PPT Lecture Notes
... value indicates an increase in refractive power. 4. One is a -3 diopter (concave) lens. The negative value indicates an decrease in refractive power. 5. Put one on top of the other, and they “cancel”. ...
... value indicates an increase in refractive power. 4. One is a -3 diopter (concave) lens. The negative value indicates an decrease in refractive power. 5. Put one on top of the other, and they “cancel”. ...
Seven Important Factors When Selecting a Machine
... lenses. A common test specification for the resolution of a lens is line pairs per millimeter (lp/mm). This describes the minimum distance the lens can resolve the difference between equal sized black and white reference objects. Then, lens resolution exceeded that of the cameras, so camera resoluti ...
... lenses. A common test specification for the resolution of a lens is line pairs per millimeter (lp/mm). This describes the minimum distance the lens can resolve the difference between equal sized black and white reference objects. Then, lens resolution exceeded that of the cameras, so camera resoluti ...
Optics - MIT Fab Lab
... where f is the focal length of the lens. This is the lens equation, giving the relationship between where a ray starts on the axis on one side of the lens and where it crosses the axis on the other side. Notice that the angles have dropped out of this equation: all rays starting at the same distance ...
... where f is the focal length of the lens. This is the lens equation, giving the relationship between where a ray starts on the axis on one side of the lens and where it crosses the axis on the other side. Notice that the angles have dropped out of this equation: all rays starting at the same distance ...
Astronomy 101 Lab: Telescopes
... Introduction: You will study different lenses and mirrors to determine their focal lengths. From what you learn, you will build a simple refracting telescope and you will analyze a simple reflecting telescope. Write all of your answers on the answer sheet. You don’t need to submit the procedure. Eac ...
... Introduction: You will study different lenses and mirrors to determine their focal lengths. From what you learn, you will build a simple refracting telescope and you will analyze a simple reflecting telescope. Write all of your answers on the answer sheet. You don’t need to submit the procedure. Eac ...
Chapter 17 A modern optics laboratory for undergraduate students
... superluminal information, light-gravity interaction) and engineers (i.e. fiber optics, storage of information in a bulk of matter, transparency of dielectrics). The primary goal of this laboratory course is to lead the undergraduate students to the discovery, through experimental investigation, of t ...
... superluminal information, light-gravity interaction) and engineers (i.e. fiber optics, storage of information in a bulk of matter, transparency of dielectrics). The primary goal of this laboratory course is to lead the undergraduate students to the discovery, through experimental investigation, of t ...
INTRODUCTION
... the ‘Second Window’. This window is attractive as it can support the highest data rate due to lowest dispersion. In 1990s the communication was shifted to 1550nm window, so called ‘Third Window’ due to invention of the Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA). The EDFA can amplify light only in a narrow ...
... the ‘Second Window’. This window is attractive as it can support the highest data rate due to lowest dispersion. In 1990s the communication was shifted to 1550nm window, so called ‘Third Window’ due to invention of the Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier (EDFA). The EDFA can amplify light only in a narrow ...
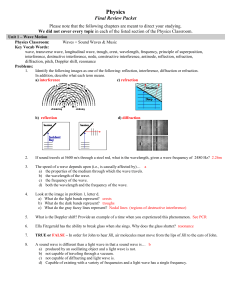
Physics Final Review Packet
... b) What do the dark bands represent? troughs c) What do the gray fuzzy lines represent? Nodal lines (regions of destructive interference) ...
... b) What do the dark bands represent? troughs c) What do the gray fuzzy lines represent? Nodal lines (regions of destructive interference) ...
A method for characterizing longitudinal chromatic aberration of
... us to remove the chromatic effect of the collimating lens from the final results presented in the following figures. It should be noted, however, that for most objective lenses the effect of the collimating lens on the overall longitudinal chromatic aberration was negligible. Indeed, we believe the ...
... us to remove the chromatic effect of the collimating lens from the final results presented in the following figures. It should be noted, however, that for most objective lenses the effect of the collimating lens on the overall longitudinal chromatic aberration was negligible. Indeed, we believe the ...
1 Macleod ‐ Thin Film Optics
... sufficiently high angles of incidence is total. More recently it has been found that when metal layers are added to the totally reflecting surface, light that is polarized with the electric vector in the plane of incidence (p‐polarization) behaves in a strange way. Provided the metal is of the co ...
... sufficiently high angles of incidence is total. More recently it has been found that when metal layers are added to the totally reflecting surface, light that is polarized with the electric vector in the plane of incidence (p‐polarization) behaves in a strange way. Provided the metal is of the co ...
optical fiber communication - GTU e
... emission, which results in high output power (~100 mW) as well as other benefits related to the nature of coherent light. ...
... emission, which results in high output power (~100 mW) as well as other benefits related to the nature of coherent light. ...
A high numerical aperture (NA = 0.92)
... than 100 × 100 lattice sites in a typical optical lattice. Figure 1(b) shows a close-up, recorded with our objective lens, of two adjacent cesium atoms, which are trapped in an optical lattice with a lattice constant of 612 nm. Lens design. Due to their large collection angle, objective lenses with ...
... than 100 × 100 lattice sites in a typical optical lattice. Figure 1(b) shows a close-up, recorded with our objective lens, of two adjacent cesium atoms, which are trapped in an optical lattice with a lattice constant of 612 nm. Lens design. Due to their large collection angle, objective lenses with ...
Automotive Optical Solutions for the Automotive
... Liechtenstein that Dr. Max Auwärter – in cooperation with Emil G. Bührle – founded the company Balzers in the village of Balzers, in the Principality of Liechtenstein, in 1946. At that time the technology of vacuum deposition was still in its early stages. With very few exceptions, high vacuum syste ...
... Liechtenstein that Dr. Max Auwärter – in cooperation with Emil G. Bührle – founded the company Balzers in the village of Balzers, in the Principality of Liechtenstein, in 1946. At that time the technology of vacuum deposition was still in its early stages. With very few exceptions, high vacuum syste ...
Microscopy
... and focus until you achieve optimal contrast. For most samples, the optimal condenser position is near the top. The microscope used in this exercise is not parfocal and the system will need to be adjusted for each objective. ...
... and focus until you achieve optimal contrast. For most samples, the optimal condenser position is near the top. The microscope used in this exercise is not parfocal and the system will need to be adjusted for each objective. ...
Lecture 24
... The XYZ (CIE) basis uses X,Y coordinates to represent color, and Z to represent brightness. Allows colors to be plotted in 2D. They are related to R,G,B by a linear ...
... The XYZ (CIE) basis uses X,Y coordinates to represent color, and Z to represent brightness. Allows colors to be plotted in 2D. They are related to R,G,B by a linear ...
Geometrical Optics: Curved Mirrors Worksheet Part I:
... the object in a “ray diagram”. As you move the object (with the slider) or move the point source, there is a ray that always passes through the focal point. Describe that ray-- this is a ray generally included in a ray diagram. ...
... the object in a “ray diagram”. As you move the object (with the slider) or move the point source, there is a ray that always passes through the focal point. Describe that ray-- this is a ray generally included in a ray diagram. ...
Optical fibres
... 1.4Applications of optical fibres in industry and medicine 1.4.1 Optical fibre in communication The conventional method of communication has more limitation toward signal security and also affected by change in atmospheric factors. To overcome these limitations and factors, te optical fibres are int ...
... 1.4Applications of optical fibres in industry and medicine 1.4.1 Optical fibre in communication The conventional method of communication has more limitation toward signal security and also affected by change in atmospheric factors. To overcome these limitations and factors, te optical fibres are int ...
chapter9-Section4
... The remedy for this problem, originally thought to be insoluble by none other than Newton himself, was discovered around 1733 by C. M. Hall and later (in 1758) developed and patented by John Dolland, a London optician. ...
... The remedy for this problem, originally thought to be insoluble by none other than Newton himself, was discovered around 1733 by C. M. Hall and later (in 1758) developed and patented by John Dolland, a London optician. ...
FA15Lec17 Optical Traps.Two
... Get power spectrum of bead in an optical trap. Noise is not distributed evenly across all frequencies in an optical trap. Most noise at low f. fc ...
... Get power spectrum of bead in an optical trap. Noise is not distributed evenly across all frequencies in an optical trap. Most noise at low f. fc ...