Many other important inventions involve the use of
... diameter about 10 micrometers), single-mode transmitters, receivers, amplifiers and other components are generally more expensive than multi-mode components. Fiber optic sensors Fibers have many uses in remote sensing. In some applications, the sensor is itself an optical fiber. In other cases, fibe ...
... diameter about 10 micrometers), single-mode transmitters, receivers, amplifiers and other components are generally more expensive than multi-mode components. Fiber optic sensors Fibers have many uses in remote sensing. In some applications, the sensor is itself an optical fiber. In other cases, fibe ...
unit –iii fiber optics and applications part-a 2
... Principle:When light travels from a denser to a rarer medium, at a particular angle of incidence called critical angle, the ray emerges along the surface of separation. When the angle of incidence exceeds the critical angle, the incident ray is reflected in the same medium and the phenomenon is call ...
... Principle:When light travels from a denser to a rarer medium, at a particular angle of incidence called critical angle, the ray emerges along the surface of separation. When the angle of incidence exceeds the critical angle, the incident ray is reflected in the same medium and the phenomenon is call ...
Scattered Light Predictions for Aluminum Painted Reflectors in
... lamp with an aluminize reflector showed excellent correlation with the actual measurements as shown in Figure 9. A correlation coefficient of 0.975 was achieved. Figure 11. Far-field light distribution comparison between the ASAP model and Photometer measurements for SHLA painted reflector ...
... lamp with an aluminize reflector showed excellent correlation with the actual measurements as shown in Figure 9. A correlation coefficient of 0.975 was achieved. Figure 11. Far-field light distribution comparison between the ASAP model and Photometer measurements for SHLA painted reflector ...
Light-More-interference
... The index of refraction, n, is a function of wavelength. The angle of refraction is varies for different wavelengths of light. The index of refraction generally decreases with increasing wavelength. The means that red light ( = 600 nm) bends less than does blue light ( = 470 nm). ...
... The index of refraction, n, is a function of wavelength. The angle of refraction is varies for different wavelengths of light. The index of refraction generally decreases with increasing wavelength. The means that red light ( = 600 nm) bends less than does blue light ( = 470 nm). ...
The radiated fields of the fundamental mode of photonic crystal fibers
... which is far from the starting point of the Fraunhofer region. For an extended source of electromagnetic radiation, the Fraunhofer region appears at a characteristic distance 2D2 /λ from the source where the parameter D is defined by the maximum linear dimension of the source. For a PCF D ∼ 2Λ, so F ...
... which is far from the starting point of the Fraunhofer region. For an extended source of electromagnetic radiation, the Fraunhofer region appears at a characteristic distance 2D2 /λ from the source where the parameter D is defined by the maximum linear dimension of the source. For a PCF D ∼ 2Λ, so F ...
Analytical Expression for the Standing Wave Intensity in Photoresist
... Table I with the results of Eq. (3) graphed in Fig. 2. Recently, use of a thin contrast-enhancement layer on top of the photoresist has been shown to improve resolution.6 This type of resist system can be modeled with the use of Eq. (4). The condition that the photoresist be homogeneous is true only ...
... Table I with the results of Eq. (3) graphed in Fig. 2. Recently, use of a thin contrast-enhancement layer on top of the photoresist has been shown to improve resolution.6 This type of resist system can be modeled with the use of Eq. (4). The condition that the photoresist be homogeneous is true only ...
Michelson interferometer
... (air). Therefore the beam travelling towards mirror S2 is in effect reflected inside the glass plate, off an optically thinner medium; the beam returning from mirror S1 in air is reflected from the metal film applied on the denser medium (glass). In the latter case, for reasons that are not obvious, ...
... (air). Therefore the beam travelling towards mirror S2 is in effect reflected inside the glass plate, off an optically thinner medium; the beam returning from mirror S1 in air is reflected from the metal film applied on the denser medium (glass). In the latter case, for reasons that are not obvious, ...
Polarized light and polarizers
... Ey (z, t) = A1 e−(α/2)z cos(ωt − kz) + A2 e+(α/2)z cos(ωt + kz) α= ...
... Ey (z, t) = A1 e−(α/2)z cos(ωt − kz) + A2 e+(α/2)z cos(ωt + kz) α= ...
Integrated Optics
... 3. The modulating signal and the optical wave travel along the waveguide. However, the optical energy is mostly confined to the dielectric waveguide wich has refractive index of about 2.2. The modulating signal fields are not well confined to the substrate. There is substantial field above the subst ...
... 3. The modulating signal and the optical wave travel along the waveguide. However, the optical energy is mostly confined to the dielectric waveguide wich has refractive index of about 2.2. The modulating signal fields are not well confined to the substrate. There is substantial field above the subst ...
Looking through walls and around corners with
... were obtained with a Cannon EOS-400D SLR camera. Presented images are median-filtered and low-pass filtered with a rectangular 3x3 pixels kernel. In the optimization process, the SLM (Hamamatsu LCOS-SLM X10468) was divided to 4800 (80x60) equally sized square segments, and the phase of the different ...
... were obtained with a Cannon EOS-400D SLR camera. Presented images are median-filtered and low-pass filtered with a rectangular 3x3 pixels kernel. In the optimization process, the SLM (Hamamatsu LCOS-SLM X10468) was divided to 4800 (80x60) equally sized square segments, and the phase of the different ...
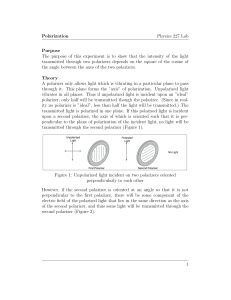
Polarization Physics 227 Lab Purpose The purpose of this
... polarizer, only half will be transmitted though the polarizer. (Since in reality no polarizer is ”ideal”, less than half the light will be transmitted.) The transmitted light is polarized in one plane. If this polarized light is incident upon a second polarizer, the axis of which is oriented such th ...
... polarizer, only half will be transmitted though the polarizer. (Since in reality no polarizer is ”ideal”, less than half the light will be transmitted.) The transmitted light is polarized in one plane. If this polarized light is incident upon a second polarizer, the axis of which is oriented such th ...
EM theory - McMaster University > ECE
... S1 is zero since the number of bullets entering this surface is the same as the number of bullets leaving the surface. In other words, there is no source or sink of bullets in the region S1 . In this case, we say that the divergence is zero. Imagine a surface S2 that encloses the gun man. There is a ...
... S1 is zero since the number of bullets entering this surface is the same as the number of bullets leaving the surface. In other words, there is no source or sink of bullets in the region S1 . In this case, we say that the divergence is zero. Imagine a surface S2 that encloses the gun man. There is a ...
Synopses by Kim Larsen
... which breaks up the expression into a beam profile dependent term, a beam and path dependent term, and the figure of merit for the window defined in Equation 1. The only approximation to completely determine the figure of merit is to assume that the surface absorption effects are significantly smal ...
... which breaks up the expression into a beam profile dependent term, a beam and path dependent term, and the figure of merit for the window defined in Equation 1. The only approximation to completely determine the figure of merit is to assume that the surface absorption effects are significantly smal ...
Reflection properties, anomalous group velocity and negative
... as Photonic Band Gap Material (PBG), are periodic arrangement of dielectric or metallic elements with high refractive index contrast in one-, two-, and three-dimensions. PBG structures are characterized by the presence of well defined forbidden frequency bands (photonic band gap), where the propagat ...
... as Photonic Band Gap Material (PBG), are periodic arrangement of dielectric or metallic elements with high refractive index contrast in one-, two-, and three-dimensions. PBG structures are characterized by the presence of well defined forbidden frequency bands (photonic band gap), where the propagat ...
Surface plasmon resonance microscopy

Surface Plasmon Resonance Microscopy (SPRM) is a label free analytical tool that combines the surface plasmon resonance of metallic surfaces with imaging of the metallic surface.The heterogeneity of the refractive index of the metallic surface imparts high contrast images, caused by the shift in the resonance angle.SPRM can achieve a thickness sensitivity of few tenths of nanometer and lateral resolution achieves values of micrometer scale.SPRM is used to characterize surfaces, self-assembled monolayers, multilayer films, metal nanoparticles, oligonucleotides arrays, binding and reduction reactions.Surface Plasmon polaritons are surface electromagnetic waves coupled to oscillating free electrons of a metallic surface that propagate along a metal/dielectric interface.Since polaritons are highly sensitive to small changes in the refractive index of the metallic material,it can be used as a biosensing tool that does not require labeling. SPRM measurements can be made in real-time.Wang and collaborators studied the binding kinetics of membrane proteins in single cells.The experimental setup of an SPRM can be seen in the Figure 1, where an adherent cell is grown on a gold film and placed in an inverted microscope, p-polarized light was used to create the surface plasmons on the gold film and a CCD camera was used to create the SPR image.