
BASIC THEORY OF PARTIAL COHERENCE
... From (13) it is clear that the image mutual intensity is no longer of the same form as the object mutual intensity; i.e., the image of an incoherent object is not incoherent but is partially coherent. This result will be seen to have rather far-reaching implications in the problems of image formatio ...
... From (13) it is clear that the image mutual intensity is no longer of the same form as the object mutual intensity; i.e., the image of an incoherent object is not incoherent but is partially coherent. This result will be seen to have rather far-reaching implications in the problems of image formatio ...
PHYS 1111 Mechanics, Waves, & Thermodynamics
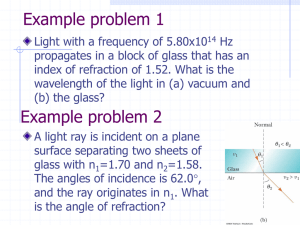
... This implies that the speed of light inside the medium depends on The dependence of wave speed v and n on is called dispersion Since n=n(), Snell’s law of refraction implies that different wavelength light is bent at different refraction angles 2() for a given 1 ...
... This implies that the speed of light inside the medium depends on The dependence of wave speed v and n on is called dispersion Since n=n(), Snell’s law of refraction implies that different wavelength light is bent at different refraction angles 2() for a given 1 ...
Diffractive Optical Elements
... HOLOEYE utilizes its steadily growing experience in the design and simulation of diffractive optical elements to offer its customers a competitive solution. Both in-house developed and commercially available state-of-the-art software tools are used for the DOE design process. ...
... HOLOEYE utilizes its steadily growing experience in the design and simulation of diffractive optical elements to offer its customers a competitive solution. Both in-house developed and commercially available state-of-the-art software tools are used for the DOE design process. ...
LM 3188 - LASER DUST MONITOR
... • Internal calibration filter • Analog and digital display Cable Monitor ...
... • Internal calibration filter • Analog and digital display Cable Monitor ...
Optics
... (i) For image formation, it is not necessary that object should be present in front of mirror. (ii) It is not possible to locate an object by a single ray. It is for this reason that the surface of reflecting mirror is not visible to us. Any point like A on the surface sends only one ray AC into our ...
... (i) For image formation, it is not necessary that object should be present in front of mirror. (ii) It is not possible to locate an object by a single ray. It is for this reason that the surface of reflecting mirror is not visible to us. Any point like A on the surface sends only one ray AC into our ...
10.2 Diffraction Notes
... • Destructive interference is difficult to accomplish since most natural sources of light are incoherent which means they emit light waves randomly. • It is much easier to observe light if the phases of the waves have a fixed pattern. This is called coherent. ...
... • Destructive interference is difficult to accomplish since most natural sources of light are incoherent which means they emit light waves randomly. • It is much easier to observe light if the phases of the waves have a fixed pattern. This is called coherent. ...
optical cavity
... used because of the difficulty of aligning them to the needed precision.) The geometry (resonator type) must be chosen so that the beam remains stable (that the size of the beam does not continually grow with multiple reflections, as shown below. ...
... used because of the difficulty of aligning them to the needed precision.) The geometry (resonator type) must be chosen so that the beam remains stable (that the size of the beam does not continually grow with multiple reflections, as shown below. ...
Background: Polarimetry is the measurement and interpretation of
... Background: Polarimetry is the measurement and interpretation of the electromagnetic waves can be diffracted by some compound. A sensitive and non destructive method used to determine the optical activity of substance is a polarimeter instrument. To study this instrument we will focus on stereoisome ...
... Background: Polarimetry is the measurement and interpretation of the electromagnetic waves can be diffracted by some compound. A sensitive and non destructive method used to determine the optical activity of substance is a polarimeter instrument. To study this instrument we will focus on stereoisome ...
Unwrapping Hartman-Shack Images from Highly Aberrated Eyes
... • Is the key component for adaptive optics which can improve retinal image to the highest resolution (JZ Liang et al., JOSA A 1997) ...
... • Is the key component for adaptive optics which can improve retinal image to the highest resolution (JZ Liang et al., JOSA A 1997) ...
oAkLey si BALListic det cord
... The SI Ballistic Det Cord is the perfect blend of ballistic protection and Oakley fashion. Fully compliant with the ballistic and optical standards of MIL PRF32432 and ANSI Z87.1 (2010), the SI Ballistic Det Cord is balanced for aggressive environments and covert capabilities. The SI Ballistic Det C ...
... The SI Ballistic Det Cord is the perfect blend of ballistic protection and Oakley fashion. Fully compliant with the ballistic and optical standards of MIL PRF32432 and ANSI Z87.1 (2010), the SI Ballistic Det Cord is balanced for aggressive environments and covert capabilities. The SI Ballistic Det C ...
EE119 Homework 7: Microscopes, Projectors and Photomultiplier
... The positive solution to this quadratic equation is fo = 0.5. Notice that if the working distance were larger, then fo could be larger too. But let’s use fo = 0.5here. This means that the eyepiece focal length should be 8/(3×0.5)=16/3=5.333 cm. Now we need to find some diameters for these lenses. Fo ...
... The positive solution to this quadratic equation is fo = 0.5. Notice that if the working distance were larger, then fo could be larger too. But let’s use fo = 0.5here. This means that the eyepiece focal length should be 8/(3×0.5)=16/3=5.333 cm. Now we need to find some diameters for these lenses. Fo ...
Reflecting And Refracting Light
... • We describe the path of light as straight-line rays • Reflection off a flat surface follows a simple rule: – angle in (incidence) equals angle out (reflection) – angles measured from surface “normal” (perpendicular) ...
... • We describe the path of light as straight-line rays • Reflection off a flat surface follows a simple rule: – angle in (incidence) equals angle out (reflection) – angles measured from surface “normal” (perpendicular) ...
Second Year Problem sheet 3 +answers
... This light is then removed by a Lyot stop, which consists of an undersized aperture at a pupil conjugate that masks off the light at the edge of the pupil. The size of the Lyot stop is also important. If the stop is small then it will suppress the central star well but the overall throughput of the ...
... This light is then removed by a Lyot stop, which consists of an undersized aperture at a pupil conjugate that masks off the light at the edge of the pupil. The size of the Lyot stop is also important. If the stop is small then it will suppress the central star well but the overall throughput of the ...
Chapter 18
... Two converging lenses having focal lengths of 10.0 cm and 20.0 cm are placed 50.0 cm apart, as shown in the figure. The final image is to be located between the lenses, at the position indicated. (a) How far to the left of the first lens should the object be positioned? (b) What is the overall magni ...
... Two converging lenses having focal lengths of 10.0 cm and 20.0 cm are placed 50.0 cm apart, as shown in the figure. The final image is to be located between the lenses, at the position indicated. (a) How far to the left of the first lens should the object be positioned? (b) What is the overall magni ...
Chapter 23
... Two converging lenses having focal lengths of 10.0 cm and 20.0 cm are placed 50.0 cm apart, as shown in the figure. The final image is to be located between the lenses, at the position indicated. (a) How far to the left of the first lens should the object be positioned? (b) What is the overall magni ...
... Two converging lenses having focal lengths of 10.0 cm and 20.0 cm are placed 50.0 cm apart, as shown in the figure. The final image is to be located between the lenses, at the position indicated. (a) How far to the left of the first lens should the object be positioned? (b) What is the overall magni ...




















![Spherical mirrors in the paraxial approximation [Pages 181-187]. Assignment 2](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008539460_1-d375c81ee0822c3c0b88887d5bbb056f-300x300.png)