Sub-THz Electron Spin Resonance spectroscopy based on a Martin
... up to fhν = 750 GHz[41] and free electron lasers (FEL) can provide highest irradiation power (several kW) in pulsed or quasi-cw high-field ESR.[42–45] However, these spectrometers are highly specialized and operate in one dedicated high-field environment,[41] and a very recent commercial system prov ...
... up to fhν = 750 GHz[41] and free electron lasers (FEL) can provide highest irradiation power (several kW) in pulsed or quasi-cw high-field ESR.[42–45] However, these spectrometers are highly specialized and operate in one dedicated high-field environment,[41] and a very recent commercial system prov ...
All solid-state continuous wave tunable blue light source by
... a Nd:YAG laser operating at 946 nm??? it is also possible to generate blue light at 473 nm. These sources have a high doubling efficiency, but they are not tunable. Compact sources generating tunable blue light could be particularly useful for spectroscopic experiments. One possibility is an intraca ...
... a Nd:YAG laser operating at 946 nm??? it is also possible to generate blue light at 473 nm. These sources have a high doubling efficiency, but they are not tunable. Compact sources generating tunable blue light could be particularly useful for spectroscopic experiments. One possibility is an intraca ...
Inverse scattering for frequency-scanned full-field
... where the delta functions enforce the conditions of the coordinate transformation. This operator concisely contains both the kernel and the coordinate transformations expressed in Eq. (10). To obtain the measurements needed to reconstruct 共r兲, one must vary both k and . In practice, however, it is ...
... where the delta functions enforce the conditions of the coordinate transformation. This operator concisely contains both the kernel and the coordinate transformations expressed in Eq. (10). To obtain the measurements needed to reconstruct 共r兲, one must vary both k and . In practice, however, it is ...
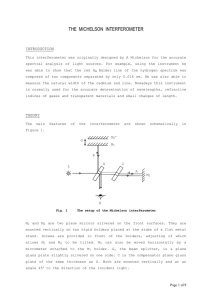
Michelson Interferometer
... to the path difference is 4πd/λ . Also, an additional phase shift of π is introduced because beam A is reflected off the outer side while beam B is reflected off the inner side of the beam splitter. Therefore, the total phase difference is δ = 4πd/λ - π . ...
... to the path difference is 4πd/λ . Also, an additional phase shift of π is introduced because beam A is reflected off the outer side while beam B is reflected off the inner side of the beam splitter. Therefore, the total phase difference is δ = 4πd/λ - π . ...
V. experimental setup of all-optical tunable delay
... it is tuning the wide range of signal pulse .This research shows tunable optical delay by using the OptiSystem software .So, optical delay is important in optical system due to these above factors. In this proposed method, system was used wavelength converter and dispersive element to generate tunab ...
... it is tuning the wide range of signal pulse .This research shows tunable optical delay by using the OptiSystem software .So, optical delay is important in optical system due to these above factors. In this proposed method, system was used wavelength converter and dispersive element to generate tunab ...
Ray Diagrams Powerpoint
... Reflection is when light changes direction by bouncing off a surface. When light is reflected off a mirror, it hits the mirror at the same angle (the incidence angle, θi) as it reflects off the mirror (the reflection angle, θr). ...
... Reflection is when light changes direction by bouncing off a surface. When light is reflected off a mirror, it hits the mirror at the same angle (the incidence angle, θi) as it reflects off the mirror (the reflection angle, θr). ...
Document
... Reflection is when light changes direction by bouncing off a surface. When light is reflected off a mirror, it hits the mirror at the same angle (the incidence angle, θi) as it reflects off the mirror (the reflection angle, θr). ...
... Reflection is when light changes direction by bouncing off a surface. When light is reflected off a mirror, it hits the mirror at the same angle (the incidence angle, θi) as it reflects off the mirror (the reflection angle, θr). ...
The speed of information in a `fast-light` optical medium
... slightly longer than the time required to detect the same information travelling through a vacuum, even though u g in the medium vastly exceeds c. Our observations are therefore consistent with relativistic causality and help to resolve the controversies surrounding superluminal pulse propagation. T ...
... slightly longer than the time required to detect the same information travelling through a vacuum, even though u g in the medium vastly exceeds c. Our observations are therefore consistent with relativistic causality and help to resolve the controversies surrounding superluminal pulse propagation. T ...
Absorbance Spectroscopy and Beer`s Law
... Beer's las describes the absorption behavior only of dilute solutions and in this sense is a limiting law. At concentrations exceeding about 0.01 M, the average distance between ions or molecules of the absorbing species are diminished to the point where each particle affects the charge distribution ...
... Beer's las describes the absorption behavior only of dilute solutions and in this sense is a limiting law. At concentrations exceeding about 0.01 M, the average distance between ions or molecules of the absorbing species are diminished to the point where each particle affects the charge distribution ...
Geometric Optics - Mr. Gabrielse's Physics
... Reflection is when light changes direction by bouncing off a surface. When light is reflected off a mirror, it hits the mirror at the same angle (θi, the incidence angle) as it reflects off the mirror (θr, the reflection angle). ...
... Reflection is when light changes direction by bouncing off a surface. When light is reflected off a mirror, it hits the mirror at the same angle (θi, the incidence angle) as it reflects off the mirror (θr, the reflection angle). ...
Snell`s Law
... Propagation of Light – Ray (Geometric) Optics Main assumption: light travels in a straight-line path in a uniform medium and changes its direction when it meets the surface of a different medium or if the optical properties of the medium are nonuniform ...
... Propagation of Light – Ray (Geometric) Optics Main assumption: light travels in a straight-line path in a uniform medium and changes its direction when it meets the surface of a different medium or if the optical properties of the medium are nonuniform ...
About Optical Fiber - University of Vaasa
... Optical Fiber provides a very large bandwidth data rates. Based on its requirements and needs, Networks communication ...
... Optical Fiber provides a very large bandwidth data rates. Based on its requirements and needs, Networks communication ...