English
... The well cellar was of poor construction quality (from 1977): the concrete showed protruding gravel from the cement, pouring faults, no reinforcement and a thickness of 17 cm. The location also had soft spots and bumps. The foot print of the hoist base beam was too small for the force to be adeq ...
... The well cellar was of poor construction quality (from 1977): the concrete showed protruding gravel from the cement, pouring faults, no reinforcement and a thickness of 17 cm. The location also had soft spots and bumps. The foot print of the hoist base beam was too small for the force to be adeq ...
Saving the Planet with Pesticides and Plastic:
... the soil savings, many cover crops are legumes which add nitrogen to the soil. Soil organic matter is enhanced from the increase in plant residues. The cover also suppresses weeds, reducing weed control costs. The residues can insulate the soil and the young plants of the next crop from cold snaps. ...
... the soil savings, many cover crops are legumes which add nitrogen to the soil. Soil organic matter is enhanced from the increase in plant residues. The cover also suppresses weeds, reducing weed control costs. The residues can insulate the soil and the young plants of the next crop from cold snaps. ...
Task 3 - WordPress.com
... Task 4 adapted from Semantics, J I Saeed, Blackwell Publishing Limited 2009 and Tasks 1 – 3 adapted from Semantics: a coursebook, J R Hurford, B Heasley & M B Smith, CUP 2007 ...
... Task 4 adapted from Semantics, J I Saeed, Blackwell Publishing Limited 2009 and Tasks 1 – 3 adapted from Semantics: a coursebook, J R Hurford, B Heasley & M B Smith, CUP 2007 ...
October 27 - Arnoldia
... which must be drawn from the crippled roots. As a rule the larger the root area lifted with a plant and the corresponding allowance for root spread in the new location, not crowding or bunching the roots in an inadequate hole, the more satisfactory the results will be. It should be remembered that m ...
... which must be drawn from the crippled roots. As a rule the larger the root area lifted with a plant and the corresponding allowance for root spread in the new location, not crowding or bunching the roots in an inadequate hole, the more satisfactory the results will be. It should be remembered that m ...
What is Soil?
... Soil covers much of the land on Earth. All soils are made up of sand, silt, or clay. This describes the particle sizes, not the type of parent material it is composed of. Parent materials are the types of rocks and minerals it is derived from. Soils have other components: air, water and organic matt ...
... Soil covers much of the land on Earth. All soils are made up of sand, silt, or clay. This describes the particle sizes, not the type of parent material it is composed of. Parent materials are the types of rocks and minerals it is derived from. Soils have other components: air, water and organic matt ...
Under Our Feet: Soil Microorganisms as Primary Drivers of Essential
... which are less than 0.8mm wide but can get as long as several metres. They are helpful, but could also be harmful, to soil organisms. Fungi are helpful because they have the ability to break down nutrients that other organisms cannot. They then release them into the soil, and other organisms get to ...
... which are less than 0.8mm wide but can get as long as several metres. They are helpful, but could also be harmful, to soil organisms. Fungi are helpful because they have the ability to break down nutrients that other organisms cannot. They then release them into the soil, and other organisms get to ...
caution - CDMS.net
... 1. Foliage that comes in contact with Soil-Mend may be damaged. For best results test application rates on a small area to determine plant tolerance and/or rinse foliage immediately after it comes in contact with solutions containing SOIL-MEND. 2. SOIL-MEND is known to be incompatible with certain t ...
... 1. Foliage that comes in contact with Soil-Mend may be damaged. For best results test application rates on a small area to determine plant tolerance and/or rinse foliage immediately after it comes in contact with solutions containing SOIL-MEND. 2. SOIL-MEND is known to be incompatible with certain t ...
THE DISTRIBUTION OF MICROORGANISMS IN DIFFERENT
... was found 4 different ways of soil usage and tillage: plough-field area (without vegetation and with harvest residues) the most common way, with 42 samples, pasture and forest with 3 samples and vineyard with 2 samples. GPS technology (Global Positionin System) was used to locate representative site ...
... was found 4 different ways of soil usage and tillage: plough-field area (without vegetation and with harvest residues) the most common way, with 42 samples, pasture and forest with 3 samples and vineyard with 2 samples. GPS technology (Global Positionin System) was used to locate representative site ...
Pathways 2 and 3
... including undecomposed plant and animal tissues, their partial decomposition products, and the soil biomass. Thus, this term includes: ...
... including undecomposed plant and animal tissues, their partial decomposition products, and the soil biomass. Thus, this term includes: ...
Mineral_Nutrition_talk
... when application coincides with periods of high nitrogen demand by trees ...
... when application coincides with periods of high nitrogen demand by trees ...
Environmental Science - University of Tennessee Extension
... On humus. Humus is the “leftovers” after bacteria, fungi, arthropods and worms have had their fill of plant litter. Fungi are common here because they can make some of the enzymes needed to degrade the hard-to-digest compounds in humus. On the surface of soil aggregates. Many aggregates (“clumps”) a ...
... On humus. Humus is the “leftovers” after bacteria, fungi, arthropods and worms have had their fill of plant litter. Fungi are common here because they can make some of the enzymes needed to degrade the hard-to-digest compounds in humus. On the surface of soil aggregates. Many aggregates (“clumps”) a ...
Thermal signatures of land mines buried in mineral and organic soils
... to ensure optimal conditions for thermovision measurements. This includes choosing proper times and camera adjustments for making measurements. Good understanding of energy transport phenomena in the soil medium is crucial in this task. In our paper we present a physical model which describes heat t ...
... to ensure optimal conditions for thermovision measurements. This includes choosing proper times and camera adjustments for making measurements. Good understanding of energy transport phenomena in the soil medium is crucial in this task. In our paper we present a physical model which describes heat t ...
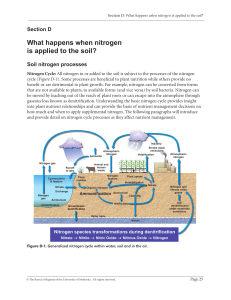
What happens when nitrogen is applied to the soil?
... Mineralization: Mineralization is the process by which organic nitrogen (N) is converted to inorganic, or plant available N (Figure D-2). Specifically, mineralization is the conversion of organic N to NH4+(ammonium). This process is very important for plant growth as organic N is not available for p ...
... Mineralization: Mineralization is the process by which organic nitrogen (N) is converted to inorganic, or plant available N (Figure D-2). Specifically, mineralization is the conversion of organic N to NH4+(ammonium). This process is very important for plant growth as organic N is not available for p ...
Earth Science: 5.2 Soil - sleepingdogstudios.com
... microorganisms also contribute. Earthworms , for example, mix soil as they burrow and feed on the organic matter it contains. ...
... microorganisms also contribute. Earthworms , for example, mix soil as they burrow and feed on the organic matter it contains. ...
Plant density, litter and bare soil effects on actual evaporation and
... important to include a function to alter soil evaporation according to surface soil water content. Pasture litter can reduce bare soil evaporation when soil surface conditions are wet. Soil water retained underneath the litter would be available for pasture growth. High litter did not appear to stop ...
... important to include a function to alter soil evaporation according to surface soil water content. Pasture litter can reduce bare soil evaporation when soil surface conditions are wet. Soil water retained underneath the litter would be available for pasture growth. High litter did not appear to stop ...
SOIL POLLUTION
... aldrin, malathion, dieldrin, furodan, etc. The remnants of such pesticides used on pests may get adsorbed by the soil particles, which then contaminate root crops grown in that soil. The consumption of such crops causes the pesticides remnants to enter human biological systems, affecting them advers ...
... aldrin, malathion, dieldrin, furodan, etc. The remnants of such pesticides used on pests may get adsorbed by the soil particles, which then contaminate root crops grown in that soil. The consumption of such crops causes the pesticides remnants to enter human biological systems, affecting them advers ...
2 «Schwarze Kiefern», ФРГ - G-global www.group
... will develop approaches to bioremediation measures. The effectiveness of the research program for the implementation of bioremediation measures will be successful only if will take into account all the sanitary and environmental contamination of soil criteria and ranking areas for these indicators. ...
... will develop approaches to bioremediation measures. The effectiveness of the research program for the implementation of bioremediation measures will be successful only if will take into account all the sanitary and environmental contamination of soil criteria and ranking areas for these indicators. ...
Microbial Activity in Arsenic Contaminated Soil
... The purpose of CCA is to prevent rot and damage to lumber from termites, effectively acting as a pesticide, in addition to strengthening the lumber. During the 1940’s the lumber industry began its large-scale treatment of lumber with chromated copper arsenate (CCA) for preservation. ...
... The purpose of CCA is to prevent rot and damage to lumber from termites, effectively acting as a pesticide, in addition to strengthening the lumber. During the 1940’s the lumber industry began its large-scale treatment of lumber with chromated copper arsenate (CCA) for preservation. ...
Soil Characteristics
... Soil Drainage • Permeability – Soil permeability is the property of the soil pore system that allows fluid to flow. It is generally the pore sizes and their connectivity that determines whether a soil has high or low permeability. Water will flow easily through soil with large pores with good conne ...
... Soil Drainage • Permeability – Soil permeability is the property of the soil pore system that allows fluid to flow. It is generally the pore sizes and their connectivity that determines whether a soil has high or low permeability. Water will flow easily through soil with large pores with good conne ...
Soil Characteristics
... Soil Drainage • Permeability – Soil permeability is the property of the soil pore system that allows fluid to flow. It is generally the pore sizes and their connectivity that determines whether a soil has high or low permeability. Water will flow easily through soil with large pores with good conne ...
... Soil Drainage • Permeability – Soil permeability is the property of the soil pore system that allows fluid to flow. It is generally the pore sizes and their connectivity that determines whether a soil has high or low permeability. Water will flow easily through soil with large pores with good conne ...
3rd Grade Science - Rocks, Minerals, Fossils Checkpoint
... large, colored crystals from inside minerals. ...
... large, colored crystals from inside minerals. ...
Appendix K Soil biota - Defra Science Search
... The structure and processes of terrestrial ecosystems are profoundly dependant upon a functioning soil biota. The biota is responsible for processing carbon, nutrient cycling, structural genesis and maintenance, pathogenicity and symbionts. It drives many above ground processes. However, in the majo ...
... The structure and processes of terrestrial ecosystems are profoundly dependant upon a functioning soil biota. The biota is responsible for processing carbon, nutrient cycling, structural genesis and maintenance, pathogenicity and symbionts. It drives many above ground processes. However, in the majo ...