Endocrinology II
... receiving suboptimal cortisol or cortisone replacement may be at risk of developing symptoms of cortisol deficiency when growth hormone therapy is initiated. This is due to the inhibitory effect of growth hormone on 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1, the enzyme that converts cortisone to c ...
... receiving suboptimal cortisol or cortisone replacement may be at risk of developing symptoms of cortisol deficiency when growth hormone therapy is initiated. This is due to the inhibitory effect of growth hormone on 11-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1, the enzyme that converts cortisone to c ...
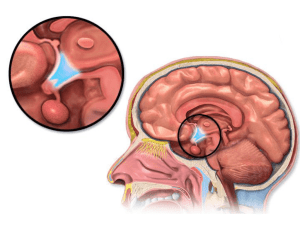
The hypothalamus
... accelerator for pituitary and other parasellar tumors causes a risk of hypopituitarism similar to that of conventional irradiation. ...
... accelerator for pituitary and other parasellar tumors causes a risk of hypopituitarism similar to that of conventional irradiation. ...
Endorphin Mediates Behavioral Despair and the Effect of Ethanol on
... Experiment 3, Tail Suspension Test With EtOH Interactions between b-E and EtOH were evaluated using the Tail Suspension Test (TST). The FST and TST are thought to reflect the same substrates (Cryan et al., 2005; Kulkarni and Dhir, 2007) but at least in our hands, the TST is less variable and we were ...
... Experiment 3, Tail Suspension Test With EtOH Interactions between b-E and EtOH were evaluated using the Tail Suspension Test (TST). The FST and TST are thought to reflect the same substrates (Cryan et al., 2005; Kulkarni and Dhir, 2007) but at least in our hands, the TST is less variable and we were ...
posterior pituitary hormones
... • Explain hypothalamus as the major integrative site for the neuroendocrine system. • Contrast anterior and posterior pituitary lobes with respect to cell types, vascular supply, development, and innervations. • Identify posterior pituitary hormones (oxytocin & vasopressin). • List target tissues fo ...
... • Explain hypothalamus as the major integrative site for the neuroendocrine system. • Contrast anterior and posterior pituitary lobes with respect to cell types, vascular supply, development, and innervations. • Identify posterior pituitary hormones (oxytocin & vasopressin). • List target tissues fo ...
Neuroanatomy Ch 17 792-805 [4-20
... and dorsomedial nucleus -arcuate nucleus projects to median eminence to control anterior pituitary 5. posterior hypothalamic region (mammillary) – medial mammillary nucleus, intermediate mammillary nucleus, lateral mammillary nucleus and posterior hypothalamic nucleus Hypothalamic Control of Autonom ...
... and dorsomedial nucleus -arcuate nucleus projects to median eminence to control anterior pituitary 5. posterior hypothalamic region (mammillary) – medial mammillary nucleus, intermediate mammillary nucleus, lateral mammillary nucleus and posterior hypothalamic nucleus Hypothalamic Control of Autonom ...
СПИСЪК НА ПУБЛИКАЦИИ И РЕЗЮМЕТА
... parameter were found. Thrombomodulin and TAT plasma concentrations were reduced by all of the hormones (p<0.001). The results of the study indicate that thyroid hormonal axis is substantially involved in regulation to anticoagulation via antithrombin III by increasing its activity and suppressing TA ...
... parameter were found. Thrombomodulin and TAT plasma concentrations were reduced by all of the hormones (p<0.001). The results of the study indicate that thyroid hormonal axis is substantially involved in regulation to anticoagulation via antithrombin III by increasing its activity and suppressing TA ...
Virtual Rat Endocrine Lab
... pituitary gland. Because the anterior pituitary gland secretes multiple hormones, it is frequently referred to as the ‘‘master gland.’’ For this experiment, we will focus on the hypothalamus only as a regulator of the anterior pituitary gland. Figure 1(a) and 1(b) shows the relationship between the ...
... pituitary gland. Because the anterior pituitary gland secretes multiple hormones, it is frequently referred to as the ‘‘master gland.’’ For this experiment, we will focus on the hypothalamus only as a regulator of the anterior pituitary gland. Figure 1(a) and 1(b) shows the relationship between the ...
UNDERSTANDING CONGENITAL ADRENAL HYPERPLASIA
... There are many types of CAH. The most common (80-90% of all cases) is saltlosing CAH. The loss of salt in the urine is uncontrolled (due to the low levels of aldosterone) and can cause dehydration, low blood pressure and vomiting. The levels of salt (sodium and chloride) and sugar (glucose) fall in ...
... There are many types of CAH. The most common (80-90% of all cases) is saltlosing CAH. The loss of salt in the urine is uncontrolled (due to the low levels of aldosterone) and can cause dehydration, low blood pressure and vomiting. The levels of salt (sodium and chloride) and sugar (glucose) fall in ...
Pituitary and Hypothalamus Disorders MBBS III Seminar
... Normal Anatomy & Function • The pituitary is located at the base of the brain, in a small depression of the sphenoid bone (sella turcica). • Purpose: control the activity of many other endocrine glands. “ Master gland” • Has two lobes, the anterior & posterior lobes. ...
... Normal Anatomy & Function • The pituitary is located at the base of the brain, in a small depression of the sphenoid bone (sella turcica). • Purpose: control the activity of many other endocrine glands. “ Master gland” • Has two lobes, the anterior & posterior lobes. ...
S10 Clinicalbiochem2 DrNansy Hypothalamus And Pituitary
... • Acts directly on many tissues to modulate metabolism. Metabolic fuels (glucose, free fatty acids) in turn modify GH secretion • It is essential for normal growth, although in the main it acts indirectly by stimulating the liver to produce insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), also known as somatom ...
... • Acts directly on many tissues to modulate metabolism. Metabolic fuels (glucose, free fatty acids) in turn modify GH secretion • It is essential for normal growth, although in the main it acts indirectly by stimulating the liver to produce insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), also known as somatom ...
Endocrine Test Review
... When diagnosed at a young age, dwarfism is treated byA removal of the thyroid gland B radiation therapy C administering supplemental growth hormones D administering iodine supplements ...
... When diagnosed at a young age, dwarfism is treated byA removal of the thyroid gland B radiation therapy C administering supplemental growth hormones D administering iodine supplements ...
The roles of the different hormones in your body
... thyroid. Some physicians prescribe a combination of T4 and T3 so the body does not have to work so hard in making the conversion and readily use the active hormone T3. Naturally derived thyroid medications such as Armour Thyroid, Nature thyroid, or desiccated thyroids that are utilized by compoundin ...
... thyroid. Some physicians prescribe a combination of T4 and T3 so the body does not have to work so hard in making the conversion and readily use the active hormone T3. Naturally derived thyroid medications such as Armour Thyroid, Nature thyroid, or desiccated thyroids that are utilized by compoundin ...
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Thyroid Axis - Open Michigan
... Public Domain – Government: Works that are produced by the U.S. Government. (17 USC § 105) Public Domain – Expired: Works that are no longer protected due to an expired copyright term. Public Domain – Self Dedicated: Works that a copyright holder has dedicated to the public domain. ...
... Public Domain – Government: Works that are produced by the U.S. Government. (17 USC § 105) Public Domain – Expired: Works that are no longer protected due to an expired copyright term. Public Domain – Self Dedicated: Works that a copyright holder has dedicated to the public domain. ...
ENDOCRINE “PITUITARY“ EMERGENCIES
... e-threatening. Treatment consists of ABC upport, blockade of excessive catecholamine ctivity with propranolol, inhibition of the ynthesis of new thyroid hormone with PTU, ockade of peripheral conversion of T4 to T3 th hydrocortisone, and treatment of the ...
... e-threatening. Treatment consists of ABC upport, blockade of excessive catecholamine ctivity with propranolol, inhibition of the ynthesis of new thyroid hormone with PTU, ockade of peripheral conversion of T4 to T3 th hydrocortisone, and treatment of the ...
Isolated corticotrophin deficiency
... the late afternoon and impaired quality of life. Recent studies indicate that thrice-daily regimens more closely mimics the physiological steroid circadian profile [65, 66]. Long-acting glucocorticoids can also be used in equivalent doses (1 mg hydrocortisone = 1.25 mg cortisone acetate = 0.2 mg pre ...
... the late afternoon and impaired quality of life. Recent studies indicate that thrice-daily regimens more closely mimics the physiological steroid circadian profile [65, 66]. Long-acting glucocorticoids can also be used in equivalent doses (1 mg hydrocortisone = 1.25 mg cortisone acetate = 0.2 mg pre ...
Hypothalamus and Pituitary
... • CRH and ADH both synthesized in hypothalamus – ADH is released by posertior pituitary and reaches anterior pituitary via inferior hypophyseal artery. ...
... • CRH and ADH both synthesized in hypothalamus – ADH is released by posertior pituitary and reaches anterior pituitary via inferior hypophyseal artery. ...
PITUITARY HORMONES: An Overview
... factors enhances secretion of Pituitary Hormones; • Specific functions are as follows: • TRH: Induces secretion of TSH and Prolactin; • GnRH: Induces secretion of LH and FSH; • GHRH: Induces secretion of GH; • Gherelin: Peptide hormone released from epithelial cells lining the fundus of the stomach ...
... factors enhances secretion of Pituitary Hormones; • Specific functions are as follows: • TRH: Induces secretion of TSH and Prolactin; • GnRH: Induces secretion of LH and FSH; • GHRH: Induces secretion of GH; • Gherelin: Peptide hormone released from epithelial cells lining the fundus of the stomach ...
The Association of Major Depression, Conduct Disorder, and
... with decreased cortisol levels (Woodman et al. 1978). However, the role of cortisol in teen girls with CD is less known. Susman et al. (1999) showed no evidence of an association between cortisol levels in pregnant adolescents with CD, whereas Pajer et al. (2001) found that girls with CD did have de ...
... with decreased cortisol levels (Woodman et al. 1978). However, the role of cortisol in teen girls with CD is less known. Susman et al. (1999) showed no evidence of an association between cortisol levels in pregnant adolescents with CD, whereas Pajer et al. (2001) found that girls with CD did have de ...
Slide 1
... • Describe the general characteristics of hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting (hypophysiotropic) hormones and describe their route of transport from the hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary. • Identify appropriate hypothalamic hormones that control the secretion of each of the anterior pituitary ...
... • Describe the general characteristics of hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting (hypophysiotropic) hormones and describe their route of transport from the hypothalamus to the anterior pituitary. • Identify appropriate hypothalamic hormones that control the secretion of each of the anterior pituitary ...
Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis
.png?width=300)
The hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA or HTPA axis), also known as the limbic–hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (LHPA axis) and, occasionally, as the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal–gonadotropic axis, is a complex set of direct influences and feedback interactions among three endocrine glands: the hypothalamus, the pituitary gland (a pea-shaped structure located below the hypothalamus), and the adrenal (also called ""suprarenal"") glands (small, conical organs on top of the kidneys).The interactions among these organs constitute the HPA axis, a major part of the neuroendocrine system that controls reactions to stress and regulates many body processes, including digestion, the immune system, mood and emotions, sexuality, and energy storage and expenditure. It is the common mechanism for interactions among glands, hormones, and parts of the midbrain that mediate the general adaptation syndrome (GAS). While steroid hormones are produced mainly in vertebrates, the physiological role of the HPA axis and corticosteroids in stress response is so fundamental that analogous systems can be found in invertebrates and monocellular organisms as well.