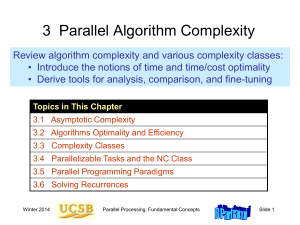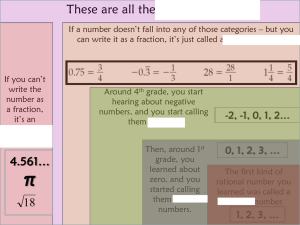
Time-Memory Trade-Off for Lattice Enumeration in a Ball
... Algorithm), a.k.a. Wagner algorithm. The input of the GBA algorithm is a list L0 of m = 2wr q n/w pairs (xi , ai )0≤i≤m−1 where xi is sampled as a Gaussian vector in the lattice generated by A with width s and ai = A−1 xi . The aim of this algorithm is to find a vector ...
... Algorithm), a.k.a. Wagner algorithm. The input of the GBA algorithm is a list L0 of m = 2wr q n/w pairs (xi , ai )0≤i≤m−1 where xi is sampled as a Gaussian vector in the lattice generated by A with width s and ai = A−1 xi . The aim of this algorithm is to find a vector ...
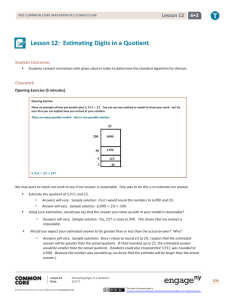
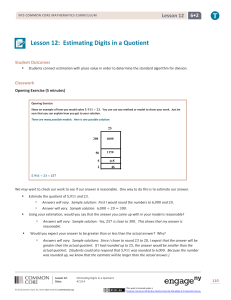
Grade 6 Mathematics Module 2, Topic C, Lesson 12
... In the previous problem, we used 100 to approximate the quotient 4,732 ÷ 52. How did we know that our actual quotient would be in the 90s and not 100 as our approximation suggested? When using your estimate, how do you know if your estimate is too big? ...
... In the previous problem, we used 100 to approximate the quotient 4,732 ÷ 52. How did we know that our actual quotient would be in the 90s and not 100 as our approximation suggested? When using your estimate, how do you know if your estimate is too big? ...
File - BCA Second Grade
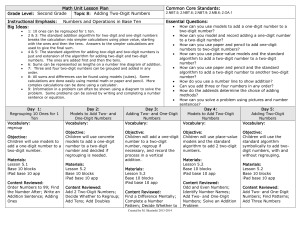
... with the ones and then the tens. Answers to the simpler calculations are used to give the final sum. 4 & 5: The standard algorithm for adding two-digit and two-digit numbers is just and extension of the algorithm for adding two-digit and two-digit numbers. The ones are added first and then the tens. ...
... with the ones and then the tens. Answers to the simpler calculations are used to give the final sum. 4 & 5: The standard algorithm for adding two-digit and two-digit numbers is just and extension of the algorithm for adding two-digit and two-digit numbers. The ones are added first and then the tens. ...
A+B
... an upper, but not a lower, bound on the worst-case time required for the algorithm as a function of the input size. • Table 2 displays the time needed to solve problems of various sizes with an algorithm using the indicated number of bit operations. Every bit operation takes nanosecond. Times of mor ...
... an upper, but not a lower, bound on the worst-case time required for the algorithm as a function of the input size. • Table 2 displays the time needed to solve problems of various sizes with an algorithm using the indicated number of bit operations. Every bit operation takes nanosecond. Times of mor ...
decision analysis - CIS @ Temple University
... The Hungarian method is a combinatorial optimization algorithm which solves the assignment problem in polynomial time. It was developed and published by Harold Kuhn in 1955, who gave the name "Hungarian method" because the algorithm was largely based on the earlier works of two Hungarian mathematic ...
... The Hungarian method is a combinatorial optimization algorithm which solves the assignment problem in polynomial time. It was developed and published by Harold Kuhn in 1955, who gave the name "Hungarian method" because the algorithm was largely based on the earlier works of two Hungarian mathematic ...
Sample Newton Problem Set Solutions
... If we add the three side sums then we include each corner number twice. So the sum of the three side sums equals the sum of all numbers plus the three corner numbers. The largest sum of the three corner numbers is 7 + 6 + 5 = 18 and the smallest sum is 2 + 3 + 4 = 9. Hence the sum of the three side ...
... If we add the three side sums then we include each corner number twice. So the sum of the three side sums equals the sum of all numbers plus the three corner numbers. The largest sum of the three corner numbers is 7 + 6 + 5 = 18 and the smallest sum is 2 + 3 + 4 = 9. Hence the sum of the three side ...