Czytaj więcej - Instytut Mikroekologii
... “professional” gut bacteria. Staphylococci are skin commensals and the S. aureus strains colonizing the infants mostly derive from their parents skin flora (Lindberg et al. 2004). Half of the strains produced one or more toxins with superantigen function, i.e. SEA-D (S. aureus-enterotoxin A, B, C, D ...
... “professional” gut bacteria. Staphylococci are skin commensals and the S. aureus strains colonizing the infants mostly derive from their parents skin flora (Lindberg et al. 2004). Half of the strains produced one or more toxins with superantigen function, i.e. SEA-D (S. aureus-enterotoxin A, B, C, D ...
Surgery Resident Half Day
... • Nosocomial infections are common and have associated morbidity and mortality • Most nosocomial infections are preventable – Hand hygiene is one of the most effective ways to reduce nosocomial infections ...
... • Nosocomial infections are common and have associated morbidity and mortality • Most nosocomial infections are preventable – Hand hygiene is one of the most effective ways to reduce nosocomial infections ...
Treatment Outcomes for Serious Infections Caused by Methicillin
... and susceptibility definitions below) whose isolate was referred to our laboratory during the period of 1 May 2001 through 31 January 2003 were eligible for inclusion in this study. A questionnaire was sent to the referring clinician to obtain the patient’s demographic characteristics and data on co ...
... and susceptibility definitions below) whose isolate was referred to our laboratory during the period of 1 May 2001 through 31 January 2003 were eligible for inclusion in this study. A questionnaire was sent to the referring clinician to obtain the patient’s demographic characteristics and data on co ...
document
... The Problem 1. Antibiotic resistant infection is a significant and growing cause of morbidity and mortality; 2. The medical profession is increasingly concerned; 3. Vancomycin resistance has occurred: no new antibiotics are available. ...
... The Problem 1. Antibiotic resistant infection is a significant and growing cause of morbidity and mortality; 2. The medical profession is increasingly concerned; 3. Vancomycin resistance has occurred: no new antibiotics are available. ...
Microbiological examination to investigate the differences in
... odontogenic infections have declined dramatically over the years. This reduction in mortality is not attributed to the use of penicillin but is due to the application of the principles of the initial establishment of airway security, followed by early and aggressive surgical drainage of all anatomic ...
... odontogenic infections have declined dramatically over the years. This reduction in mortality is not attributed to the use of penicillin but is due to the application of the principles of the initial establishment of airway security, followed by early and aggressive surgical drainage of all anatomic ...
Alexandre Apfel and Tudor Gradinariu with additions by Ms. S. Smith
... May be applied after broad spectrum ...
... May be applied after broad spectrum ...
Musculoskeletal Infection Pathway Executive Summary
... • Source evaluation: Send pus (not a swab) for Gram stain and bacterial culture, and if possible tissue/synovium for pathology. If joint fluid, send for bacterial culture, Gram stain, cell count, differential and fluid to hold. If unusual case or exposures, consult ID for further testing/culturi ...
... • Source evaluation: Send pus (not a swab) for Gram stain and bacterial culture, and if possible tissue/synovium for pathology. If joint fluid, send for bacterial culture, Gram stain, cell count, differential and fluid to hold. If unusual case or exposures, consult ID for further testing/culturi ...
Incorporating Rapid Diagnostic Microbiology Testing into
... chain reaction methicillin-resistant Satphylococcus aureus/S. aureus blood culture test in patients with S. aureus bacteremia. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;51:10174-80. Nagel JL, Huang AM, Kunapuli A, et al. Impact of antimicrobial stewardship intervention on Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcus Blood Culture ...
... chain reaction methicillin-resistant Satphylococcus aureus/S. aureus blood culture test in patients with S. aureus bacteremia. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;51:10174-80. Nagel JL, Huang AM, Kunapuli A, et al. Impact of antimicrobial stewardship intervention on Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcus Blood Culture ...
Caused by - FranklinPiercePA
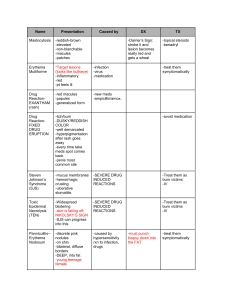
... COLOR -well demarcated -hyperpigmentation after rash goes away -every time take meds spot comes back -penis most common site ...
... COLOR -well demarcated -hyperpigmentation after rash goes away -every time take meds spot comes back -penis most common site ...
Canine Bacterial Skin Infections, “Pyoderma”
... recurrent superficial pyoderma is a common and frustrating problem. If a specific underlying cause (such as allergies) cannot be determined (and controlled) then efforts must be made to control the bacterial population on the skin’s surface. In these cases frequent use of appropriate antibacterial s ...
... recurrent superficial pyoderma is a common and frustrating problem. If a specific underlying cause (such as allergies) cannot be determined (and controlled) then efforts must be made to control the bacterial population on the skin’s surface. In these cases frequent use of appropriate antibacterial s ...
KEY - Cobb Learning
... Introduction: Thousands of different types of bacteria are known and have been observed, and there are possibly many more that have not yet been observed. How can a scientist tell these organisms apart when they are so small? One way is the bacteria's characteristic shape or pattern of joining toget ...
... Introduction: Thousands of different types of bacteria are known and have been observed, and there are possibly many more that have not yet been observed. How can a scientist tell these organisms apart when they are so small? One way is the bacteria's characteristic shape or pattern of joining toget ...
Rita K - Universa Medicina
... children and fall to two times per year in adult. Assuming that each episode last about 4 days, then a 70 year old people may have spent about 1-2 years suffering from URI. (4) URI do not contribute significantly to deaths in children, but they cause considerable burden of disability. (2) The sympto ...
... children and fall to two times per year in adult. Assuming that each episode last about 4 days, then a 70 year old people may have spent about 1-2 years suffering from URI. (4) URI do not contribute significantly to deaths in children, but they cause considerable burden of disability. (2) The sympto ...
IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences (IOSR-JPBS) e-ISSN: 2278-3008, p-ISSN:2319-7676.
... trend towards more resistant isolates in all groups of patients. Prolonged or repeated exposure to antimicrobial agents and the consequent antibiotic pressure increase the risk of colonization and infection with multi resistant bacteria (Master and Joshi, 2003). Most of the gram negative isolates sh ...
... trend towards more resistant isolates in all groups of patients. Prolonged or repeated exposure to antimicrobial agents and the consequent antibiotic pressure increase the risk of colonization and infection with multi resistant bacteria (Master and Joshi, 2003). Most of the gram negative isolates sh ...
Personal Service Establishments: Looking at Infections Risks
... MRSA. J Hosp Infect. 2001 Nov;49(3):225-7. 12. Mele A, Corona R, Tosti ME, Palumbo F, Moiraghi A, Novaco F, et al. Beauty treatments and risk of parenterally transmitted hepatitis: results from the hepatitis surveillance system in Italy. Scand J ...
... MRSA. J Hosp Infect. 2001 Nov;49(3):225-7. 12. Mele A, Corona R, Tosti ME, Palumbo F, Moiraghi A, Novaco F, et al. Beauty treatments and risk of parenterally transmitted hepatitis: results from the hepatitis surveillance system in Italy. Scand J ...
Présentation PowerPoint - Physiologie et Thérapeutique Ecole Véto
... Before treatment : E. coli R (0.01 to 0.1%) After IV. :Decrease of total E coli , slight increase of E. coli R (4 to 8 %) Back to initial level After repeated IM (3d) : Decrease below LoD E. coli (2 days), fast growth (~ 3 106 ufc/g 1 d). E. coli R followed to a slow decrease back to initial level a ...
... Before treatment : E. coli R (0.01 to 0.1%) After IV. :Decrease of total E coli , slight increase of E. coli R (4 to 8 %) Back to initial level After repeated IM (3d) : Decrease below LoD E. coli (2 days), fast growth (~ 3 106 ufc/g 1 d). E. coli R followed to a slow decrease back to initial level a ...
When to use antibiotics in the cirrhotic patient?
... In SBP where the commonest organisms are E. coli, Streptococcus viridans and Enterobacter spp., preferred antibiotic regimens are cefotaxime (2 g/6 h or 2 g/12 h IV) or amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (1-0.2 g /8 h then 0.5-0.125 g/8 h PO) or ofloxacin (400 mg/12 h PO) [11-14]. Courses should not last l ...
... In SBP where the commonest organisms are E. coli, Streptococcus viridans and Enterobacter spp., preferred antibiotic regimens are cefotaxime (2 g/6 h or 2 g/12 h IV) or amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (1-0.2 g /8 h then 0.5-0.125 g/8 h PO) or ofloxacin (400 mg/12 h PO) [11-14]. Courses should not last l ...
Microbial Metabolism
... • They are polysaccharides in cell wall (G+ bacteria) or LPS (G- bacteria). • They are highly resistant to high heat (not being destroyed heating at 121C for 15-20 min), but can be destroyed by heating to 250 C for 30 min. • They can be removed from most fluid materials by adsorption ...
... • They are polysaccharides in cell wall (G+ bacteria) or LPS (G- bacteria). • They are highly resistant to high heat (not being destroyed heating at 121C for 15-20 min), but can be destroyed by heating to 250 C for 30 min. • They can be removed from most fluid materials by adsorption ...
AS Microbiology and Antibiotic Resistance Sep 2012
... • Inappropriate and excessive use of antibiotics is a major factor contributing to emerging antibiotic resistance • Determinants of resistance are selected for by antibiotic use • Multiple mechanisms exist for bacteria to become resistant to antibiotics • Antibiotic resistance is a problem in outpat ...
... • Inappropriate and excessive use of antibiotics is a major factor contributing to emerging antibiotic resistance • Determinants of resistance are selected for by antibiotic use • Multiple mechanisms exist for bacteria to become resistant to antibiotics • Antibiotic resistance is a problem in outpat ...
Slide 1
... The “intermediate” category includes isolates with antimicrobial agent MICs that approach usually attainable blood and tissue levels and for which response rates may be lower than for susceptible isolates. The intermediate category implies clinical efficacy in body sites where the drugs are physiolo ...
... The “intermediate” category includes isolates with antimicrobial agent MICs that approach usually attainable blood and tissue levels and for which response rates may be lower than for susceptible isolates. The intermediate category implies clinical efficacy in body sites where the drugs are physiolo ...
Endocarditis: Some Basics - UCSF | Department of Medicine
... • The category “Possible IE” should be defined as at least 1 major and 1 minor criterion or 3 minor criteria • The minor criterion of echocardiographic findings consistent with endocarditis but not meeting a major criterion should be eliminated, due to the widespread use of the more accurate transes ...
... • The category “Possible IE” should be defined as at least 1 major and 1 minor criterion or 3 minor criteria • The minor criterion of echocardiographic findings consistent with endocarditis but not meeting a major criterion should be eliminated, due to the widespread use of the more accurate transes ...
13. Clark B, McKendrick M. A review of viral gastroenteritis. Curr
... One billion people have poor excess to water and about 2.6 billion lack basic sanitation facilities worldwide [1]. Ten to eleven million children die before the age of five in low and middle income countries [2]. Among many other infectious diseases, diarrohea is an important cause of morbidity and ...
... One billion people have poor excess to water and about 2.6 billion lack basic sanitation facilities worldwide [1]. Ten to eleven million children die before the age of five in low and middle income countries [2]. Among many other infectious diseases, diarrohea is an important cause of morbidity and ...
In Vitro and In Vivo Antibacterial Activities of Omadacycline, a Novel
... MICs of omadacycline, tetracycline, and doxycycline on characterized tetracycline-resistant Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Omadacycline demonstrated activity against the Gram-positive pathogens S. aureus, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium, S. pneumoniae, and beta-hemolytic strep ...
... MICs of omadacycline, tetracycline, and doxycycline on characterized tetracycline-resistant Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Omadacycline demonstrated activity against the Gram-positive pathogens S. aureus, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium, S. pneumoniae, and beta-hemolytic strep ...
Laboratory Exercise # 11: Differentiation of the Species
... Staphylococcus species is the Catalase test. In this test we are testing for the ability of the bacteria to produce the enzyme catalase. This enzyme breaks down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. Hydrogen peroxide, as well as superoxides, can be metabolic end products of the production of ATP ...
... Staphylococcus species is the Catalase test. In this test we are testing for the ability of the bacteria to produce the enzyme catalase. This enzyme breaks down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. Hydrogen peroxide, as well as superoxides, can be metabolic end products of the production of ATP ...
Staphylococcus aureus (Wood 46)
... low a-toxin-producing variant produce the same extracellular proteins. However, in the variant, five components (a to e), including the a-toxin, were present in reduced amounts relative to the levels produced by the parent organism. The changes in bacterial density, total extracellular protein and h ...
... low a-toxin-producing variant produce the same extracellular proteins. However, in the variant, five components (a to e), including the a-toxin, were present in reduced amounts relative to the levels produced by the parent organism. The changes in bacterial density, total extracellular protein and h ...
Staphylococcus aureus

Staphylococcus aureus is a gram-positive coccal bacterium that is a member of the Firmicutes, and is frequently found in the respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction. Although S. aureus is not always pathogenic, it is a common cause of skin infections such as abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing potent protein toxins, and expressing cell-surface proteins that bind and inactivate antibodies. The emergence of antibiotic-resistant forms of S. aureus such as MRSA is a worldwide problem in clinical medicine.Staphylococcus was first identified in 1880 in Aberdeen, Scotland, by the surgeon Sir Alexander Ogston in pus from a surgical abscess in a knee joint. This name was later appended to Staphylococcus aureus by Friedrich Julius Rosenbach, who was credited by the official system of nomenclature at the time. An estimated 20% of the human population are long-term carriers of S. aureus which can be found as part of the normal skin flora and in the nostrils. S. aureus is the most common species of Staphylococcus to cause Staph infections and is a successful pathogen due to a combination of nasal carriage and bacterial immunoevasive strategies.S. aureus can cause a range of illnesses, from minor skin infections, such as pimples, impetigo, boils, cellulitis, folliculitis, carbuncles, scalded skin syndrome, and abscesses, to life-threatening diseases such as pneumonia, meningitis, osteomyelitis, endocarditis, toxic shock syndrome, bacteremia, and sepsis. Its incidence ranges from skin, soft tissue, respiratory, bone, joint, endovascular to wound infections. It is still one of the five most common causes of hospital-acquired infections and is often the cause of postsurgical wound infections. Each year, around 500,000 patients in United States' hospitals contract a staphylococcal infection.