Why is the competition paradigm so prevalent? based on
... Prior to 1980s: Several researchers felt that competition was more NB than other ecological processes After 1980s: Researchers questioned why competition was necessarily the most NB interaction. Predation seems more NB in marine habitats. Do communities have to be in equilibrium? Does competition e ...
... Prior to 1980s: Several researchers felt that competition was more NB than other ecological processes After 1980s: Researchers questioned why competition was necessarily the most NB interaction. Predation seems more NB in marine habitats. Do communities have to be in equilibrium? Does competition e ...
Interspecific Competition
... environment, which results in population increase if it becomes more abundant ...
... environment, which results in population increase if it becomes more abundant ...
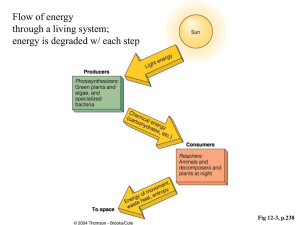
Characteristics of Life
... Two or more joined atoms of the same or different elements. “Molecules of life” are complex carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, DNA, and RNA. ...
... Two or more joined atoms of the same or different elements. “Molecules of life” are complex carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, DNA, and RNA. ...
Environmental Problems, Their Causes, and the Issue of
... Endangered species management Wildlife reserves and ecological ...
... Endangered species management Wildlife reserves and ecological ...
Marine Ecology
... • Since we know some of the organisms that live there, we can also study their interactions (w/ each other and w/I the community structure) ...
... • Since we know some of the organisms that live there, we can also study their interactions (w/ each other and w/I the community structure) ...
From to the : A Three-Part Co-op in Wildlife Biology
... Acknowledgements: I would like to thank Stesha Pasachnik and all of her colleagues, my colleagues from the University of Montana, and all of the staff and interns at LRWC. Thank you to my friends and colleagues for providing me with their beautiful pictures! I would also like to thank Sarah Klionsky ...
... Acknowledgements: I would like to thank Stesha Pasachnik and all of her colleagues, my colleagues from the University of Montana, and all of the staff and interns at LRWC. Thank you to my friends and colleagues for providing me with their beautiful pictures! I would also like to thank Sarah Klionsky ...
Lecture notes for community ecology
... Community structure is determined by number of species, which species, and their relative abundance MEASURE: species present or richness, diversity Can be at any level of physical space and ...
... Community structure is determined by number of species, which species, and their relative abundance MEASURE: species present or richness, diversity Can be at any level of physical space and ...
File
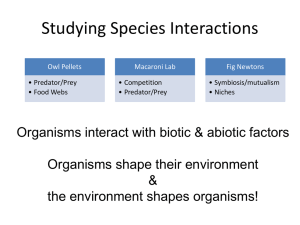
... Symbiotic Species Interactions: Mutualism Reproductive mutualism: pollination Nutritional mutualism Nutritional/protection mutualism ...
... Symbiotic Species Interactions: Mutualism Reproductive mutualism: pollination Nutritional mutualism Nutritional/protection mutualism ...
CH 8
... Symbiotic Species Interactions: Mutualism Reproductive mutualism: pollination Nutritional mutualism Nutritional/protection mutualism ...
... Symbiotic Species Interactions: Mutualism Reproductive mutualism: pollination Nutritional mutualism Nutritional/protection mutualism ...
Chapter 8
... Symbiotic Species Interactions: Commensalism Species interaction that benefits one and has little or no effect on the other Example: Small plants growing in shade of larger plants ...
... Symbiotic Species Interactions: Commensalism Species interaction that benefits one and has little or no effect on the other Example: Small plants growing in shade of larger plants ...
Ecology… in a Nutshell
... How the tree or other organisms within the video display reproduction (provide 3-4 examples) using the following terms: How the tree or other organisms within the video display genetics How the tree or other organisms show energy and matter (provide 3-4 examples) List 4-5 various populations ...
... How the tree or other organisms within the video display reproduction (provide 3-4 examples) using the following terms: How the tree or other organisms within the video display genetics How the tree or other organisms show energy and matter (provide 3-4 examples) List 4-5 various populations ...
HOW DO YOU CATCH YOUR FOOD?
... also deposits her eggs in a type of “female” flower that will not set fruit. The fruits of figs are actually nutlets formed within the fruiting structure, called a fig. The tiny fruits impart the crunch to figs and Fig Newtons. The deposited pollen not only enables the fruits to grow, but also becom ...
... also deposits her eggs in a type of “female” flower that will not set fruit. The fruits of figs are actually nutlets formed within the fruiting structure, called a fig. The tiny fruits impart the crunch to figs and Fig Newtons. The deposited pollen not only enables the fruits to grow, but also becom ...
What do Ecologists Study?
... – Anti-predation: cryptic and warning colorations, mobbing, displays ...
... – Anti-predation: cryptic and warning colorations, mobbing, displays ...
PPT
... • Based on taxonomically diverse community in eastern U.S. – Decline of migrants equal to ~ 1% / year. ...
... • Based on taxonomically diverse community in eastern U.S. – Decline of migrants equal to ~ 1% / year. ...
Ficus rubiginosa

Ficus rubiginosa, the rusty fig, Port Jackson fig, or little-leaf fig (damun in the Sydney language) is a species of flowering plant in the family Moraceae that is native to eastern Australia. It is a banyan of the genus Ficus which contains around 750 species worldwide in warm climates, including the common fig (Ficus carica). Ficus rubiginosa can grow to 30 m (100 ft) high and nearly as wide with a buttressed trunk, and glossy green leaves.