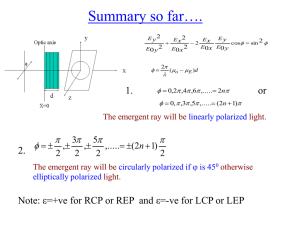
optically active substances.
... LCP) beams with same amplitude and wavelength. Any plane polarized light wave can be obtained as a superposition of a left circularly polarized and a right circularly polarized light wave, whose amplitude is identical. This is the base of Fresnel’s theory of optical rotation Try it mathematically to ...
... LCP) beams with same amplitude and wavelength. Any plane polarized light wave can be obtained as a superposition of a left circularly polarized and a right circularly polarized light wave, whose amplitude is identical. This is the base of Fresnel’s theory of optical rotation Try it mathematically to ...
Part 4 - MZA Associates Corporation
... where the phase (green waves, f) is equal to a particular value (r). • Light travels in a straight line (light blue arrows) normal to the wavefront. • 2p discontinuities, intensity variations, and interference complicate matters. ...
... where the phase (green waves, f) is equal to a particular value (r). • Light travels in a straight line (light blue arrows) normal to the wavefront. • 2p discontinuities, intensity variations, and interference complicate matters. ...
- Free Documents
... Different LED chip technologies emit light in specific regions of the visible light spectrum and produce different intensity levels. Blue and white LEDs are much more expensive than the other colours. amber. The colour of an LED is determined by the semiconductor material. The coloured packages are ...
... Different LED chip technologies emit light in specific regions of the visible light spectrum and produce different intensity levels. Blue and white LEDs are much more expensive than the other colours. amber. The colour of an LED is determined by the semiconductor material. The coloured packages are ...
Synchrotrons
... Electrons that collide with the anode help complete the circuit. Electrons that do not pass through the hole in the anode complete the circuit. ...
... Electrons that collide with the anode help complete the circuit. Electrons that do not pass through the hole in the anode complete the circuit. ...
University of Groningen Microscopic derivation of electromagnetic
... to as the Abraham–Minkowski controversy. The Einstein–Laub theory is intended to include the electrostriction and magnetostriction effects, but it turned out to be in disagreement with many experiments. By using the Helmholtz force density, which in fact was originally written for timeindependent ma ...
... to as the Abraham–Minkowski controversy. The Einstein–Laub theory is intended to include the electrostriction and magnetostriction effects, but it turned out to be in disagreement with many experiments. By using the Helmholtz force density, which in fact was originally written for timeindependent ma ...
... contributions from different NOA mechanism and nonlinear rotation of polarization ellipse takes place and therefore we cannot distinguish between these contributions. In some cases polarization tends to become circular, the sign of rotation depending on the orientation of initial polarization with e ...
Perturbation Theory
... space. The coefficients dµ would all be zero in the λ → 0 limit so they are at most first order in λ. Then that last term is second order in λ. You might then argue that we should drop the last term in Equation ??, but probably hβ | H1 | µi is more important that hν | H1 | µi since it connects to th ...
... space. The coefficients dµ would all be zero in the λ → 0 limit so they are at most first order in λ. Then that last term is second order in λ. You might then argue that we should drop the last term in Equation ??, but probably hβ | H1 | µi is more important that hν | H1 | µi since it connects to th ...
Light Measurement Handbook
... While these thermal detectors have a very flat spectral responsivity, they suffer from temperature sensitivity, and usually must be artificially cooled. Another strategy employed by thermal detectors is to modulate incident light with a chopper. This allows the detector to measure differentially bet ...
... While these thermal detectors have a very flat spectral responsivity, they suffer from temperature sensitivity, and usually must be artificially cooled. Another strategy employed by thermal detectors is to modulate incident light with a chopper. This allows the detector to measure differentially bet ...
physics - Regents
... Base your answers to questions 71 through 75 on the information below and on your knowledge of physics. Pluto orbits the Sun at an average distance of 5.91 × 1012 meters. Pluto’s diameter is 2.30 × 106 meters and its mass is 1.31 × 1022 kilograms. Charon orbits Pluto with their centers separated by ...
... Base your answers to questions 71 through 75 on the information below and on your knowledge of physics. Pluto orbits the Sun at an average distance of 5.91 × 1012 meters. Pluto’s diameter is 2.30 × 106 meters and its mass is 1.31 × 1022 kilograms. Charon orbits Pluto with their centers separated by ...
Thomas Young (scientist)
.jpg?width=300)
Thomas Young (13 June 1773 – 10 May 1829) was an English polymath and physician. Young made notable scientific contributions to the fields of vision, light, solid mechanics, energy, physiology, language, musical harmony, and Egyptology. He ""made a number of original and insightful innovations""in the decipherment of Egyptian hieroglyphs (specifically the Rosetta Stone) before Jean-François Champollion eventually expanded on his work. He was mentioned by, among others, William Herschel, Hermann von Helmholtz, James Clerk Maxwell, and Albert Einstein. Young has been described as ""The Last Man Who Knew Everything"".