Ph 76 ADVANCED PHYSICS LABORATORY — ATOMIC AND
... If the atoms in the vapor cell had a single excited state but two hyperfine ground states (we call them both “ground” states because neither can decay via an allowed transition), and the separation of the ground states was less than the Doppler width, then one might see a spectrum like in Figure 4. ...
... If the atoms in the vapor cell had a single excited state but two hyperfine ground states (we call them both “ground” states because neither can decay via an allowed transition), and the separation of the ground states was less than the Doppler width, then one might see a spectrum like in Figure 4. ...
materials Volume Holograms in Photopolymers: Comparison between Analytical and Rigorous Theories
... Photopolymers are useful for different applications due to the refractive index variations and relief profiles generated [1–8]. There are many types of photopolymers that may be differentiated by the type of binder, since this component determines to a great extent the choice of monomer, dye and ini ...
... Photopolymers are useful for different applications due to the refractive index variations and relief profiles generated [1–8]. There are many types of photopolymers that may be differentiated by the type of binder, since this component determines to a great extent the choice of monomer, dye and ini ...
Министерство высшего и среднего специального образования
... compared with itself as it was during earlier exposure. Thus the dimensions of the object during two or more conditions can be compared. 3) When the measuring object is to be compared with a ...
... compared with itself as it was during earlier exposure. Thus the dimensions of the object during two or more conditions can be compared. 3) When the measuring object is to be compared with a ...
Poisson’s spot with molecules Please share
... membranes, perhaps even from two-dimensional 共2D兲 crystals such as graphene. Furthermore, the on-axis interference condition giving rise to the Poisson spot is wavelength independent, which means that experiments can be carried out using a polychromatic source. Thus, the Poisson-spot configuration c ...
... membranes, perhaps even from two-dimensional 共2D兲 crystals such as graphene. Furthermore, the on-axis interference condition giving rise to the Poisson spot is wavelength independent, which means that experiments can be carried out using a polychromatic source. Thus, the Poisson-spot configuration c ...
Acoustooptic interaction of two light beams in a paratellurite crystal
... characteristic features of the AO interaction in birefringent crystals is multiple diffraction of light by ultrasound [1, 2, 6–14], in particular, the double Bragg interaction. In the case of double diffraction, the conditions for the Bragg synchronism are fulfilled at a fixed ultrasound frequency f ...
... characteristic features of the AO interaction in birefringent crystals is multiple diffraction of light by ultrasound [1, 2, 6–14], in particular, the double Bragg interaction. In the case of double diffraction, the conditions for the Bragg synchronism are fulfilled at a fixed ultrasound frequency f ...
Accelerating Light Beams along Arbitrary Convex
... peak intensity follows a continuous parabolic curve as they propagate in free space, just like the quantum-mechanical ‘‘Airy wave packet’’ [3] that inspired their invention. Optical Airy beams are now becoming of practical importance. Examples of recent applications range from optical manipulation o ...
... peak intensity follows a continuous parabolic curve as they propagate in free space, just like the quantum-mechanical ‘‘Airy wave packet’’ [3] that inspired their invention. Optical Airy beams are now becoming of practical importance. Examples of recent applications range from optical manipulation o ...
Mode Structure of Active Resonators
... homogeneously excitated active medium results in axially symmetric gain variations. The interaction can always be describedin terms of the propagation constant (real and imaginary part) which may then be used for calculating the change of laser I. INTRODUCTION parameters. It has been shown by the th ...
... homogeneously excitated active medium results in axially symmetric gain variations. The interaction can always be describedin terms of the propagation constant (real and imaginary part) which may then be used for calculating the change of laser I. INTRODUCTION parameters. It has been shown by the th ...
Beam manipulation: prisms vs. mirrors
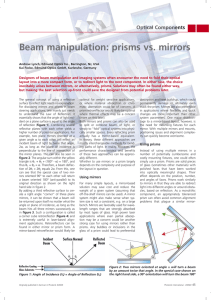
... inevitably arises between mirrors, or alternatively, prisms. Solutions may often be found either way, but making the best selection up-front could save the designer from potential problems later. The general concept of using a reflective surface to reflect light needs no explanation. For discussing ...
... inevitably arises between mirrors, or alternatively, prisms. Solutions may often be found either way, but making the best selection up-front could save the designer from potential problems later. The general concept of using a reflective surface to reflect light needs no explanation. For discussing ...
Tailored Complex Potentials and Friedel`s Law in Atom Optics
... physics this is known as a violation of Friedel’s law. [S0031-9007(97)04304-4] PACS numbers: 03.75. – b, 42.25. – p, 61.12.Bt ...
... physics this is known as a violation of Friedel’s law. [S0031-9007(97)04304-4] PACS numbers: 03.75. – b, 42.25. – p, 61.12.Bt ...
Fourier-domain holography in photorefractive quantum-well films
... vides an enhanced rejection of diffuse scattered light owing to its inherent insensitivity to an incoherent background. PRQW devices have been used to image through turbid media to depths up to 13 mean-free path5,6 and have used low-coherence light.7,8 Holographic OCI has also produced the first de ...
... vides an enhanced rejection of diffuse scattered light owing to its inherent insensitivity to an incoherent background. PRQW devices have been used to image through turbid media to depths up to 13 mean-free path5,6 and have used low-coherence light.7,8 Holographic OCI has also produced the first de ...
Novel 3-D microscopy techniques - Purdue University Cytometry
... confocal and multiphoton microscopy. Optical sections through a glomerulus from an acid-fucsinstained monkey kidney pathology sample imaged by confocal microscopy with 2 µW of 532-nm light (left, columns 1 and 2) and multiphoton microscopy with 4.3 mW of 1047-nm light (descanned; right, columns 3 an ...
... confocal and multiphoton microscopy. Optical sections through a glomerulus from an acid-fucsinstained monkey kidney pathology sample imaged by confocal microscopy with 2 µW of 532-nm light (left, columns 1 and 2) and multiphoton microscopy with 4.3 mW of 1047-nm light (descanned; right, columns 3 an ...
Review !x
... ! We can see that the intensity varies from 0 to 4Imax ! Covering one slit, we get a constant intensity of Imax ! If we illuminate both slits with light that has random phases, we would observe a constant intensity of 2Imax ! Only when we illuminate both slits with coherent light do we observe the o ...
... ! We can see that the intensity varies from 0 to 4Imax ! Covering one slit, we get a constant intensity of Imax ! If we illuminate both slits with light that has random phases, we would observe a constant intensity of 2Imax ! Only when we illuminate both slits with coherent light do we observe the o ...
- Phasics
... limited in terms of focusability by thermal effects. Because most of the broadband flash-lamp energy cannot be transferred to the laser pulses, it is dissipated as heat in the amplifiers. The consequent temperature rise deforms the amplifying materials,1 which results in disturbance of the laser pul ...
... limited in terms of focusability by thermal effects. Because most of the broadband flash-lamp energy cannot be transferred to the laser pulses, it is dissipated as heat in the amplifiers. The consequent temperature rise deforms the amplifying materials,1 which results in disturbance of the laser pul ...
Measurement of transparent plates with
... images at a sequence of wavelengths and leastsquares fitting of the first-order terms to calculate surface and optical thickness profiles.7,8 Here I propose to measure transparent plates by using a wavelength-tuned laser Fizeau interferometer and a PSI algorithm that directly suppresses interference ...
... images at a sequence of wavelengths and leastsquares fitting of the first-order terms to calculate surface and optical thickness profiles.7,8 Here I propose to measure transparent plates by using a wavelength-tuned laser Fizeau interferometer and a PSI algorithm that directly suppresses interference ...
Holography

Holography is the science and practice of making holograms. Typically, a hologram is a photographic recording of a light field, rather than of an image formed by a lens, and it is used to display a fully three-dimensional image of the holographed subject, which is seen without the aid of special glasses or other intermediate optics. The hologram itself is not an image and it is usually unintelligible when viewed under diffuse ambient light. It is an encoding of the light field as an interference pattern of seemingly random variations in the opacity, density, or surface profile of the photographic medium. When suitably lit, the interference pattern diffracts the light into a reproduction of the original light field and the objects that were in it appear to still be there, exhibiting visual depth cues such as parallax and perspective that change realistically with any change in the relative position of the observer.In its pure form, holography requires the use of laser light for illuminating the subject and for viewing the finished hologram. In a side-by-side comparison under optimal conditions, a holographic image is visually indistinguishable from the actual subject, if the hologram and the subject are lit just as they were at the time of recording. A microscopic level of detail throughout the recorded volume of space can be reproduced. In common practice, however, major image quality compromises are made to eliminate the need for laser illumination when viewing the hologram, and sometimes, to the extent possible, also when making it. Holographic portraiture often resorts to a non-holographic intermediate imaging procedure, to avoid the hazardous high-powered pulsed lasers otherwise needed to optically ""freeze"" living subjects as perfectly as the extremely motion-intolerant holographic recording process requires. Holograms can now also be entirely computer-generated and show objects or scenes that never existed.Holography should not be confused with lenticular and other earlier autostereoscopic 3D display technologies, which can produce superficially similar results but are based on conventional lens imaging. Stage illusions such as Pepper's Ghost and other unusual, baffling, or seemingly magical images are also often incorrectly called holograms.