slides
... • AM fungi thrive on decomposing organic matter and obtain large amounts of nitrogen from it. • The fungus itself is much richer in N than plant roots, and calculations suggest that there is as much nitrogen in AM fungi globally as in roots. • Since fungal hyphae (the threads of which the fungus is ...
... • AM fungi thrive on decomposing organic matter and obtain large amounts of nitrogen from it. • The fungus itself is much richer in N than plant roots, and calculations suggest that there is as much nitrogen in AM fungi globally as in roots. • Since fungal hyphae (the threads of which the fungus is ...
Soil Notes PowerPoint
... form one meter of soil Soil forms by weathering and decomposition. Faster in warmer climates Why? ...
... form one meter of soil Soil forms by weathering and decomposition. Faster in warmer climates Why? ...
Abstract
... through which they pass and the influence of such pressure on soil structure is expected to be most pronounced at maturity, when the roots also have high content of polysaccharide which is known to play important role in soil structure stabilizing effect of organic matter. Yet, little is known about ...
... through which they pass and the influence of such pressure on soil structure is expected to be most pronounced at maturity, when the roots also have high content of polysaccharide which is known to play important role in soil structure stabilizing effect of organic matter. Yet, little is known about ...
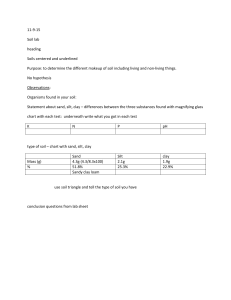
11-9-15 Soils Lab
... Purpose: to determine the different makeup of soil including living and non-living things. No hypothesis Observations: Organisms found in your soil: Statement about sand, silt, clay – differences between the three substances found with magnifying glass chart with each test: underneath write what you ...
... Purpose: to determine the different makeup of soil including living and non-living things. No hypothesis Observations: Organisms found in your soil: Statement about sand, silt, clay – differences between the three substances found with magnifying glass chart with each test: underneath write what you ...
Soils - sabresocials.com
... the soil. Capillary action brings water and dissolved minerals close to the surface. Great for plants. (but) Common in dry desert regions. 4. Translocation. This is the movement of solid material from on place to another by water or by animals. Helps to mix the soil. ...
... the soil. Capillary action brings water and dissolved minerals close to the surface. Great for plants. (but) Common in dry desert regions. 4. Translocation. This is the movement of solid material from on place to another by water or by animals. Helps to mix the soil. ...
Abstract - UvA/FNWI
... In times of accelerated climate change, both natural and man-made landscapes experience changes in the turnover of soil organic matter. Especially on ecosystems with low levels of plant available nutrients and low turnover times (Leifeld, 2005). Since 1999, the VOLCAN project has been set up in orde ...
... In times of accelerated climate change, both natural and man-made landscapes experience changes in the turnover of soil organic matter. Especially on ecosystems with low levels of plant available nutrients and low turnover times (Leifeld, 2005). Since 1999, the VOLCAN project has been set up in orde ...
Soils
... different soils throughout the world. Five important factors influence the specific soil that develops. ...
... different soils throughout the world. Five important factors influence the specific soil that develops. ...
11/22/05 1:21 PM
... SXRF we found NiO, a direct byproduct of the refining process, present as discrete, spherical particles throughout all of the soil types and treatments. Micro-XAFS enabled us to probe beyond the obvious NiO particles which revealed that Ni was present as organic complexes in the organic soils, while ...
... SXRF we found NiO, a direct byproduct of the refining process, present as discrete, spherical particles throughout all of the soil types and treatments. Micro-XAFS enabled us to probe beyond the obvious NiO particles which revealed that Ni was present as organic complexes in the organic soils, while ...
014 Greenhouse gas fluxes at the Wolfson field lab
... The soil monoliths are 0.8 m in diameter and 1 m deep, enough to be representative of field soil conditions. Each is equipped with systems for controlling moisture and temperature of the soil. Gases emitted from the surface can be monitored and dissolved solutes passing out of the bottom, temperatur ...
... The soil monoliths are 0.8 m in diameter and 1 m deep, enough to be representative of field soil conditions. Each is equipped with systems for controlling moisture and temperature of the soil. Gases emitted from the surface can be monitored and dissolved solutes passing out of the bottom, temperatur ...
CRSC 6 – Introduction to Precision Agriculture
... variability in soil related characteristics. 2. List three major areas of potential resulting from input variation and crop response. ...
... variability in soil related characteristics. 2. List three major areas of potential resulting from input variation and crop response. ...
Types of Organic Matter (SOM) - NRCS
... microbes for energy - ave. time to decompostition is 1 - 3 years • Living - organisms such as bacteria, fungi, nematodes, protozoa, earthworms, arthropods, and living roots • Fresh - dead plant material, organic material, detrisus, surface residue, etc. that have only begun to show signs of decay ...
... microbes for energy - ave. time to decompostition is 1 - 3 years • Living - organisms such as bacteria, fungi, nematodes, protozoa, earthworms, arthropods, and living roots • Fresh - dead plant material, organic material, detrisus, surface residue, etc. that have only begun to show signs of decay ...
Chapter 2-section 3 geology notes
... III. How does conservation plowing help conserve soil? The previous year’s crop residue protects the soil. A. Contour plowing- farmers plow their fields along the curves of a slope t o slow runoff of excess rainfall. B. Conservation plowing- farmers disturb the soil and plant cover as little as poss ...
... III. How does conservation plowing help conserve soil? The previous year’s crop residue protects the soil. A. Contour plowing- farmers plow their fields along the curves of a slope t o slow runoff of excess rainfall. B. Conservation plowing- farmers disturb the soil and plant cover as little as poss ...
Pesticide mobility in soils with different uses
... zones which could be exploited for agricultural purposes, once remediated. In these cases pesticide application is needed. However, the use of pesticides for the control of pests, a widely adopted agricultural practice, may impair environmental safety because of pesticide leaching to deeper soil lay ...
... zones which could be exploited for agricultural purposes, once remediated. In these cases pesticide application is needed. However, the use of pesticides for the control of pests, a widely adopted agricultural practice, may impair environmental safety because of pesticide leaching to deeper soil lay ...
These pages in word
... The health of the soil ecosystem depends on environmental conditions, including: climate, topography, parent material (the mineral grains or bedrock on which soil is built), frequency of disturbance. ...
... The health of the soil ecosystem depends on environmental conditions, including: climate, topography, parent material (the mineral grains or bedrock on which soil is built), frequency of disturbance. ...
TYPES OF SOIL Mansi Jain B.Ed VDIT SOIL
... Kashmir, Sikkim & Arunachal Pradesh. Crops: Tea, Coffee, Spices & Tropical Fruits. ...
... Kashmir, Sikkim & Arunachal Pradesh. Crops: Tea, Coffee, Spices & Tropical Fruits. ...
Phosphorus Issues and Protocol Development for Risk Assessment in Florida Watersheds
... Phosphorus issues in Florida’s major watersheds, the Suwannee River (SRB) and Lake Okeechobee (LOB) Basins are of a different nature. The karst-dominated Lower SRB spans several Florida counties where agricultural activities have the potential to affect the groundwater, springs and estuary via verti ...
... Phosphorus issues in Florida’s major watersheds, the Suwannee River (SRB) and Lake Okeechobee (LOB) Basins are of a different nature. The karst-dominated Lower SRB spans several Florida counties where agricultural activities have the potential to affect the groundwater, springs and estuary via verti ...
PurOSil - Gbc India
... improves porosity and drainage of soil and promote the health of the soil's root system. The addition of PurÖSil to soil helps to promote the healthy growth of living plants. The intricate pore structure of diatoms keeps the pores in the soil open and controls the water supply to the roots, holding ...
... improves porosity and drainage of soil and promote the health of the soil's root system. The addition of PurÖSil to soil helps to promote the healthy growth of living plants. The intricate pore structure of diatoms keeps the pores in the soil open and controls the water supply to the roots, holding ...
Soils - Cloudfront.net
... What do you think soil is? Why do you think soil is important? What do you think soil is made from? Which of the things below do you think you can find naturally in soil? ...
... What do you think soil is? Why do you think soil is important? What do you think soil is made from? Which of the things below do you think you can find naturally in soil? ...
GLACIAL EROSIONAL FEATURES
... 2) organic matter - consist of dead leaves, stems, roots, insect remains, droppings, etc.; 1-7% (Sometimes humus forms - a dark, brown or black, soft, spongy residue of organic matter that remains after the bulk of it has decomposed, serves as a major source of plant nutrients & it increases the soi ...
... 2) organic matter - consist of dead leaves, stems, roots, insect remains, droppings, etc.; 1-7% (Sometimes humus forms - a dark, brown or black, soft, spongy residue of organic matter that remains after the bulk of it has decomposed, serves as a major source of plant nutrients & it increases the soi ...
soil and weathering
... 1. the process by which natural forces break down rocks and soil 2. the makeup of rock or soil describing the minerals or elements present in it 4. weathering the breakdown of rock into smaller pieces of the same material without any change to its composition 7. horizon a soil layer with physical an ...
... 1. the process by which natural forces break down rocks and soil 2. the makeup of rock or soil describing the minerals or elements present in it 4. weathering the breakdown of rock into smaller pieces of the same material without any change to its composition 7. horizon a soil layer with physical an ...
Back To Organic Farming
... The top 9 inches of our soil is where plant growth is sustained and therefore this is the area that is the mainspring of our agricultural production. Our health and indeed, our life itself depend on the change taking place in these 9 inches of soil. According to Nature’s design, trees and the ’micro ...
... The top 9 inches of our soil is where plant growth is sustained and therefore this is the area that is the mainspring of our agricultural production. Our health and indeed, our life itself depend on the change taking place in these 9 inches of soil. According to Nature’s design, trees and the ’micro ...