A Microscopic Approach to Van-der
... consisting of NA particles and a cluster B consisting of NB particles as the sum over all two-body interactions between a particle i in cluster A and a particle j in cluster B. The potential energy of the interaction is then given by ...
... consisting of NA particles and a cluster B consisting of NB particles as the sum over all two-body interactions between a particle i in cluster A and a particle j in cluster B. The potential energy of the interaction is then given by ...
The Electron and the Holographic Mass Solution
... This solution, as well as being significantly accurate, gives us insight into the physical and mechanical dynamics of the granular Planck scale vacuum structure of spacetime and its role in the source of angular momentum, mass and charge. The definition clearly demonstrates that the differential an ...
... This solution, as well as being significantly accurate, gives us insight into the physical and mechanical dynamics of the granular Planck scale vacuum structure of spacetime and its role in the source of angular momentum, mass and charge. The definition clearly demonstrates that the differential an ...
B 0
... continuous (Lorentz (LV)) or discrete (T & CPT (CPTV)) and/or induced decoherence of quantum matter Parametrization: Standard Model Extension (SME) and beyond… Selected Tests in particle physics: From Cosmic photons and ultra-high energy neutrinos experimental to low-energy antiprotons & antimatter ...
... continuous (Lorentz (LV)) or discrete (T & CPT (CPTV)) and/or induced decoherence of quantum matter Parametrization: Standard Model Extension (SME) and beyond… Selected Tests in particle physics: From Cosmic photons and ultra-high energy neutrinos experimental to low-energy antiprotons & antimatter ...
Standard Model at the LHC (Lecture 1: Theoretical Recap) M. Schott
... Still usually use GF to express strength of weak interaction as the is the quantity that is precisely determined in muon decay Weak Current Summary Weak interaction is of form Vector-Axial-vector (V-A): ...
... Still usually use GF to express strength of weak interaction as the is the quantity that is precisely determined in muon decay Weak Current Summary Weak interaction is of form Vector-Axial-vector (V-A): ...
Spectral Reflectance and Emittance of Particulate
... at temperatures close to that of the sample and differ by about 5C. High signal-to-noise data are obtained with a sample surface temperature about 150C above the near-ambient interferometer and shield temperatures in about 20 min with a spectral resolution of about 3 cm-1. The spectral emittance (v) ...
... at temperatures close to that of the sample and differ by about 5C. High signal-to-noise data are obtained with a sample surface temperature about 150C above the near-ambient interferometer and shield temperatures in about 20 min with a spectral resolution of about 3 cm-1. The spectral emittance (v) ...
Electron and the Holographic Mass
... threshold of ~ 1MeV, below which it ‘appears’ point-like and structure-less [3]. ...
... threshold of ~ 1MeV, below which it ‘appears’ point-like and structure-less [3]. ...
Document
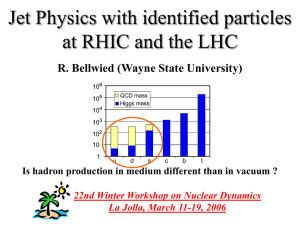
... show the color factor (non-Abelian energy loss ?). High pt strange baryon production in AA enhanced instead of suppressed compared to pp . Is this due to simple canonical suppression in pp ? Any predictions for charmed baryons ? Large associated particle yield in AA compared to pp. Long range Dh cor ...
... show the color factor (non-Abelian energy loss ?). High pt strange baryon production in AA enhanced instead of suppressed compared to pp . Is this due to simple canonical suppression in pp ? Any predictions for charmed baryons ? Large associated particle yield in AA compared to pp. Long range Dh cor ...
The search for magnetic monopoles
... charge, gD, and a mass of no more than 200 GeV/c 2. However, closer analysis showed that the track was probably produced instead by a platinum nucleus. Another monopole candidate was seen in 1982 in an experiment with a superconducting ring carried out by Blas Cabrera of Stanford University.9 The cu ...
... charge, gD, and a mass of no more than 200 GeV/c 2. However, closer analysis showed that the track was probably produced instead by a platinum nucleus. Another monopole candidate was seen in 1982 in an experiment with a superconducting ring carried out by Blas Cabrera of Stanford University.9 The cu ...
The Search for Matter--Anti-Matter Asymmetries in the
... couples fermions of the same generation. The Standard Model explains coupling between quark generations in terms of the Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa (CKM) matrix. d ...
... couples fermions of the same generation. The Standard Model explains coupling between quark generations in terms of the Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa (CKM) matrix. d ...
New insights into soft gluons and gravitons. In
... In QED, one may show that the exponent of the soft function contains only connected subdiagrams. By a subdiagram, we mean the graph that remains when the hard external lines have been removed. Examples of QED “webs” are shown in figure 2, and one can indeed see that they all correspond to connected ...
... In QED, one may show that the exponent of the soft function contains only connected subdiagrams. By a subdiagram, we mean the graph that remains when the hard external lines have been removed. Examples of QED “webs” are shown in figure 2, and one can indeed see that they all correspond to connected ...
Lee and Yang, Parity Violation Paper
... actions conserve parity. (Any small mixing of parities characterized by 5'&3&10—"would not aGect the arguments here. ) Consequently the p rays carry away definite parities. Thus the observed probability function must be an even function of y~. This property eliminates the possibility of forming a ps ...
... actions conserve parity. (Any small mixing of parities characterized by 5'&3&10—"would not aGect the arguments here. ) Consequently the p rays carry away definite parities. Thus the observed probability function must be an even function of y~. This property eliminates the possibility of forming a ps ...
Symmetrical FET Modeling
... equivalent circuit. Thus, a big opportunity of reducing the number of measurement points and the complexity of modeling is overlooked. Therefore, a new small-signal model is proposed to address the intrinsic symmetry present in such devices. Second, the small-signal parameters of the symmetrical mod ...
... equivalent circuit. Thus, a big opportunity of reducing the number of measurement points and the complexity of modeling is overlooked. Therefore, a new small-signal model is proposed to address the intrinsic symmetry present in such devices. Second, the small-signal parameters of the symmetrical mod ...