Phase contrast and DIC - Nikon Imaging Center at UCSF
... Sensitive to phase gradients Contrast best along the direction of shear Objects appear shaded or in pseudo 3D relief ...
... Sensitive to phase gradients Contrast best along the direction of shear Objects appear shaded or in pseudo 3D relief ...
TEM - UiO
... dynamical scattering for 2-beam conditions The image intensity varies sinusoidally depending on the thickness and on the beam used for imaging. ...
... dynamical scattering for 2-beam conditions The image intensity varies sinusoidally depending on the thickness and on the beam used for imaging. ...
physical optics - Sakshi Education
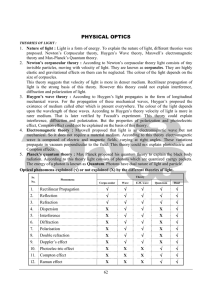
... sources where as in Fresnel’s biprism two virtual images of same original source are used as two coherent sources. 31. In Lloyd’s one original source and its image are used as coherent sources. Interference of light : 32. When two light waves of nearly same amplitude, same frequency and traveling in ...
... sources where as in Fresnel’s biprism two virtual images of same original source are used as two coherent sources. 31. In Lloyd’s one original source and its image are used as coherent sources. Interference of light : 32. When two light waves of nearly same amplitude, same frequency and traveling in ...
Deep Horizontal Atmospheric Turbulence Modeling and Simulation with a Liquid
... In order to test an adaptive optic systems being developed at the Naval Postgraduate School (NPS), a Liquid Crystal (LC) Spatial Light Modulator (SLM) is being used to generate atmospheric turbulence in the laboratory on a laser beam. Using a LC SLM in combination with software that generates atmosp ...
... In order to test an adaptive optic systems being developed at the Naval Postgraduate School (NPS), a Liquid Crystal (LC) Spatial Light Modulator (SLM) is being used to generate atmospheric turbulence in the laboratory on a laser beam. Using a LC SLM in combination with software that generates atmosp ...
Other photon-lithographies
... • Fluorescence emission (at l3) varies with the square of the excitation intensity. • The photon density must be approximately one million times required to generate the same number of one photon absorptions. • The focal point of mode-locked pulsed lasers (very high peak power) can have such ...
... • Fluorescence emission (at l3) varies with the square of the excitation intensity. • The photon density must be approximately one million times required to generate the same number of one photon absorptions. • The focal point of mode-locked pulsed lasers (very high peak power) can have such ...
Observation of optical polarization Möbius strips
... Möbius strips (16). Möbius strips are 3D objects that possess only a single surface and a single boundary component (17, 18) and have been observed in chemistry, biology (19), particle physics (20), and materials science (21–23). In our experiment, these 3D objects are created by the tight focusing ...
... Möbius strips (16). Möbius strips are 3D objects that possess only a single surface and a single boundary component (17, 18) and have been observed in chemistry, biology (19), particle physics (20), and materials science (21–23). In our experiment, these 3D objects are created by the tight focusing ...
geometrical optics
... An optical lens is a piece of glass or other transparent material used to direct or control rays of light. The refraction of light at the surface of a lens depends on its shape, its index of refraction, and the nature of the medium surrounding it (usually air), in accordance with Snell’s Law. Lenses ...
... An optical lens is a piece of glass or other transparent material used to direct or control rays of light. The refraction of light at the surface of a lens depends on its shape, its index of refraction, and the nature of the medium surrounding it (usually air), in accordance with Snell’s Law. Lenses ...
IMPORTANT FEATURES FOR A RIGHT - pi
... function, analogous to formula (5) with input beam radius r. In other words, to generate a flattop laser spot in the focal plane the input beam should have essentially non-uniform profile. Like in previous cases the interference pattern in the space between the lens and its focal plane isn’t constan ...
... function, analogous to formula (5) with input beam radius r. In other words, to generate a flattop laser spot in the focal plane the input beam should have essentially non-uniform profile. Like in previous cases the interference pattern in the space between the lens and its focal plane isn’t constan ...
polarization 3
... when e-ray and o- ray overlap on each other after emerging from an anisotropic crystal plate, they cannot produce interference fringes as in a double slit experiment On the other hand, they combine to produce different states of polarisation depending upon their optical path difference When the ...
... when e-ray and o- ray overlap on each other after emerging from an anisotropic crystal plate, they cannot produce interference fringes as in a double slit experiment On the other hand, they combine to produce different states of polarisation depending upon their optical path difference When the ...
Technical Digest Post-Deadline Papers
... We propose the use of a new method in which a grating reduces stray light from adjacent layers. A schematic of the optical pickup is shown in Fig. 1. A focusing lens, a grating, and a reflector are attached in the return path from a multilayer disc to a normal pickup. The reflection from the multi-l ...
... We propose the use of a new method in which a grating reduces stray light from adjacent layers. A schematic of the optical pickup is shown in Fig. 1. A focusing lens, a grating, and a reflector are attached in the return path from a multilayer disc to a normal pickup. The reflection from the multi-l ...
Reflection, Refraction and the Prism
... of the path of light through any optical system. However, as seen in the chapter on Light, the Huygens wavefront construction can be become complicated, especially in systems with a large number of optical components. A simpler approach to track the behavior of light is based on the propagation of l ...
... of the path of light through any optical system. However, as seen in the chapter on Light, the Huygens wavefront construction can be become complicated, especially in systems with a large number of optical components. A simpler approach to track the behavior of light is based on the propagation of l ...
Tutorial on Optomechanical Beam Steering Mechanisms
... Beam divergence or imaging Aperture/vignetting Spectral range Throughput We will provide tables with some semi-quantitative comparisons of these parameters at the end of this paper. ...
... Beam divergence or imaging Aperture/vignetting Spectral range Throughput We will provide tables with some semi-quantitative comparisons of these parameters at the end of this paper. ...
Reflection and Refraction of Plane Waves
... waves, we expect that the reversepropagating and must produce their own reflected waves and transmitted waves. ...
... waves, we expect that the reversepropagating and must produce their own reflected waves and transmitted waves. ...
Fabrication of two-layer integrated phase mask for
... the case of positive resist, the overexposed material is then dissolved away in the postexposure processing. The underexposed region forms a periodic network and acts as a 3D photonic crystal template. For negative photoresists, the underexposed regions can then be selectively removed using a develo ...
... the case of positive resist, the overexposed material is then dissolved away in the postexposure processing. The underexposed region forms a periodic network and acts as a 3D photonic crystal template. For negative photoresists, the underexposed regions can then be selectively removed using a develo ...
Special Optical Elements
... l or the thickness of the layer is changed so that the two reflected waves are now in phase (i.e., the layer is l2 thick), then the total reflectivity at this wavelength is increased, although still quite low [about 10% from only two surfaces, Fig. 3.3(C,D)]. The total reflectivity can be increased ...
... l or the thickness of the layer is changed so that the two reflected waves are now in phase (i.e., the layer is l2 thick), then the total reflectivity at this wavelength is increased, although still quite low [about 10% from only two surfaces, Fig. 3.3(C,D)]. The total reflectivity can be increased ...
Fabry-Perot Interferometer FABRYPEROT.TEX KB 20020122
... is more or less blocked. These conditions can be adjusted by changing the wavelength and/or the geometry. Thus Fabry-Perot plates can be used to measure or to control light wavelengths or to measure geometric properties. The geometric conditions are defined by several properties including thickness, ...
... is more or less blocked. These conditions can be adjusted by changing the wavelength and/or the geometry. Thus Fabry-Perot plates can be used to measure or to control light wavelengths or to measure geometric properties. The geometric conditions are defined by several properties including thickness, ...
Non-specular reflection of convergent beams from Iiquid-solid interface
... profiles of the reflected beam for w 0 =2 .1 X, for which 2 0,„=17°, when 0R =45° and a,=0.08 k . The results are plotted in Figures 4 and 5 for angles of incidence 0 0 =45° and 48 .3° . Since the half-width of the frequency spectrum for this beam is 0 .11 k, which is greater than a,, these paramete ...
... profiles of the reflected beam for w 0 =2 .1 X, for which 2 0,„=17°, when 0R =45° and a,=0.08 k . The results are plotted in Figures 4 and 5 for angles of incidence 0 0 =45° and 48 .3° . Since the half-width of the frequency spectrum for this beam is 0 .11 k, which is greater than a,, these paramete ...
Holography

Holography is the science and practice of making holograms. Typically, a hologram is a photographic recording of a light field, rather than of an image formed by a lens, and it is used to display a fully three-dimensional image of the holographed subject, which is seen without the aid of special glasses or other intermediate optics. The hologram itself is not an image and it is usually unintelligible when viewed under diffuse ambient light. It is an encoding of the light field as an interference pattern of seemingly random variations in the opacity, density, or surface profile of the photographic medium. When suitably lit, the interference pattern diffracts the light into a reproduction of the original light field and the objects that were in it appear to still be there, exhibiting visual depth cues such as parallax and perspective that change realistically with any change in the relative position of the observer.In its pure form, holography requires the use of laser light for illuminating the subject and for viewing the finished hologram. In a side-by-side comparison under optimal conditions, a holographic image is visually indistinguishable from the actual subject, if the hologram and the subject are lit just as they were at the time of recording. A microscopic level of detail throughout the recorded volume of space can be reproduced. In common practice, however, major image quality compromises are made to eliminate the need for laser illumination when viewing the hologram, and sometimes, to the extent possible, also when making it. Holographic portraiture often resorts to a non-holographic intermediate imaging procedure, to avoid the hazardous high-powered pulsed lasers otherwise needed to optically ""freeze"" living subjects as perfectly as the extremely motion-intolerant holographic recording process requires. Holograms can now also be entirely computer-generated and show objects or scenes that never existed.Holography should not be confused with lenticular and other earlier autostereoscopic 3D display technologies, which can produce superficially similar results but are based on conventional lens imaging. Stage illusions such as Pepper's Ghost and other unusual, baffling, or seemingly magical images are also often incorrectly called holograms.