climatic factors in land degradation climatic factors in land degradation
... Climatic Factors in Land Degradation Climate exerts a strong influence over dry land vegetation type, biomass and diversity. Climatic stresses account for 62.5% of all the stresses on land degradation in Africa (Natural Resources Conservation Service of the United States Department of Agriculture) ...
... Climatic Factors in Land Degradation Climate exerts a strong influence over dry land vegetation type, biomass and diversity. Climatic stresses account for 62.5% of all the stresses on land degradation in Africa (Natural Resources Conservation Service of the United States Department of Agriculture) ...
Weathering and Erosion
... Glaciers in North America over the past 2.0 x 106 years • Ice covered most of New York several times in the ...
... Glaciers in North America over the past 2.0 x 106 years • Ice covered most of New York several times in the ...
Getting to Know: Erosion by Water
... Flowing water acts as an agent of erosion because it contains small pieces of rock and sediment. These particles can wear down and erode the rocks in a riverbed. If a river contains a lot of fast-moving water, it can rapidly erode Earth’s surface. In addition to canyons, many landforms result from t ...
... Flowing water acts as an agent of erosion because it contains small pieces of rock and sediment. These particles can wear down and erode the rocks in a riverbed. If a river contains a lot of fast-moving water, it can rapidly erode Earth’s surface. In addition to canyons, many landforms result from t ...
Now! - Cave Creek USD
... Directions: Write the correct term from the word bank on the line next to its definition. alluvial fan ...
... Directions: Write the correct term from the word bank on the line next to its definition. alluvial fan ...
6th Grade Earth Science
... one place to another deposition __________ - sediments that form during weathering and erosion are deposited in another location During the process of deposition, the _______ and shape direction of a river’s flow changes ________ As rivers flow to the oceans they carry ________ sediments Dissolved m ...
... one place to another deposition __________ - sediments that form during weathering and erosion are deposited in another location During the process of deposition, the _______ and shape direction of a river’s flow changes ________ As rivers flow to the oceans they carry ________ sediments Dissolved m ...
1 - BC Learning Network
... 6. What is biological weathering? Give an example of this. 7. How does physical weathering contribute to chemical weathering? 8. What controls the type of soil that is formed? 9. Which layers of soil have most of the plant roots? 7.2 Running Water 1. What is the most important agent of erosion? What ...
... 6. What is biological weathering? Give an example of this. 7. How does physical weathering contribute to chemical weathering? 8. What controls the type of soil that is formed? 9. Which layers of soil have most of the plant roots? 7.2 Running Water 1. What is the most important agent of erosion? What ...
1-20-15 About 2 inches of soil across the earth Soil
... organisms, water, gases, nutrients, and micro organisms. About 38% of earth's surface (land) is used for agriculture. Forestry Soil cycles nutrients Flow of energy Medications can come from soils. Soil formation is affected by: 1. Climate - long term. Soils form faster in warm, moist climates 2. Org ...
... organisms, water, gases, nutrients, and micro organisms. About 38% of earth's surface (land) is used for agriculture. Forestry Soil cycles nutrients Flow of energy Medications can come from soils. Soil formation is affected by: 1. Climate - long term. Soils form faster in warm, moist climates 2. Org ...
Water Erosion - University of Wyoming
... Yes… turbulent eddies in surface runoff are key drivers More important: concentrated flow paths into rills and gullies Break erosion down into categories ...
... Yes… turbulent eddies in surface runoff are key drivers More important: concentrated flow paths into rills and gullies Break erosion down into categories ...
soil study guide 2015
... Conservation of soil - a method to maintain the fertility of the soil by protecting the soil from erosion and nutrient loss. Contour plowing - forms ridges, slows the water flow and helps save precious topsoil. Terraced farming - uses "steps" that are built into the side of a mountain or hill. Good ...
... Conservation of soil - a method to maintain the fertility of the soil by protecting the soil from erosion and nutrient loss. Contour plowing - forms ridges, slows the water flow and helps save precious topsoil. Terraced farming - uses "steps" that are built into the side of a mountain or hill. Good ...
Name: Date: Period: _____
... earthflow, or slump What is dark organic material found in topsoil? – humus, tephra, or talus What is primarily responsible for dissolving limestone & forming large caverns? – abrasion, carbonic acid or hydrolysis What is the break up of rock due to processes at the earth’s surface? – erosion or wea ...
... earthflow, or slump What is dark organic material found in topsoil? – humus, tephra, or talus What is primarily responsible for dissolving limestone & forming large caverns? – abrasion, carbonic acid or hydrolysis What is the break up of rock due to processes at the earth’s surface? – erosion or wea ...
Download the Full Factsheet
... Management actions to consider There are a number of actions that can be taken to reduce wind erosion: • Minimising erosion by increasing the number of high production crops, in terms of vegetative growth, grown in a rotation. • Minimising the number of cultivations consider herbicides for the job i ...
... Management actions to consider There are a number of actions that can be taken to reduce wind erosion: • Minimising erosion by increasing the number of high production crops, in terms of vegetative growth, grown in a rotation. • Minimising the number of cultivations consider herbicides for the job i ...
15 mts and erosion handout
... Soil Formation o When rocks, animal life, plant life, air, water, and chemicals interact o ...
... Soil Formation o When rocks, animal life, plant life, air, water, and chemicals interact o ...
ABSTRACT Twaibu
... design safe and economic foundations. Erosion, as one of the catastrophic events, has features like rills or dunes on murram/dirt/gravel roads that create a threat to the road users, constructors, and maintainers. These result in increased accident risks, raised costs, and a remarkable effect on the ...
... design safe and economic foundations. Erosion, as one of the catastrophic events, has features like rills or dunes on murram/dirt/gravel roads that create a threat to the road users, constructors, and maintainers. These result in increased accident risks, raised costs, and a remarkable effect on the ...
Sound Erosions - Region of Peel
... one location and moved to another. Erosion changes the landscape by wearing down mountains, filling in valleys, and making rivers appear and disappear. It is usually a slow and gradual process that occurs over thousands or millions of years. But erosion can be speeded up by such human activities as ...
... one location and moved to another. Erosion changes the landscape by wearing down mountains, filling in valleys, and making rivers appear and disappear. It is usually a slow and gradual process that occurs over thousands or millions of years. But erosion can be speeded up by such human activities as ...
Constructive and Destructive study guide
... manage the destructive force of water erosion. 3. Levees help to contain the flow of water. Rivers naturally create their own levees through the process of deposition. During flooding periods man-made levees may be added. They help to control the destructive force of water erosion. 4. Storm-Drainage ...
... manage the destructive force of water erosion. 3. Levees help to contain the flow of water. Rivers naturally create their own levees through the process of deposition. During flooding periods man-made levees may be added. They help to control the destructive force of water erosion. 4. Storm-Drainage ...
Agents of Erosion Notes
... & sediment are transported from one location to another. The running water of the Colorado River cut down into the rock and formed the Grand Canyon over millions of years. ...
... & sediment are transported from one location to another. The running water of the Colorado River cut down into the rock and formed the Grand Canyon over millions of years. ...
2974b719ed02e1d05b6180accf6894840a8bcccc
... 21. How do minerals get dissolved and moved to lower horizons? leaching 22. Arêtes and cirques are features that are associated with which agent of erosion? glaciers 23. What is the most important factor that determines a soil’s characteristic? Soil composition 24. Slump, creep, landslides, and mudf ...
... 21. How do minerals get dissolved and moved to lower horizons? leaching 22. Arêtes and cirques are features that are associated with which agent of erosion? glaciers 23. What is the most important factor that determines a soil’s characteristic? Soil composition 24. Slump, creep, landslides, and mudf ...
Chapter 2-section 3 geology notes
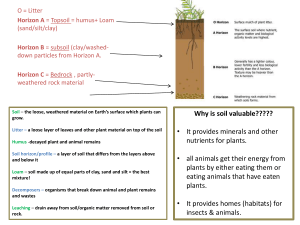
... Fertile soil is valuable because there is a limited supply. Less than 1/8 of the land on Earth have soils suitable for farming. ...
... Fertile soil is valuable because there is a limited supply. Less than 1/8 of the land on Earth have soils suitable for farming. ...
Case Study: Desertification in the Sahel - IBGeography
... expand, contributing to a soil’s nutrient loss; fallow periods are shorter, leading to nutrient exhaustion and smaller yields; the agricultural machinery compacts the soil making it vulnerable to wind/water erosion; marginal (arid/steep) land is used for growing crops (e.g. in Niger, millet fields h ...
... expand, contributing to a soil’s nutrient loss; fallow periods are shorter, leading to nutrient exhaustion and smaller yields; the agricultural machinery compacts the soil making it vulnerable to wind/water erosion; marginal (arid/steep) land is used for growing crops (e.g. in Niger, millet fields h ...