High-refractive-index composite materials for
... fiber. First, we notice that for frequencies outside of bandgaps, elevated material loss leads to flattening of the rapid oscillations in the fundamental mode loss. The explanation is that large material losses cause strong attenuation of the outgoing traveling waves inside the reflector over the se ...
... fiber. First, we notice that for frequencies outside of bandgaps, elevated material loss leads to flattening of the rapid oscillations in the fundamental mode loss. The explanation is that large material losses cause strong attenuation of the outgoing traveling waves inside the reflector over the se ...
Chapter 3 - Optoelectronics Research Centre
... glasses have pulled away. Using this method, it is also difficult to obtain clean surfaces. This is illustrated in Figure 3.2. When observed under an optical microscope, it shows a wedge shaped void or mound trailing way from each hole, pointing away from where the fibre had been scribed. While surf ...
... glasses have pulled away. Using this method, it is also difficult to obtain clean surfaces. This is illustrated in Figure 3.2. When observed under an optical microscope, it shows a wedge shaped void or mound trailing way from each hole, pointing away from where the fibre had been scribed. While surf ...
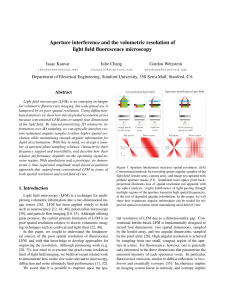
Aperture interference and the volumetric resolution of light field
... incorporate wave optics, they do not incorporate these wave optics considerations into their design criteria, and conclude that if the system dimensions are large, as is generally true in photography, then a geometric model is adequate. Additionally, for the random coded aperture, they conclude that ...
... incorporate wave optics, they do not incorporate these wave optics considerations into their design criteria, and conclude that if the system dimensions are large, as is generally true in photography, then a geometric model is adequate. Additionally, for the random coded aperture, they conclude that ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-ISSN: 2278-4861.
... matched (sync) then they are added together, resulting sine wave has twice the amplitude of the individual waves. In contrast, when two waves are completely out of sync, then resulting wave has no amplitude because two light waves cancel each other out [4]. Silicon is not considered to exhibit good ...
... matched (sync) then they are added together, resulting sine wave has twice the amplitude of the individual waves. In contrast, when two waves are completely out of sync, then resulting wave has no amplitude because two light waves cancel each other out [4]. Silicon is not considered to exhibit good ...
Experimental methods of molecular matter
... on experimental methods for handling the quantum motion of compound systems from diatomic molecules to clusters or biomolecules. Molecular quantum optics offers many challenges and innovative prospects: already the combination of two atoms into one molecule takes several well-established methods fro ...
... on experimental methods for handling the quantum motion of compound systems from diatomic molecules to clusters or biomolecules. Molecular quantum optics offers many challenges and innovative prospects: already the combination of two atoms into one molecule takes several well-established methods fro ...
Optical frequency combs: From frequency metrology to - JILA-PFC
... being determined with increasing precision using improved precision laser tools [16]. Optical frequency standards play an important role for applications in navigation or very long baseline interferometry, gravitational wave detection [17], optical communications [18], and modern length and frequenc ...
... being determined with increasing precision using improved precision laser tools [16]. Optical frequency standards play an important role for applications in navigation or very long baseline interferometry, gravitational wave detection [17], optical communications [18], and modern length and frequenc ...
New concept of laser fusion driver using Stimulated Brillouin
... phases are not matched. 2. Phase difference between the beams should be less than /4 for constructive interference at the boundary of the combination not give spatial spiking. 3. It is necessary to control the phases of the SBS waves to match the phase difference between the neighboring beams less ...
... phases are not matched. 2. Phase difference between the beams should be less than /4 for constructive interference at the boundary of the combination not give spatial spiking. 3. It is necessary to control the phases of the SBS waves to match the phase difference between the neighboring beams less ...
Influence of optical forces on nonlinear optical frequency conversion
... Optomechanical devices based on the transverse gradient force, generally consist of a substrate and a suspended waveguide [5] or two parallel waveguides [6]. The deformation contributes to the effective index change and has been widely used to tune the linear characteristics such as phase, coupling ...
... Optomechanical devices based on the transverse gradient force, generally consist of a substrate and a suspended waveguide [5] or two parallel waveguides [6]. The deformation contributes to the effective index change and has been widely used to tune the linear characteristics such as phase, coupling ...
Structural and optical properties of visible active
... Figure 3 depicts XRD spectra of nano-WO3 films at different Ptot. The structural distortions of the cornersharing WO6 octahedra comprising the WO3 unit cell are quite complex and make definitive assignments of WO3 phases from XRD data alone rather difficult, despite the apparent simple stoichiometry of ...
... Figure 3 depicts XRD spectra of nano-WO3 films at different Ptot. The structural distortions of the cornersharing WO6 octahedra comprising the WO3 unit cell are quite complex and make definitive assignments of WO3 phases from XRD data alone rather difficult, despite the apparent simple stoichiometry of ...
Brochure of Optical Spectrum Analyzer MS9740A
... Up to 300 channels can be evaluated and data required for WDM signal analysis, such as center wavelength, level, SNR, etc., are displayed on one screen. Specification of the noise location, which is required at OSNR analysis, can be selected using two estimation methods; 2-point interpolation, and n ...
... Up to 300 channels can be evaluated and data required for WDM signal analysis, such as center wavelength, level, SNR, etc., are displayed on one screen. Specification of the noise location, which is required at OSNR analysis, can be selected using two estimation methods; 2-point interpolation, and n ...
Application of Digital Phase-shift Shadow Moiré to Micro
... which is solely dependent on z. However it concerns only a first estimate and as will be shown below, this approach works very well. So a first estimate of ∆φ(x,y) (and hence z(x,y)) will be calculated from Equation (6), where the intensity distributions Ik are provided by multiplying the virtual re ...
... which is solely dependent on z. However it concerns only a first estimate and as will be shown below, this approach works very well. So a first estimate of ∆φ(x,y) (and hence z(x,y)) will be calculated from Equation (6), where the intensity distributions Ik are provided by multiplying the virtual re ...
Interferometry
Interferometry is a family of techniques in which waves, usually electromagnetic, are superimposed in order to extract information about the waves. Interferometry is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy (and its applications to chemistry), quantum mechanics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, remote sensing, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, and velocimetry.Interferometers are widely used in science and industry for the measurement of small displacements, refractive index changes and surface irregularities. In analytical science, interferometers are used in continuous wave Fourier transform spectroscopy to analyze light containing features of absorption or emission associated with a substance or mixture. An astronomical interferometer consists of two or more separate telescopes that combine their signals, offering a resolution equivalent to that of a telescope of diameter equal to the largest separation between its individual elements.