materials in modern communications systems
... In Fresnel diffraction, the image plane is near the aperture and light travels directly from the aperture to the image plane (see Figure 5-4) In Fraunhofer diffraction, the image plane is far from the aperture, and there is a lens between the aperture and the image plane (see Figure 5-6) Fresnel dif ...
... In Fresnel diffraction, the image plane is near the aperture and light travels directly from the aperture to the image plane (see Figure 5-4) In Fraunhofer diffraction, the image plane is far from the aperture, and there is a lens between the aperture and the image plane (see Figure 5-6) Fresnel dif ...
24 Geometrical Optics
... focal point —– A point at which rays of light or other radiation converge or from which they appear to diverge, as after refraction or reflection in an optical system. focal plane —– The plane containing the focal point, on which parallel rays focus. positive lens —– Converging lens. negative lens —– ...
... focal point —– A point at which rays of light or other radiation converge or from which they appear to diverge, as after refraction or reflection in an optical system. focal plane —– The plane containing the focal point, on which parallel rays focus. positive lens —– Converging lens. negative lens —– ...
Light and Optics Unit Test
... c. a beam d. a solid 2. Which of the following is NOT a primary color? a. red b. blue c. yellow d. green 3. When most light passes through a surface but some rays are reflected the surface is called: a. transparent b. translucent c. opaque d. clear 4. If the angle of reflection off a smooth surface ...
... c. a beam d. a solid 2. Which of the following is NOT a primary color? a. red b. blue c. yellow d. green 3. When most light passes through a surface but some rays are reflected the surface is called: a. transparent b. translucent c. opaque d. clear 4. If the angle of reflection off a smooth surface ...
View
... • Production of a magnified image of the lamp filament that is focused at the level of the aperture plane of the condensor. • Opening or closing this diaphragm controls the angle of the light cone that reaches the specimen, which is determining the image resolution along with the numerical aperture ...
... • Production of a magnified image of the lamp filament that is focused at the level of the aperture plane of the condensor. • Opening or closing this diaphragm controls the angle of the light cone that reaches the specimen, which is determining the image resolution along with the numerical aperture ...
Optical forces and torques in non
... limit, when the particle’s size is no greater than the wavelength of light. In this limit, the three terms in g(r) may be interpreted as distinct mechanisms by which a beam of light exerts forces on illuminated objects. The first two terms in Eq. (3) constitute the familiar phase-gradient contributi ...
... limit, when the particle’s size is no greater than the wavelength of light. In this limit, the three terms in g(r) may be interpreted as distinct mechanisms by which a beam of light exerts forces on illuminated objects. The first two terms in Eq. (3) constitute the familiar phase-gradient contributi ...
Optical forces and torques in non-uniform beams of
... limit, when the particle’s size is no greater than the wavelength of light. In this limit, the three terms in g(r) may be interpreted as distinct mechanisms by which a beam of light exerts forces on illuminated objects. The first two terms in Eq. (3) constitute the familiar phase-gradient contributi ...
... limit, when the particle’s size is no greater than the wavelength of light. In this limit, the three terms in g(r) may be interpreted as distinct mechanisms by which a beam of light exerts forces on illuminated objects. The first two terms in Eq. (3) constitute the familiar phase-gradient contributi ...
Vision and Optical Instruments
... For an eye with this typical 2.00 cm lens-to-retina distance, the power of the eye ranges from 50.0 D (for distant totally relaxed vision) to 54.0 D (for close fully accommodated vision), which is an 8% increase. This increase in power for close vision is consistent with the preceding discussion and ...
... For an eye with this typical 2.00 cm lens-to-retina distance, the power of the eye ranges from 50.0 D (for distant totally relaxed vision) to 54.0 D (for close fully accommodated vision), which is an 8% increase. This increase in power for close vision is consistent with the preceding discussion and ...
Reflectivity measurements of a quantum well
... intensity being most homogeneous at the same time; its position coincides with the focusing point of the halogen lamp and focal point of the focusing lens 1 - focusing lens 1 – forms the quasi-parallel light beam - beam splitter – reflects source light and transmits reflected light - focusing lens 2 ...
... intensity being most homogeneous at the same time; its position coincides with the focusing point of the halogen lamp and focal point of the focusing lens 1 - focusing lens 1 – forms the quasi-parallel light beam - beam splitter – reflects source light and transmits reflected light - focusing lens 2 ...
An optical fibre based evanescent wave sensor to
... where A is proportional to laL/a NA. The above equation predicts that the evanescent absorbance depends linearly on ...
... where A is proportional to laL/a NA. The above equation predicts that the evanescent absorbance depends linearly on ...
Experimental Demonstration of a 2
... correlation, equalization, filtering, and almost any element that provides a transfer function [1]. Moreover, it may be beneficial to enable an optical tapped-delay-line (OTDL) so that: (i) certain functions may be performed natively on optical data streams, and (ii) there exists the potential for o ...
... correlation, equalization, filtering, and almost any element that provides a transfer function [1]. Moreover, it may be beneficial to enable an optical tapped-delay-line (OTDL) so that: (i) certain functions may be performed natively on optical data streams, and (ii) there exists the potential for o ...
Department of Electrical Engineering Faculty
... optical routers and all-optical networks. The Electronic Materials Processing laboratory has extensive facilities for fabricating and characterizing semiconductor and optical devices. The Laser Electronics Laboratory houses graduate research projects centered on the characterization, development and ...
... optical routers and all-optical networks. The Electronic Materials Processing laboratory has extensive facilities for fabricating and characterizing semiconductor and optical devices. The Laser Electronics Laboratory houses graduate research projects centered on the characterization, development and ...
Tutorial_Mansuripur_CDvsDVD
... operate at more then 32X boosting data transfer rates beyond 4.8 MB/s, and the improvement has mostly come from the increase in spin rates. The other components have mostly remained unchanged. It seems at this point, that further increase in spindle speed may be impractical due to loss in drive perf ...
... operate at more then 32X boosting data transfer rates beyond 4.8 MB/s, and the improvement has mostly come from the increase in spin rates. The other components have mostly remained unchanged. It seems at this point, that further increase in spindle speed may be impractical due to loss in drive perf ...
- Free Documents
... Optical Concepts .The Optical Fiber Very thin strands of pure silica glass through which laser light travels in optical networks . ...
... Optical Concepts .The Optical Fiber Very thin strands of pure silica glass through which laser light travels in optical networks . ...
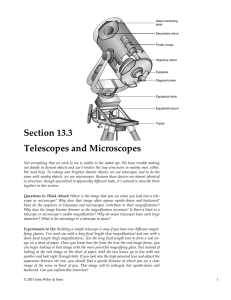
A301.Ch5.Telescopes
... penny viewed from 3.6 km. The resolution of the human eye is about 60 arcsec. For best telescopes, e.g. adaptive optics or HST 0.05 arc sec, radio interferometer 0.001 arc sec. [See below] ...
... penny viewed from 3.6 km. The resolution of the human eye is about 60 arcsec. For best telescopes, e.g. adaptive optics or HST 0.05 arc sec, radio interferometer 0.001 arc sec. [See below] ...