12.5 Total Internal Reflection
... Light is travelling more slowly in the first medium than in the second. The angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle (no refraction occurs; all light is reflected back into the medium) ...
... Light is travelling more slowly in the first medium than in the second. The angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle (no refraction occurs; all light is reflected back into the medium) ...
Modulation of Light
... is responsible for the different emission frequencies observed under steady state when a “1” or “0” is transmitted. Source chirp combined with fiber dispersion limits the transmission distance, so directly modulated lasers, even if cheaper, are limited to short range applications. ...
... is responsible for the different emission frequencies observed under steady state when a “1” or “0” is transmitted. Source chirp combined with fiber dispersion limits the transmission distance, so directly modulated lasers, even if cheaper, are limited to short range applications. ...
Setting the stage
... measured spectra of PAHs ranging in size from C10H8 to C130H28. Spectra of PAHs in neutral and singly charged (+/–) states. Spectra of a few multiply charged ...
... measured spectra of PAHs ranging in size from C10H8 to C130H28. Spectra of PAHs in neutral and singly charged (+/–) states. Spectra of a few multiply charged ...
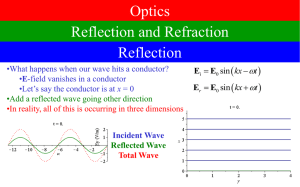
Reflect/Refract
... •For the next week, we will always make this approximation Mirror •It’s called geometric optics •Physical optics will come later •In geometric optics, light waves are represented by rays •You can think of light as if it is made of little particles •In fact, waves and particles act very similarly •Fi ...
... •For the next week, we will always make this approximation Mirror •It’s called geometric optics •Physical optics will come later •In geometric optics, light waves are represented by rays •You can think of light as if it is made of little particles •In fact, waves and particles act very similarly •Fi ...
Beyond Snel`s law: Refraction of a nano-beam of light.
... Light refraction is one of the most commonly observed optical phenomena. When light wave is transmitted from one optical medium into another at an oblique angle, its direction of propagation changes. If the light is a wide plane wave incident on a relatively large and flat interface of two different ...
... Light refraction is one of the most commonly observed optical phenomena. When light wave is transmitted from one optical medium into another at an oblique angle, its direction of propagation changes. If the light is a wide plane wave incident on a relatively large and flat interface of two different ...
FT-IR Glossary - Thermo Fisher Scientific
... and FT-NIR applications. This is the detector recommended for all but the most challenging measurements when the highest sensitivity is required. Integrating Sphere A device used in diffuse-reflectance spectroscopy. When using an integrating sphere, the light beam is angled into the sphere and trave ...
... and FT-NIR applications. This is the detector recommended for all but the most challenging measurements when the highest sensitivity is required. Integrating Sphere A device used in diffuse-reflectance spectroscopy. When using an integrating sphere, the light beam is angled into the sphere and trave ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... electron. The emitted light due to the stimulated emission has the same wavelength, phase, and direction as the incident light. Therefore, the light generated by the stimulated emission is highly monochromatic, coherent, and directional. In the stimulated emission, one incident photon generates two ...
... electron. The emitted light due to the stimulated emission has the same wavelength, phase, and direction as the incident light. Therefore, the light generated by the stimulated emission is highly monochromatic, coherent, and directional. In the stimulated emission, one incident photon generates two ...
Improved period of a slowly rotating cool magnetic CP star HD 188041
... The model light curve shows a symmetric minimum passing to a flat maximum in which the brightness changes only a little. The coefficients determining its amplitude and shape are A1 = (0.0438 ± 0.008)mag, A2 = (0.0126 ± 0.008)mag. ...
... The model light curve shows a symmetric minimum passing to a flat maximum in which the brightness changes only a little. The coefficients determining its amplitude and shape are A1 = (0.0438 ± 0.008)mag, A2 = (0.0126 ± 0.008)mag. ...
The Cosmic Perspective Light and Matter
... The SI unit for temperature (T) is the kelvin. The Kelvin scale is a thermodynamic (absolute) temperature scale where absolute zero, the theoretical absence of all thermal energy, is zero kelvin (0 K). T(K) = T(°C) + 273.15° For example the average surface temperatures of Mercury and Mars are about ...
... The SI unit for temperature (T) is the kelvin. The Kelvin scale is a thermodynamic (absolute) temperature scale where absolute zero, the theoretical absence of all thermal energy, is zero kelvin (0 K). T(K) = T(°C) + 273.15° For example the average surface temperatures of Mercury and Mars are about ...