Ossification - Evolutionary Morphology of Vertebrates
... skull reinforcement occurs almost simultaneously, with a whole set of perichondral bones arising especially at places of high mechanical load. The suspensorium becomes protected against dislocation in an anteroposterior direction through a ligamentous connection, which even becomes partially ossifie ...
... skull reinforcement occurs almost simultaneously, with a whole set of perichondral bones arising especially at places of high mechanical load. The suspensorium becomes protected against dislocation in an anteroposterior direction through a ligamentous connection, which even becomes partially ossifie ...
anatomy of the head and neck
... for articulating with the lower jaw between them. The inferior surface of the anterior root carries an articular tubercle (tuberculum articulare), which prevents anterior dislocation of the head of the mandible when the mouth is opened very wide. 2. The tympanic part (pars tympani ...
... for articulating with the lower jaw between them. The inferior surface of the anterior root carries an articular tubercle (tuberculum articulare), which prevents anterior dislocation of the head of the mandible when the mouth is opened very wide. 2. The tympanic part (pars tympani ...
Aberrant Internal Carotid Artery: Clinical Implications
... Right internal carotid artery in this case had a sigmoid tortuosity. Convexity of the sigmoid loop was facing laterally in its lower part and medially in its upper part (Fig. 1). This medially directed convexity extended between pharynx and pre-vertebral muscles at the level of soft palate. At this ...
... Right internal carotid artery in this case had a sigmoid tortuosity. Convexity of the sigmoid loop was facing laterally in its lower part and medially in its upper part (Fig. 1). This medially directed convexity extended between pharynx and pre-vertebral muscles at the level of soft palate. At this ...
III. Syndesmology
... they are generally somewhat enlarged; and consist of spongy cancellous tissue with a thin coating of compact substance. In the flat bones, the articulations usually take place at the edges; and in the short bones at various parts of their surfaces. The layer of compact bone which forms the joint sur ...
... they are generally somewhat enlarged; and consist of spongy cancellous tissue with a thin coating of compact substance. In the flat bones, the articulations usually take place at the edges; and in the short bones at various parts of their surfaces. The layer of compact bone which forms the joint sur ...
Course Notes - MSU Denver Sites
... 1) SHOULDER GIRDLE - SCAPULA, CLAVICLE 2) BRACHIUM - ARM 3) ANTEBRACHIUM -FOREARM 4) CUBITAL FOSSA 6) METACARPALS 7) PHALANGES ...
... 1) SHOULDER GIRDLE - SCAPULA, CLAVICLE 2) BRACHIUM - ARM 3) ANTEBRACHIUM -FOREARM 4) CUBITAL FOSSA 6) METACARPALS 7) PHALANGES ...
CONTENTS
... A.just below the head B.on the posterior surface of the distal end C.on the lateral margin of the distal end D.on the interosseous border E.halfway down on the lateral side of the shaft 26.The olecranon process of the ulna lies ...
... A.just below the head B.on the posterior surface of the distal end C.on the lateral margin of the distal end D.on the interosseous border E.halfway down on the lateral side of the shaft 26.The olecranon process of the ulna lies ...
Blood supply of the Upper Limb
... Discuss the radial and ulnar arteries with their relations and branches. Describe the formation of superficial and deep palmar arches. Explain the formation of dorsal venous arch. Discuss the superficial veins of the upper limb. Describe the formation of axillary vein. ...
... Discuss the radial and ulnar arteries with their relations and branches. Describe the formation of superficial and deep palmar arches. Explain the formation of dorsal venous arch. Discuss the superficial veins of the upper limb. Describe the formation of axillary vein. ...
Abnormal Branching of the Axillary Artery: Subscapular
... normally at the inferior border of teres major muscle where onwards it continues as the brachial artery. Pectoralis minor muscle crosses it and so divides it into three parts which are proximal, posterior and distal to the muscle. Conventionally, the proximal part (first part) gives superior thoraci ...
... normally at the inferior border of teres major muscle where onwards it continues as the brachial artery. Pectoralis minor muscle crosses it and so divides it into three parts which are proximal, posterior and distal to the muscle. Conventionally, the proximal part (first part) gives superior thoraci ...
LOW BACK BIOMECHANICS DURING WALKING OF INDIVIDUALS
... analysis, and spinal tissue degeneration. ...
... analysis, and spinal tissue degeneration. ...
Normal variations of cervical-petrosal Internal Carotid Artery
... Non-bifurcating carotid artery is an extremely rare anatomical variation of cervical carotid artery (12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17). It can be classified into two types according to its course at the proximal portion. One runs into carotid canal in straight course (Fig.11). The other shows significant tort ...
... Non-bifurcating carotid artery is an extremely rare anatomical variation of cervical carotid artery (12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17). It can be classified into two types according to its course at the proximal portion. One runs into carotid canal in straight course (Fig.11). The other shows significant tort ...
I. Anterior intercostal veins
... - Its lateral cutaneous branch is called the intercostobrachial nerve which supplies the base of the axilla and upper part of the medial side of arm and does not divide into anterior and posterior branches. 3. Lower five intercostal nerves - They reach the anterior abdominal wall at the anterior end ...
... - Its lateral cutaneous branch is called the intercostobrachial nerve which supplies the base of the axilla and upper part of the medial side of arm and does not divide into anterior and posterior branches. 3. Lower five intercostal nerves - They reach the anterior abdominal wall at the anterior end ...
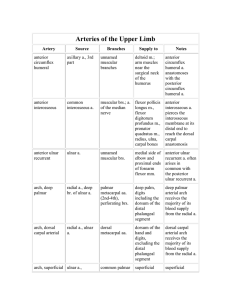
Arteries of the Upper Limb
... dorsal scapular a. anastomoses with the suprascapular a. and the subscapular a. to form the scapular anastomosis; dorsal scapular a is a branch of the transverse cervical a. in ~30% of cases ...
... dorsal scapular a. anastomoses with the suprascapular a. and the subscapular a. to form the scapular anastomosis; dorsal scapular a is a branch of the transverse cervical a. in ~30% of cases ...
on the anatomy of the red bird of paradise, with comparative remarks
... Neither of the cervicodorsalribs possessuncinate processesin Corvus or Cyanocitta;this is another character in which one expects to find some variation in a large series of skeletons. In each species, all five of the true ribs articulate ...
... Neither of the cervicodorsalribs possessuncinate processesin Corvus or Cyanocitta;this is another character in which one expects to find some variation in a large series of skeletons. In each species, all five of the true ribs articulate ...
Slide 1
... Discuss the radial and ulnar arteries with their relations and branches. Describe the formation of superficial and deep palmar arches. Explain the formation of dorsal venous arch. Discuss the superficial veins of the upper limb. Describe the formation of axillary vein. ...
... Discuss the radial and ulnar arteries with their relations and branches. Describe the formation of superficial and deep palmar arches. Explain the formation of dorsal venous arch. Discuss the superficial veins of the upper limb. Describe the formation of axillary vein. ...
Venous Collateral Circulation of the Extracranial
... hemodynamics regulation (Vignes et al. 2007). The SSS vascular caliber increases from anterior to posterior, because of the penetration of arachnoid villi inside ...
... hemodynamics regulation (Vignes et al. 2007). The SSS vascular caliber increases from anterior to posterior, because of the penetration of arachnoid villi inside ...
Branches
... Discuss the radial and ulnar arteries with their relations and branches. Describe the formation of superficial and deep palmar arches. Explain the formation of dorsal venous arch. Discuss the superficial veins of the upper limb. Describe the formation of axillary vein. ...
... Discuss the radial and ulnar arteries with their relations and branches. Describe the formation of superficial and deep palmar arches. Explain the formation of dorsal venous arch. Discuss the superficial veins of the upper limb. Describe the formation of axillary vein. ...
morphometry of jugular foramen and determination of standard
... posterior end of the petro-occipital fissure and the anterior part of jugular foramen is allows the cranial nerves IXth, Xth, XIth the direction of the nerves from behind forwards within the jugular foramen and sometimes jugular tubercle it has acted as a groove and later it becomes enter of the for ...
... posterior end of the petro-occipital fissure and the anterior part of jugular foramen is allows the cranial nerves IXth, Xth, XIth the direction of the nerves from behind forwards within the jugular foramen and sometimes jugular tubercle it has acted as a groove and later it becomes enter of the for ...
Clinical anatomy of the superior cluneal nerve in relation
... Lower back pain (LBP) is estimated to have a prevalence of 85–90%. There are many aetiological factors for LBP but even with the use of new imaging techniques no obvious cause can be found in approximately 50% of these cases.1 One of the many missed causes of LBP is entrapment of the medial branch o ...
... Lower back pain (LBP) is estimated to have a prevalence of 85–90%. There are many aetiological factors for LBP but even with the use of new imaging techniques no obvious cause can be found in approximately 50% of these cases.1 One of the many missed causes of LBP is entrapment of the medial branch o ...
Anatomy of the posterior cruciate ligament
... In full extension the anterior fibres become fully lax and the central fibres seem to be less lax while the posterior fibres tighten. During flexion up to 90 degrees the anterior and central fibre bundles tighten while the posterior fibres become slightly lax. From 90 to 120 degrees the anterior fib ...
... In full extension the anterior fibres become fully lax and the central fibres seem to be less lax while the posterior fibres tighten. During flexion up to 90 degrees the anterior and central fibre bundles tighten while the posterior fibres become slightly lax. From 90 to 120 degrees the anterior fib ...
Variation in the origin of branches of axillary artery- A case
... and ends at the lower border of the teres major muscle. It is classically divided into three parts by the pectoralis minor. There is an extensive collateral circulation associated with the subclavian and axillary arteries, particularly around the scapula. Branches emerging from axillary artery suppl ...
... and ends at the lower border of the teres major muscle. It is classically divided into three parts by the pectoralis minor. There is an extensive collateral circulation associated with the subclavian and axillary arteries, particularly around the scapula. Branches emerging from axillary artery suppl ...
Clinically-relevant variations of the carotid arterial
... brachiocephalic trunk. The CCAs of both sides divide at the upper border of the thyroid cartilage at intervertebral disc level between the third and fourth cervical vertebrae into external and internal carotid arteries.(1) The external carotid artery (ECA) extends from the level of upper border of t ...
... brachiocephalic trunk. The CCAs of both sides divide at the upper border of the thyroid cartilage at intervertebral disc level between the third and fourth cervical vertebrae into external and internal carotid arteries.(1) The external carotid artery (ECA) extends from the level of upper border of t ...
Radiographic Identification of the Primary Lateral
... Purpose: To quantitatively describe the anatomic attachment sites of the anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL), calcaneofibular ligament (CFL), and posterior talofibular ligament (PTFL) on standard radiographic views with respect to reproducible osseous landmarks to assist with intraoperative and pos ...
... Purpose: To quantitatively describe the anatomic attachment sites of the anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL), calcaneofibular ligament (CFL), and posterior talofibular ligament (PTFL) on standard radiographic views with respect to reproducible osseous landmarks to assist with intraoperative and pos ...
Abnormality of the Foramen Spinosum due to a Variation in the
... Some reports about the anatomic variations of the MMA regarding the origin, position, and intracranial branches8,9 and several anomalies of this artery6,10–12 have been reported for more than three decades; before that, embryological studies had been conducted to improve knowledge of possible anatom ...
... Some reports about the anatomic variations of the MMA regarding the origin, position, and intracranial branches8,9 and several anomalies of this artery6,10–12 have been reported for more than three decades; before that, embryological studies had been conducted to improve knowledge of possible anatom ...
Mammals. By WK Gregory..................................... 515
... Part VI. Second Note on the Evolution of the Coracoid Elements in Reptiles and Mammals. By W. K; Gregory ............................. Summary and Conclusions. By W. K. Gregory ........................ Explanation of Plates ................................................ ...
... Part VI. Second Note on the Evolution of the Coracoid Elements in Reptiles and Mammals. By W. K; Gregory ............................. Summary and Conclusions. By W. K. Gregory ........................ Explanation of Plates ................................................ ...
Vertebra

In the vertebrate spinal column, each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, the proportions of which vary according to the segment of the backbone and the species of vertebrate animal.The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the large part is the body, and the central part is the centrum. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles, two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava. There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conducts for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebra and the vertebral arch form the vertebral foramen, the larger, central opening that accommodates the spinal canal, which encloses and protects the spinal cord.Vertebrae articulate with each other to give strength and flexibility to the spinal column, and the shape at their back and front aspects determines the range of movement. Structurally, vertebrae are essentially alike across the vertebrate species, with the greatest difference seen between an aquatic animal and other vertebrate animals. As such, vertebrates take their name from the vertebrae that compose the vertebral column.