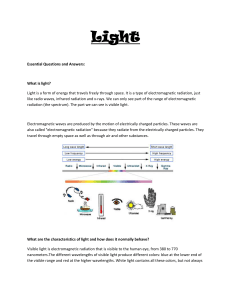
Essential Questions and Answers: What is light? Light is a form of
... Light travels in a straight line until it strikes an object. When light bounces back from an object, it is called reflected light. When light travels through material, it bends and is called refracted light. Light behaves like a traveling wave, something like waves in a string or on the surface of w ...
... Light travels in a straight line until it strikes an object. When light bounces back from an object, it is called reflected light. When light travels through material, it bends and is called refracted light. Light behaves like a traveling wave, something like waves in a string or on the surface of w ...
ray optics and optical instruments
... In order to explain the phenomena of refraction, Newton postulated that the speed of the corpuscles was greater in water or glass than in air. However, later on it was discovered that the speed of light is less in water or glass than in air. In the field of optics, Newton – the experimenter, was gre ...
... In order to explain the phenomena of refraction, Newton postulated that the speed of the corpuscles was greater in water or glass than in air. However, later on it was discovered that the speed of light is less in water or glass than in air. In the field of optics, Newton – the experimenter, was gre ...
Laser Distance and Speed Detection
... 1. Frequency of the tone or modulation. 2. Accuracy of the phase-measurement loop. This depends on signal strength, noise, and so on. 3. Stability of the modulation oscillator. 4. Number of cycles (or measurements) that can be averaged together for a range. measurement. 5. Turbulence in the air thro ...
... 1. Frequency of the tone or modulation. 2. Accuracy of the phase-measurement loop. This depends on signal strength, noise, and so on. 3. Stability of the modulation oscillator. 4. Number of cycles (or measurements) that can be averaged together for a range. measurement. 5. Turbulence in the air thro ...
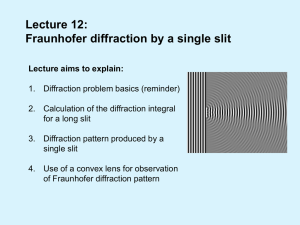
Lecture 12: Fraunhofer diffraction by a single slit
... account difference in optical path length and amplitude Why do we study diffraction on slits, circular apertures etc: to understand basics, and due to high relevance to applications ...
... account difference in optical path length and amplitude Why do we study diffraction on slits, circular apertures etc: to understand basics, and due to high relevance to applications ...
Structure and Imaging of a Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
... quadratic curves in the space between the two anodes, which was theoretically proposed by Butler (1966), as illustrated in Fig. 2.2b. Another curve of a simple funnel shape was studied by Tonomura (1973). The thermal field emission gun has an advantage of the large total current and usability without ...
... quadratic curves in the space between the two anodes, which was theoretically proposed by Butler (1966), as illustrated in Fig. 2.2b. Another curve of a simple funnel shape was studied by Tonomura (1973). The thermal field emission gun has an advantage of the large total current and usability without ...
of the Physical and Technical Faculty
... laboratory works and seminars. The seminars are primarily intended to familiarize with the studied optical phenomena, terminology, graphical and analytical apparatus. The significant part of the seminars is the use of real experiments and computer emulation, calculations studied variables, evaluatio ...
... laboratory works and seminars. The seminars are primarily intended to familiarize with the studied optical phenomena, terminology, graphical and analytical apparatus. The significant part of the seminars is the use of real experiments and computer emulation, calculations studied variables, evaluatio ...
Activity 3.1 – The Dispersion Equation Activity 3.2 – The Wavelength
... your view of the illuminated diffraction scale. The geometry is therefore slightly more complicated than it would be if the pattern were projected onto a screen, as in most textbook examples. (A very strong light source, such as a laser, is required in order to project a sharp image of a diffraction ...
... your view of the illuminated diffraction scale. The geometry is therefore slightly more complicated than it would be if the pattern were projected onto a screen, as in most textbook examples. (A very strong light source, such as a laser, is required in order to project a sharp image of a diffraction ...
Utilizing a 4-F Fourier Optical System to Learn More About Image
... compared to the computer models, we were successful in producing accurately filtered images. This was important for understanding how an image’s information is gathered on the Fourier plane. This work also helped to highlight how a low-pass filter and a high-pass filter modify images. A low-pass fil ...
... compared to the computer models, we were successful in producing accurately filtered images. This was important for understanding how an image’s information is gathered on the Fourier plane. This work also helped to highlight how a low-pass filter and a high-pass filter modify images. A low-pass fil ...
lecture5web
... • Dispersion means that different colors (frequencies/wavelengths) of light have different speeds through a material (different index of refraction), and thus refract at different angles. • In most transparent optical materials, blue (high frequency) light has a higher index than red (low frequency) ...
... • Dispersion means that different colors (frequencies/wavelengths) of light have different speeds through a material (different index of refraction), and thus refract at different angles. • In most transparent optical materials, blue (high frequency) light has a higher index than red (low frequency) ...
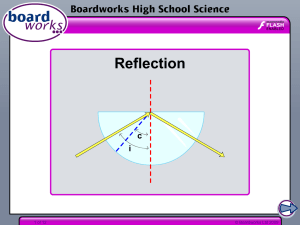
law of reflection
... They exploit total internal reflection in order to carry beams of light over long distances and along winding paths. The glass core is often encased in a layer of cladding, which prevents light escaping the core. A protective plastic jacket surrounds the whole fiber. Why are the materials used to ma ...
... They exploit total internal reflection in order to carry beams of light over long distances and along winding paths. The glass core is often encased in a layer of cladding, which prevents light escaping the core. A protective plastic jacket surrounds the whole fiber. Why are the materials used to ma ...
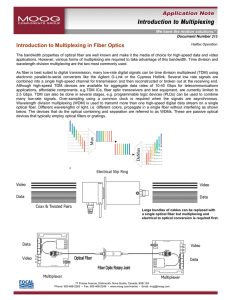
Introduction to Multiplexing in Fiber Optics
... The bandwidth properties of optical fiber are well known and make it the media of choice for high-speed data and video applications. However, various forms of multiplexing are required to take advantage of this bandwidth. Time division and wavelength division multiplexing are the two most commonly u ...
... The bandwidth properties of optical fiber are well known and make it the media of choice for high-speed data and video applications. However, various forms of multiplexing are required to take advantage of this bandwidth. Time division and wavelength division multiplexing are the two most commonly u ...
Ultrahigh-resolution full-field optical coherence microscopy using
... reflectance is imaged onto an array-based detector where it interferes with an image of the reference reflector. Images from within the tissue are typically reconstructed by arithmetic combination of the resulting interference patterns at different reference arm path lengths [1]. The advantages of F ...
... reflectance is imaged onto an array-based detector where it interferes with an image of the reference reflector. Images from within the tissue are typically reconstructed by arithmetic combination of the resulting interference patterns at different reference arm path lengths [1]. The advantages of F ...
ANSWERS - AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice – Torque
... together the sound waves get compressed and the higher the frequency. Take the case of a very fast vehicle traveling at the speed of sound; the compressions are all right on top of each other. So faster speed means closer compressions and higher frequencies. Choice I must be true because X is a high ...
... together the sound waves get compressed and the higher the frequency. Take the case of a very fast vehicle traveling at the speed of sound; the compressions are all right on top of each other. So faster speed means closer compressions and higher frequencies. Choice I must be true because X is a high ...
Imaging the Division Process in Living Tissue Culture Cells
... By eliminating the delays normally required for vibration dampening, and by fast shuttering, we have been able to double the practical image acquisition efficiency of our microscopes. While a 100- ms exposure actually requires about a 250- ms light exposure using the original turn-key system, throug ...
... By eliminating the delays normally required for vibration dampening, and by fast shuttering, we have been able to double the practical image acquisition efficiency of our microscopes. While a 100- ms exposure actually requires about a 250- ms light exposure using the original turn-key system, throug ...
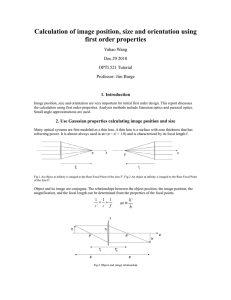
Calculation of image position, size and orientation using first order
... ∆zf=∆zL(1-m2) Tilt of optical element For thin lens, there is no significant effect if you tilt an element about its center. But large tilt will cause aberrations. For mirror, the image will tilt 2θ if you tilt the mirror by θ. You can trace the chief ray to prove it. So, we should be more careful w ...
... ∆zf=∆zL(1-m2) Tilt of optical element For thin lens, there is no significant effect if you tilt an element about its center. But large tilt will cause aberrations. For mirror, the image will tilt 2θ if you tilt the mirror by θ. You can trace the chief ray to prove it. So, we should be more careful w ...
Laser Refraction and Diffraction
... double-slit, and diffraction grating; S2 is the observation plane where the diffraction pattern was observed, and z is the distance between S1 and S2. 2. The angle of incidence should be perpendicular to the optical components (slits and grating) when using a laser beam to illuminate the slits and g ...
... double-slit, and diffraction grating; S2 is the observation plane where the diffraction pattern was observed, and z is the distance between S1 and S2. 2. The angle of incidence should be perpendicular to the optical components (slits and grating) when using a laser beam to illuminate the slits and g ...
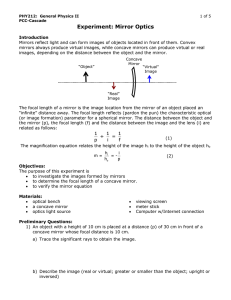
Physics 212: General Physics II
... (2) these ratios should be equal. Do your data support the magnification equation? Explain. ...
... (2) these ratios should be equal. Do your data support the magnification equation? Explain. ...
Light and Telescopes
... So – any telescope can get any magnification! You just need a very short focal length eyepiece to get 1000 X. However, you are limited by the atmosphere and the quality of your optics. For a 6-inch diameter telescope, the effective maximum magnification is about 150 X. ...
... So – any telescope can get any magnification! You just need a very short focal length eyepiece to get 1000 X. However, you are limited by the atmosphere and the quality of your optics. For a 6-inch diameter telescope, the effective maximum magnification is about 150 X. ...
A Practical Guide to Optical Trapping
... signal of 10 V pk–to–pk at a frequency of about 30 MHz generated by a PCI–bus, computer-controlled frequency generator and amplified with an RF amplifier. The induced sound wave propagates through the crystal, creating traveling regions of high and low material, and hence optical, density. A laser b ...
... signal of 10 V pk–to–pk at a frequency of about 30 MHz generated by a PCI–bus, computer-controlled frequency generator and amplified with an RF amplifier. The induced sound wave propagates through the crystal, creating traveling regions of high and low material, and hence optical, density. A laser b ...