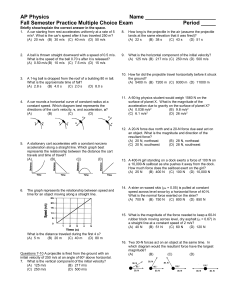
Speed - TGHSLevel1Science
... • Displacement is a measurement of how far an object has moved from its starting point. ...
... • Displacement is a measurement of how far an object has moved from its starting point. ...
Document
... We will consider effect of uniform motion on different quantities & laws of physics. We will establish a relationship between the space & time coordinates in two inertial frames of reference. The basic relations were obtained by Galileo & are ...
... We will consider effect of uniform motion on different quantities & laws of physics. We will establish a relationship between the space & time coordinates in two inertial frames of reference. The basic relations were obtained by Galileo & are ...
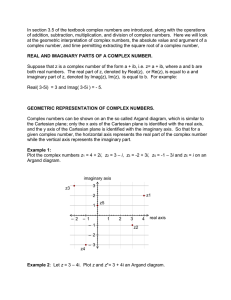
coordinates
... on a coordinate plane. The first number tells how far to move right (positive) or left (negative) from the origin. The second number tells how far to move up (positive) or down (negative). The numbers in an ordered pair are called coordinates. The first number is called the x-coordinate. The second ...
... on a coordinate plane. The first number tells how far to move right (positive) or left (negative) from the origin. The second number tells how far to move up (positive) or down (negative). The numbers in an ordered pair are called coordinates. The first number is called the x-coordinate. The second ...
Coordinate Plane
... (positive) or left (negative) from the origin. The second number tells how far to move up (positive) or down (negative). ...
... (positive) or left (negative) from the origin. The second number tells how far to move up (positive) or down (negative). ...
Minkowski diagram
The Minkowski diagram, also known as a spacetime diagram, was developed in 1908 by Hermann Minkowski and provides an illustration of the properties of space and time in the special theory of relativity. It allows a quantitative understanding of the corresponding phenomena like time dilation and length contraction without mathematical equations.The term Minkowski diagram is used in both a generic and particular sense. In general, a Minkowski diagram is a graphic depiction of a portion of Minkowski space, often where space has been curtailed to a single dimension. These two-dimensional diagrams portray worldlines as curves in a plane that correspond to motion along the spatial axis. The vertical axis is usually temporal, and the units of measurement are taken such that the light cone at an event consists of the lines of slope plus or minus one through that event.A particular Minkowski diagram illustrates the result of a Lorentz transformation. The horizontal corresponds to the usual notion of simultaneous events, for a stationary observer at the origin. The Lorentz transformation relates two inertial frames of reference, where an observer makes a change of velocity at the event (0, 0). The new time axis of the observer forms an angle α with the previous time axis, with α < π/4. After the Lorentz transformation the new simultaneous events lie on a line inclined by α to the previous line of simultaneity. Whatever the magnitude of α, the line t = x forms the universal bisector.