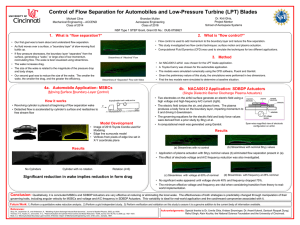
Implementation of externally-applied magnetic fields to a
... for magnetic divergence should only be applied to Faraday’s equation.10 This result was later derived by Dellar using relativist energy-momentum conservation taken to the non-relativistic limit.11 Thus, the corrected 8-wave method preserves conservation of mass, momentum, and energy, while maintaini ...
... for magnetic divergence should only be applied to Faraday’s equation.10 This result was later derived by Dellar using relativist energy-momentum conservation taken to the non-relativistic limit.11 Thus, the corrected 8-wave method preserves conservation of mass, momentum, and energy, while maintaini ...
from rheology to molecular detail
... The effective viscosity ηeff is the proportionality coefficient between the stress tensor and the effective strain tensor. These three quantities are coupled and depend on the suspension and flow. The effective viscosity calculated for shear flow is different than for e.g. straining flow. In this re ...
... The effective viscosity ηeff is the proportionality coefficient between the stress tensor and the effective strain tensor. These three quantities are coupled and depend on the suspension and flow. The effective viscosity calculated for shear flow is different than for e.g. straining flow. In this re ...
Chapter 5 Pressure Variation in Flowing Fluids
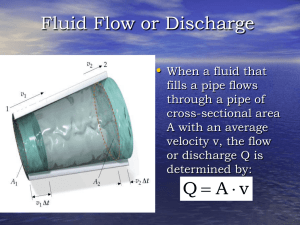
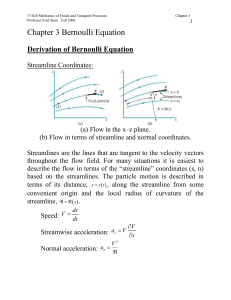
... For such devices the flowrate of liquid over the top of the weir plate is dependent on the weir height, Pw, the width of the channel, b, and the head, H, of the water above the top of the weir. Between points (1) and (2) the pressure and gravitational fields cause the fluid to accelerate from veloci ...
... For such devices the flowrate of liquid over the top of the weir plate is dependent on the weir height, Pw, the width of the channel, b, and the head, H, of the water above the top of the weir. Between points (1) and (2) the pressure and gravitational fields cause the fluid to accelerate from veloci ...