The Methodology of Profit Maximization: An Austrian
... “market power” enables it to face a downward-sloping demand curve, a situation that permits the firm to set output at a level where the price charged is a “monopoly price,” as opposed to a “competitive price” that occurs when output is set where marginal cost equals price. Figure 1 illustrates the s ...
... “market power” enables it to face a downward-sloping demand curve, a situation that permits the firm to set output at a level where the price charged is a “monopoly price,” as opposed to a “competitive price” that occurs when output is set where marginal cost equals price. Figure 1 illustrates the s ...
S - Unchain-vu
... Income elasticity of demand →Percentage change in goods demanded divided by percentage change in income →Note that income growth will lead to more demand. Other than the price elasticity of demand, income elasticity for typical goods has an upward slope →Law on diminishing marginal utility: increas ...
... Income elasticity of demand →Percentage change in goods demanded divided by percentage change in income →Note that income growth will lead to more demand. Other than the price elasticity of demand, income elasticity for typical goods has an upward slope →Law on diminishing marginal utility: increas ...
The shape of incomplete preferences
... Incomplete preferences are generally represented by imprecise (set-valued) probabilities and/or utilities. Varying degrees and types of imprecision have been modeled previously in the literature of statistical decision theory and rational choice: 1. If probabilities alone are considered to be imprec ...
... Incomplete preferences are generally represented by imprecise (set-valued) probabilities and/or utilities. Varying degrees and types of imprecision have been modeled previously in the literature of statistical decision theory and rational choice: 1. If probabilities alone are considered to be imprec ...
Perfect Competition: Short Run and Long Run
... Increase the level of an activity if its marginal benefit exceeds its marginal cost, but reduce the level if the marginal cost exceeds the marginal benefit. If possible, pick the level at which the marginal benefit equals the marginal cost. © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing ...
... Increase the level of an activity if its marginal benefit exceeds its marginal cost, but reduce the level if the marginal cost exceeds the marginal benefit. If possible, pick the level at which the marginal benefit equals the marginal cost. © 2005 Prentice Hall Business Publishing ...
FREE Sample Here
... Suppose that Q (output) depends upon the use of inputs K (capital) and L (labor) according to the production function: Q = K.5L.5 The firm has allocated $1,000 per week to buy capital and labor, where K costs $4 per unit and L costs $5 per unit. The firm seeks to maximize output subject to its $1,00 ...
... Suppose that Q (output) depends upon the use of inputs K (capital) and L (labor) according to the production function: Q = K.5L.5 The firm has allocated $1,000 per week to buy capital and labor, where K costs $4 per unit and L costs $5 per unit. The firm seeks to maximize output subject to its $1,00 ...
law of diminishing returns
... Price is found at equilibrium, where the supply and demand curves intersect. If demand curve shifts right, the price increases. If supply curve shifts left, the price increases. Foreign trade is a major player in price determination of agricultural commodities. ...
... Price is found at equilibrium, where the supply and demand curves intersect. If demand curve shifts right, the price increases. If supply curve shifts left, the price increases. Foreign trade is a major player in price determination of agricultural commodities. ...
Hedonic adaptation and the role of decision and experience utility in
... the use of different default put-asides — motivated by the belief that people do not naturally save as much money as they should. Likewise, attempts by economists and other social scientists to provide people with incentives to take their medications (Volpp et al., 2006), lose weight (Jeffrey, Thomp ...
... the use of different default put-asides — motivated by the belief that people do not naturally save as much money as they should. Likewise, attempts by economists and other social scientists to provide people with incentives to take their medications (Volpp et al., 2006), lose weight (Jeffrey, Thomp ...
Economics 1 - Bakersfield College
... 12. For a firm in perfect competition, the owner has real control which of the following? a. Both the price he charges and the quantity of product he makes. b. The price he charges, but not the quantity. c. The quantity he makes, but not the price. d. Neither the price he charges or the quantity of ...
... 12. For a firm in perfect competition, the owner has real control which of the following? a. Both the price he charges and the quantity of product he makes. b. The price he charges, but not the quantity. c. The quantity he makes, but not the price. d. Neither the price he charges or the quantity of ...
Old Midterm Examinations With Answers
... quantity supplied is greater. There are surpluses. The surpluses are stored and then sold to other countries at below market prices or given away. Farmers win while taxpayers and consumers lose. 14. Demand shifts left while supply shifts right. The quantity cannot be determined. But the price will d ...
... quantity supplied is greater. There are surpluses. The surpluses are stored and then sold to other countries at below market prices or given away. Farmers win while taxpayers and consumers lose. 14. Demand shifts left while supply shifts right. The quantity cannot be determined. But the price will d ...
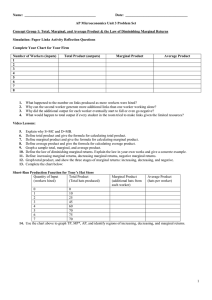
Unit3ProblemSet
... Fixed, Variable, and Marginal Cost: https://www.khanacademy.org/economics-finance-domain/microeconomics/firmeconomic-profit/average-costs-tutorial/v/fixed-variable-and-marginal-cost Marginal Cost & Average Total Cost: https://www.khanacademy.org/economics-financedomain/microeconomics/firm-econom ...
... Fixed, Variable, and Marginal Cost: https://www.khanacademy.org/economics-finance-domain/microeconomics/firmeconomic-profit/average-costs-tutorial/v/fixed-variable-and-marginal-cost Marginal Cost & Average Total Cost: https://www.khanacademy.org/economics-financedomain/microeconomics/firm-econom ...
Chapter 19
... Expected Value of Perfect Information, EVPI Suppose that a decision maker has to choose from among K possible actions, in the face of H states of nature, s1, s2, . . ., sH. Perfect information corresponds to knowledge of which state of nature will arise. The expected value of perfect information is ...
... Expected Value of Perfect Information, EVPI Suppose that a decision maker has to choose from among K possible actions, in the face of H states of nature, s1, s2, . . ., sH. Perfect information corresponds to knowledge of which state of nature will arise. The expected value of perfect information is ...