Answers to Text Questions and Problems
... 2. To build, or even rent, a new factory often takes years, certainly many months. By contrast, additional production workers can be hired in days or, at most, weeks. So the factory is far more likely to be a fixed factor over the next two months. 3. Not enough seeds for the plants needed to feed se ...
... 2. To build, or even rent, a new factory often takes years, certainly many months. By contrast, additional production workers can be hired in days or, at most, weeks. So the factory is far more likely to be a fixed factor over the next two months. 3. Not enough seeds for the plants needed to feed se ...
Answers to Text Questions and Problems Chapter 10
... socially optimal, because the marginal cost of additional highway capacity is always positive. ...
... socially optimal, because the marginal cost of additional highway capacity is always positive. ...
Chapter 3 - Memorial University
... could have produced in their next best use) What is counted as variable costs should be appropriate to the policy in question and could cover the short run (labour varies and capital is fixed) or the long run (all inputs vary) The market supply curve (similarly to the market demand curve) is the hor ...
... could have produced in their next best use) What is counted as variable costs should be appropriate to the policy in question and could cover the short run (labour varies and capital is fixed) or the long run (all inputs vary) The market supply curve (similarly to the market demand curve) is the hor ...
Monopoly
... each facing a downward sloping demand curve will produce so that price exceeds marginal cost. Firms often product similar goods that have some differences thereby differentiating themselves from other firms ...
... each facing a downward sloping demand curve will produce so that price exceeds marginal cost. Firms often product similar goods that have some differences thereby differentiating themselves from other firms ...
Chapter 10 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... groups: price-sensitive and price-insensitive. Coupons allow price-sensitive consumers to trade time for money. ...
... groups: price-sensitive and price-insensitive. Coupons allow price-sensitive consumers to trade time for money. ...
Chapter 18: Pure Monopoly
... On the graph, show the result of a decrease in a variable cost (for example, a cost of labor or of natural resources). What happens to the quantity, the price, and the economic profits? Answer: this case in handled in the same way as it was in Chapter 17. This is shown in the graph on the next page. ...
... On the graph, show the result of a decrease in a variable cost (for example, a cost of labor or of natural resources). What happens to the quantity, the price, and the economic profits? Answer: this case in handled in the same way as it was in Chapter 17. This is shown in the graph on the next page. ...
How to Study for Chapter 18 Pure Monopoly
... On the graph, show the result of a decrease in a variable cost (for example, a cost of labor or of natural resources). What happens to the quantity, the price, and the economic profits? Answer: this case in handled in the same way as it was in Chapter 17. This is shown in the graph on the next page. ...
... On the graph, show the result of a decrease in a variable cost (for example, a cost of labor or of natural resources). What happens to the quantity, the price, and the economic profits? Answer: this case in handled in the same way as it was in Chapter 17. This is shown in the graph on the next page. ...
Marginal Revenue
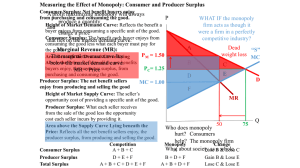
... Connecting the Pareto approach to efficiency with consumer and producer surplus Question: How did we argue that P monopoly was inefficient? We chose an individual, Joe, who Did not by a hamburger when the price was $1.50, the monopoly price. But would be a hamburger at a PM = 1.50 price of $1.40, a ...
... Connecting the Pareto approach to efficiency with consumer and producer surplus Question: How did we argue that P monopoly was inefficient? We chose an individual, Joe, who Did not by a hamburger when the price was $1.50, the monopoly price. But would be a hamburger at a PM = 1.50 price of $1.40, a ...
The Monopolist`s Demand Curve and Marginal Revenue
... marginal revenue curve of a firm with market power always lies below its demand curve. • A profit-maximizing monopolist chooses the output level at which marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue—not to price. • As a result, the monopolist produces less and sells its output at a higher price than a ...
... marginal revenue curve of a firm with market power always lies below its demand curve. • A profit-maximizing monopolist chooses the output level at which marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue—not to price. • As a result, the monopolist produces less and sells its output at a higher price than a ...
Lecture 5 - people.vcu.edu
... Notice even though Py did not enter into the uncompensated demand function for X it does enter into the compensated demand function. This example makes clear what is being held constant with the two demand forms. With uncompensated demand, expenditures are held constant, so a rise in the price of X ...
... Notice even though Py did not enter into the uncompensated demand function for X it does enter into the compensated demand function. This example makes clear what is being held constant with the two demand forms. With uncompensated demand, expenditures are held constant, so a rise in the price of X ...