IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
... well-cleaned glass substrate was first immersed into cationic precursor (vessel1) (0.1M copper complex solution at pH ~8 kept at room temperature ), so the Cu2+ ions were adsorbed onto the substrate surface; (ii) then the substrate was rinsed with distilled water to remove loosely bonded Cu 2+ ions ...
... well-cleaned glass substrate was first immersed into cationic precursor (vessel1) (0.1M copper complex solution at pH ~8 kept at room temperature ), so the Cu2+ ions were adsorbed onto the substrate surface; (ii) then the substrate was rinsed with distilled water to remove loosely bonded Cu 2+ ions ...
High speed silicon based optical modulators based on carrier
... and electrical structure performances. Integrated Mach Zehnder interferometers and resonators are compared to convert phase modulation into intensity modulation. Finally, recent results on high speed and low loss silicon optical modulator using an asymmetric Mach Zehnder interferometer are presented ...
... and electrical structure performances. Integrated Mach Zehnder interferometers and resonators are compared to convert phase modulation into intensity modulation. Finally, recent results on high speed and low loss silicon optical modulator using an asymmetric Mach Zehnder interferometer are presented ...
3D–2D–3D photonic crystal heterostructures fabricated by direct
... easily characterized by electron microscopy, but they can be characterized by optical spectroscopy. It is clear that for incidence of light normal to the 2D plane, the structure is just a Fabry–Perot cavity. The corresponding spectra can then be directly compared with spectra obtained from (numerica ...
... easily characterized by electron microscopy, but they can be characterized by optical spectroscopy. It is clear that for incidence of light normal to the 2D plane, the structure is just a Fabry–Perot cavity. The corresponding spectra can then be directly compared with spectra obtained from (numerica ...
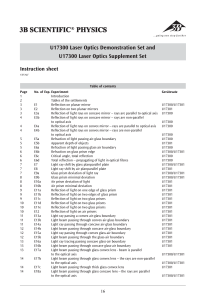
U17301 - 3B Scientific
... Reflection of light rays on concave mirror – rays are parallel to optical axis E3b Reflection of light rays on concave mirror – rays are non-parallel to optical axis E4a Reflection of light rays on convex mirror – rays are parallel to optical axis E4b Reflection of light rays on convex mirror – rays ...
... Reflection of light rays on concave mirror – rays are parallel to optical axis E3b Reflection of light rays on concave mirror – rays are non-parallel to optical axis E4a Reflection of light rays on convex mirror – rays are parallel to optical axis E4b Reflection of light rays on convex mirror – rays ...
Three-Dimensional Mapping of Near-Field Interactions via Single-Photon Tomography Benjamin D. Mangum,
... directly above the geometric center of the sphere, e.g., panel b corresponding to axis b′. Thus, we attribute the partial recovery in this case to the particular location with respect to the detailed shape of the tip-sample coupling map at which this approach curve was acquired. Specifically, at thi ...
... directly above the geometric center of the sphere, e.g., panel b corresponding to axis b′. Thus, we attribute the partial recovery in this case to the particular location with respect to the detailed shape of the tip-sample coupling map at which this approach curve was acquired. Specifically, at thi ...
Image reconstruction in diffuse optical tomography based on
... algorithm in which the light distribution within the imaging domain is approximated to provide a match to measured boundary data [21–23] and therefore providing an estimate to the optical parameters within the medium being imaged. The most commonly applied model for the estimation of NIR light propa ...
... algorithm in which the light distribution within the imaging domain is approximated to provide a match to measured boundary data [21–23] and therefore providing an estimate to the optical parameters within the medium being imaged. The most commonly applied model for the estimation of NIR light propa ...
The High Resolution Camera CXC Newsletter
... X-ray emitting shocks form. On the other end to the main sequence are the cool stars that produce X-ray emission in a magnetically heated corona like our sun. Stars of spectral type A lie between these regimes and should be X-ray dark. Yet, some of them have been detected in X-ray observations. One ...
... X-ray emitting shocks form. On the other end to the main sequence are the cool stars that produce X-ray emission in a magnetically heated corona like our sun. Stars of spectral type A lie between these regimes and should be X-ray dark. Yet, some of them have been detected in X-ray observations. One ...
IMPORTANT FEATURES FOR A RIGHT - pi
... The example c) in Fig. 1 corresponds to very important for practice case of creating a small laser spot with uniform intensity profile just in focal plane of a lens. Realizing this approach requires solving of the inverse problem – which intensity distribution should be at the entrance of a lens in ...
... The example c) in Fig. 1 corresponds to very important for practice case of creating a small laser spot with uniform intensity profile just in focal plane of a lens. Realizing this approach requires solving of the inverse problem – which intensity distribution should be at the entrance of a lens in ...
Time-Domain Large-Signal Modeling of Traveling
... 2.4, much lower than no,g [12]. Because of the very low dispersion in a transmission line, the difference between RF phase velocity and RF group velocity is negligible [12, 14]. Hence we focus on slowing the RF phase velocity to force nRF,L to approach no,g. The p-n-junction capacitance (Cj) loading ...
... 2.4, much lower than no,g [12]. Because of the very low dispersion in a transmission line, the difference between RF phase velocity and RF group velocity is negligible [12, 14]. Hence we focus on slowing the RF phase velocity to force nRF,L to approach no,g. The p-n-junction capacitance (Cj) loading ...
4.1 Simulated Emission and Photon Amplification
... Calculate the Doppler broadened linewidths in frequency and wavelength for the He-Ne laser transition for λ = 632.8nm if the gas discharge temperature is about 127°C. The atomic mass of Ne is 20.2 g/mol. The laser tube length is 40 cm. Find: (a) the linewidth in the output wavelength spectrum (b) th ...
... Calculate the Doppler broadened linewidths in frequency and wavelength for the He-Ne laser transition for λ = 632.8nm if the gas discharge temperature is about 127°C. The atomic mass of Ne is 20.2 g/mol. The laser tube length is 40 cm. Find: (a) the linewidth in the output wavelength spectrum (b) th ...
Interferometry
Interferometry is a family of techniques in which waves, usually electromagnetic, are superimposed in order to extract information about the waves. Interferometry is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy (and its applications to chemistry), quantum mechanics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, remote sensing, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, and velocimetry.Interferometers are widely used in science and industry for the measurement of small displacements, refractive index changes and surface irregularities. In analytical science, interferometers are used in continuous wave Fourier transform spectroscopy to analyze light containing features of absorption or emission associated with a substance or mixture. An astronomical interferometer consists of two or more separate telescopes that combine their signals, offering a resolution equivalent to that of a telescope of diameter equal to the largest separation between its individual elements.