Geometry Spiral Review 4
... Directions: Please show all work to receive full credit, including work necessary to complete multiple choice questions. ...
... Directions: Please show all work to receive full credit, including work necessary to complete multiple choice questions. ...
Chapter 6: Integers and the Coordinate Plane
... A ___________________________ _________________ is formed by the intersection of a horizontal number line (___-_____________) and a vertical number line (____-_________). The number lines intersect at the __________________ and separate the coordinate plane into four regions called _________________ ...
... A ___________________________ _________________ is formed by the intersection of a horizontal number line (___-_____________) and a vertical number line (____-_________). The number lines intersect at the __________________ and separate the coordinate plane into four regions called _________________ ...
Materials: 1 inch binder for math class only notebook or loose leaf
... 8.SP.1: Construct and interpret scatter plots for bivariate measurement data to investigate patterns of association between two quantities. Describe patterns such as clustering, outliers, positive or negative association, linear association, and nonlinear association. 8.SP.2: Know that straight lin ...
... 8.SP.1: Construct and interpret scatter plots for bivariate measurement data to investigate patterns of association between two quantities. Describe patterns such as clustering, outliers, positive or negative association, linear association, and nonlinear association. 8.SP.2: Know that straight lin ...
Section 1
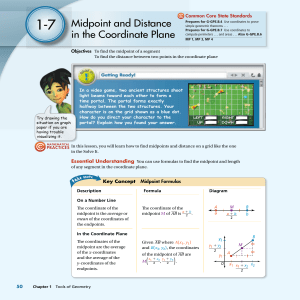
... At the end of today’s lesson, you will be able to: 1) describe what it means for something to be a segment bisector. 2) combine the ideas of segment bisector and segment addition to solve various problems. 3) use the midpoint formula to find a missing coordinate. 4) find the distance between two giv ...
... At the end of today’s lesson, you will be able to: 1) describe what it means for something to be a segment bisector. 2) combine the ideas of segment bisector and segment addition to solve various problems. 3) use the midpoint formula to find a missing coordinate. 4) find the distance between two giv ...
Geometry Chapter 1 Foundations Lesson 1
... #3. The Queens Quilt block includes 12 blue triangles. #4. The base of a rectangle is 5 more than 2 times its The base and height of each triangle are about 4 in. height. Find the perimeter and area of the Find the approximate amount of fabric used to ...
... #3. The Queens Quilt block includes 12 blue triangles. #4. The base of a rectangle is 5 more than 2 times its The base and height of each triangle are about 4 in. height. Find the perimeter and area of the Find the approximate amount of fabric used to ...
Geometry 2H Name: Similarity Part I
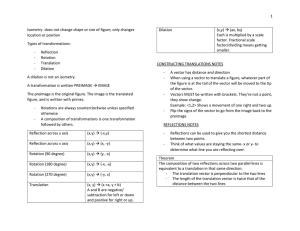
... functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. I can compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch). ...
... functions that take points in the plane as inputs and give other points as outputs. I can compare transformations that preserve distance and angle to those that do not (e.g., translation versus horizontal stretch). ...
Math 1300 Geometry review and extension exercises
... 4. Give lines in both vector and scalar parametric forms (and point-normal when working in R2 ), and planes in both point-normal and general form: (a) The line through the origin and (3, −5) (b) The line through (−1, 2) and (2, −3) (c) The line perpendicular to (2, 3) + t(1, −1) and passing through ...
... 4. Give lines in both vector and scalar parametric forms (and point-normal when working in R2 ), and planes in both point-normal and general form: (a) The line through the origin and (3, −5) (b) The line through (−1, 2) and (2, −3) (c) The line perpendicular to (2, 3) + t(1, −1) and passing through ...
View - Center for Mathematics and Teaching Inc.
... GRAPHING IN FOUR QUADRANTS When the x-axis and y-axis are extended to include negative values, they divide the coordinate plane into four regions, called quadrants. The quadrants are numbered counterclockwise using Roman numerals. 1. Label the x-axis and the y-axis. ...
... GRAPHING IN FOUR QUADRANTS When the x-axis and y-axis are extended to include negative values, they divide the coordinate plane into four regions, called quadrants. The quadrants are numbered counterclockwise using Roman numerals. 1. Label the x-axis and the y-axis. ...
1 - Collingswood High School
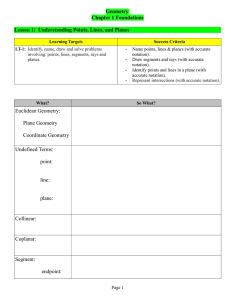
... 2) Lines intersect at a ____________________. 3) Planes intersect at a ___________________. 4) How do we represent line AB? _______________ 5) How do we refer to the line segment AB? ______________ 6) Points that lie on the same line are called _______________________. ...
... 2) Lines intersect at a ____________________. 3) Planes intersect at a ___________________. 4) How do we represent line AB? _______________ 5) How do we refer to the line segment AB? ______________ 6) Points that lie on the same line are called _______________________. ...
Cartesian coordinate system
A Cartesian coordinate system is a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely in a plane by a pair of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances from the point to two fixed perpendicular directed lines, measured in the same unit of length. Each reference line is called a coordinate axis or just axis of the system, and the point where they meet is its origin, usually at ordered pair (0, 0). The coordinates can also be defined as the positions of the perpendicular projections of the point onto the two axes, expressed as signed distances from the origin.One can use the same principle to specify the position of any point in three-dimensional space by three Cartesian coordinates, its signed distances to three mutually perpendicular planes (or, equivalently, by its perpendicular projection onto three mutually perpendicular lines). In general, n Cartesian coordinates (an element of real n-space) specify the point in an n-dimensional Euclidean space for any dimension n. These coordinates are equal, up to sign, to distances from the point to n mutually perpendicular hyperplanes.The invention of Cartesian coordinates in the 17th century by René Descartes (Latinized name: Cartesius) revolutionized mathematics by providing the first systematic link between Euclidean geometry and algebra. Using the Cartesian coordinate system, geometric shapes (such as curves) can be described by Cartesian equations: algebraic equations involving the coordinates of the points lying on the shape. For example, a circle of radius 2 in a plane may be described as the set of all points whose coordinates x and y satisfy the equation x2 + y2 = 4.Cartesian coordinates are the foundation of analytic geometry, and provide enlightening geometric interpretations for many other branches of mathematics, such as linear algebra, complex analysis, differential geometry, multivariate calculus, group theory and more. A familiar example is the concept of the graph of a function. Cartesian coordinates are also essential tools for most applied disciplines that deal with geometry, including astronomy, physics, engineering and many more. They are the most common coordinate system used in computer graphics, computer-aided geometric design and other geometry-related data processing.