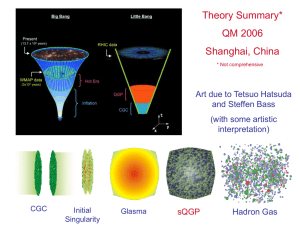
Neutrino Oscillations
... spring with a small spring constant). The first pendulum is set in motion by the experimenter while the second begins at rest. Over time, the second pendulum begins to swing under the influence of the spring, while the first pendulum's amplitude decreases as it loses energy to the second. Eventually ...
... spring with a small spring constant). The first pendulum is set in motion by the experimenter while the second begins at rest. Over time, the second pendulum begins to swing under the influence of the spring, while the first pendulum's amplitude decreases as it loses energy to the second. Eventually ...
A. What Is an Atom?
... with Democritus’s ideas. He believed that you would never end up with a particle that could not be cut. Most people believed Aristotle, even though Democritus was right: Matter is made of particles, which we call atoms. An atom is the smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still ...
... with Democritus’s ideas. He believed that you would never end up with a particle that could not be cut. Most people believed Aristotle, even though Democritus was right: Matter is made of particles, which we call atoms. An atom is the smallest particle into which an element can be divided and still ...
Higgs colloquium - High Energy Physics
... Enough energy to produce the Higgs. However, the rate is expected to be very small - 3fb-1 of data per experiment ...
... Enough energy to produce the Higgs. However, the rate is expected to be very small - 3fb-1 of data per experiment ...
Neutrons Hologram
... The intriguing interplay between collective and single-particle excitations in an exotic nucleus Nuclear reactions are among the most important processes that drive our Universe. In our Sun nuclear fusion provides the energy for the sun to radiate. In more violent cosmic events neutron capture react ...
... The intriguing interplay between collective and single-particle excitations in an exotic nucleus Nuclear reactions are among the most important processes that drive our Universe. In our Sun nuclear fusion provides the energy for the sun to radiate. In more violent cosmic events neutron capture react ...
STEM Fair Introduction Beanium Isotopes Lab
... Neutrons are made of one “up” quark and two “down” quarks ...
... Neutrons are made of one “up” quark and two “down” quarks ...
File
... Describe the motion of a charged particle introduced in a radial electric field. Describe the motion of a charged particle introduced in a uniform electric field. Understand that the volt is a measure of the electrical potential energy given to each coulomb of charge in a uniform electric field. Und ...
... Describe the motion of a charged particle introduced in a radial electric field. Describe the motion of a charged particle introduced in a uniform electric field. Understand that the volt is a measure of the electrical potential energy given to each coulomb of charge in a uniform electric field. Und ...
Chapter 4: Old Models of the Atom
... Neutrons were discovered by James Chadwick in 1932. However, this experiment is really hard to understand, so I’m not going to talk about it. ...
... Neutrons were discovered by James Chadwick in 1932. However, this experiment is really hard to understand, so I’m not going to talk about it. ...
In order to integrate general relativity with quantum
... the parallel between that space time kinematic infrastructure and the Poincare symmetry group and position operators that replaced it thus giving our current “kinematic theory”, Relativistic Quantum Theory (RQT). Likewise one notes the parallel between the earlier phenomenological forces of gravity ...
... the parallel between that space time kinematic infrastructure and the Poincare symmetry group and position operators that replaced it thus giving our current “kinematic theory”, Relativistic Quantum Theory (RQT). Likewise one notes the parallel between the earlier phenomenological forces of gravity ...
The Weak Interaction - University of Warwick
... mass) are ultra-relativistic, this implies that all neutrinos have left-handed chirality, and antineutrinos have right-handed chirality. The neutrinos can only be made in weak interactions and so are all made as left-handed chiral particles. They have no choice. This is an important but subtle point ...
... mass) are ultra-relativistic, this implies that all neutrinos have left-handed chirality, and antineutrinos have right-handed chirality. The neutrinos can only be made in weak interactions and so are all made as left-handed chiral particles. They have no choice. This is an important but subtle point ...
OscSNS: Precision Neutrino Measurements at
... The flagship cross section analyses of OscSNS are the elastic scattering νee-→ νee- (NC and CC), NC νµe-→ νµe-, NC anti-νµe-→ antiνµe-, NC νµC→ νµC, and the CC νe12C→e-12N interactions. The current world's best measurement of the νee-→ νee- interaction arises in a sample of only 191 events [6], and ...
... The flagship cross section analyses of OscSNS are the elastic scattering νee-→ νee- (NC and CC), NC νµe-→ νµe-, NC anti-νµe-→ antiνµe-, NC νµC→ νµC, and the CC νe12C→e-12N interactions. The current world's best measurement of the νee-→ νee- interaction arises in a sample of only 191 events [6], and ...
transparencies - Rencontres de Blois
... • Might be remnant of SN 393 (1600 years old). • Central compact object is present, therefore SN II. Possibly exploded in wind-blown shell recently reached by the shock. • No thermal emission detected. Most likely reason that the ambient density is low (< 0.02 cm-3). Consistent with the size for rea ...
... • Might be remnant of SN 393 (1600 years old). • Central compact object is present, therefore SN II. Possibly exploded in wind-blown shell recently reached by the shock. • No thermal emission detected. Most likely reason that the ambient density is low (< 0.02 cm-3). Consistent with the size for rea ...
Understanding Nothing - University of Southampton
... A flash of light causes a spherical wave front even if you move relative to source This only makes sense if space and time mix! ...
... A flash of light causes a spherical wave front even if you move relative to source This only makes sense if space and time mix! ...
Computation of hadronic two-point functions in Lattice QCD
... They carry so-called colour charges and interact via the strong (= colour) interaction. This force is described by Quantum Chromodynamics. In addition, quarks carry electric charges (u, c, t : + 23 e, d, s, b : − 13 e) and weak charges. They interact with other fermions both electromagnetically and ...
... They carry so-called colour charges and interact via the strong (= colour) interaction. This force is described by Quantum Chromodynamics. In addition, quarks carry electric charges (u, c, t : + 23 e, d, s, b : − 13 e) and weak charges. They interact with other fermions both electromagnetically and ...