standard operating procedure
... 3. Locate the right and left atria on top of the ventricles and compare their thickness. The walls of the atria look quite different from those of the ventricles. Note the fat surrounding the atria. 4. Locate the large blood vessels attached to the atria. The right atrium is connected to the body by ...
... 3. Locate the right and left atria on top of the ventricles and compare their thickness. The walls of the atria look quite different from those of the ventricles. Note the fat surrounding the atria. 4. Locate the large blood vessels attached to the atria. The right atrium is connected to the body by ...
The ECG hypertrophy of the right atrium and the right ventricle, the
... rheumatism, as well as signs of left ventricular hypertrophy on electrocardiogram and echocardiogram, then soft and nezvuchnye timbre noise is functional. ? ● If with systolic murmur patient has palpitations, shortness of breath and shortness of breath on exertion or at rest, he complains of a dull ...
... rheumatism, as well as signs of left ventricular hypertrophy on electrocardiogram and echocardiogram, then soft and nezvuchnye timbre noise is functional. ? ● If with systolic murmur patient has palpitations, shortness of breath and shortness of breath on exertion or at rest, he complains of a dull ...
Anatomy of the conduction system
... are bundles of atrial tissue to which some have ascribed enhanced conduction properties, there are probably really no specialized interatrial tracts (i.e., like the Purkinje fibers). Function of the sinus node is influenced profoundly by autonomic nervous system tone – increases in parasympathetic t ...
... are bundles of atrial tissue to which some have ascribed enhanced conduction properties, there are probably really no specialized interatrial tracts (i.e., like the Purkinje fibers). Function of the sinus node is influenced profoundly by autonomic nervous system tone – increases in parasympathetic t ...
Atrial septal defect

Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect in which blood flows between the atria (upper chambers) of the heart. Normally, the atria are separated by a dividing wall, the interatrial septum. If this septum is defective or absent, then oxygen-rich blood can flow directly from the left side of the heart to mix with the oxygen-poor blood in the right side of the heart, or vice versa. This can lead to lower-than-normal oxygen levels in the arterial blood that supplies the brain, organs, and tissues. However, an ASD may not produce noticeable signs or symptoms, especially if the defect is small.A ""shunt"" is the presence of a net flow of blood through the defect, either from left to right or right to left. The amount of shunting present, if any, determines the hemodynamic significance of the ASD. A ""right-to-left-shunt"" typically poses the more dangerous scenario.During development of the fetus, the interatrial septum develops to separate the left and right atria. However, a hole in the septum called the foramen ovale, allows blood from the right atrium to enter the left atrium during fetal development. This opening allows blood to bypass the nonfunctional fetal lungs while the fetus obtains its oxygen from the placenta. A layer of tissue called the septum primum acts as a valve over the foramen ovale during fetal development. After birth, the pressure in the right side of the heart drops as the lungs open and begin working, causing the foramen ovale to close entirely. In approximately 25% of adults, the foramen ovale does not entirely seal. In these cases, any elevation of the pressure in the pulmonary circulatory system (due to pulmonary hypertension, temporarily while coughing, etc.) can cause the foramen ovale to remain open. This is known as a patent foramen ovale (PFO), which is a type of atrial septal defect.