Synthesis and characterization of highly ordered functional
... the channel surfaces for influencing transport.9,10 –NH2 ligands, which are similar to –COOH ligands but positively chargeable in neutral to acid media, are able to both serve as binding sites for biomolecules such as enzymes, antibodies, and other proteins and create an electropositive environment ...
... the channel surfaces for influencing transport.9,10 –NH2 ligands, which are similar to –COOH ligands but positively chargeable in neutral to acid media, are able to both serve as binding sites for biomolecules such as enzymes, antibodies, and other proteins and create an electropositive environment ...
May2016
... a) Compute the first two permitted energy values for an electron in a box of width 0.4nm? b) Write a short note on three level and four level pumping schemes? c) Explain giving the necessary theory, the phenomenon of fraunhofer diffraction through single slit? ...
... a) Compute the first two permitted energy values for an electron in a box of width 0.4nm? b) Write a short note on three level and four level pumping schemes? c) Explain giving the necessary theory, the phenomenon of fraunhofer diffraction through single slit? ...
Problem Set 4: De Broglies Relations, Fourier Superpositions and
... m/s and also that of an electron moving with a speed of 0.99 × 108 m/s. Be careful in your choice of formulae in the second case as it is relativistic. (b) To observe small objects, one measures the diffraction of particles whose de Broglie wavelength is comparable to objects size (or features). Fin ...
... m/s and also that of an electron moving with a speed of 0.99 × 108 m/s. Be careful in your choice of formulae in the second case as it is relativistic. (b) To observe small objects, one measures the diffraction of particles whose de Broglie wavelength is comparable to objects size (or features). Fin ...
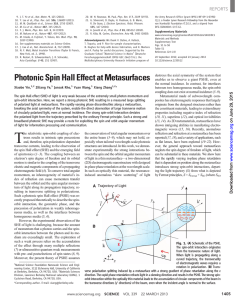
... Fig. 4. (A) Wavelength dependence of the refraction angles when excitation is normally incident onto the metasurface. The measurement was conducted for three samples with different phase gradients of 3.6, 4.0, and 4.4 rad/mm. The measured refraction angles agree well with the theoretical predictions ...
Lab Handout
... chart (or any other device to jog your memory) of the procedure to be followed. View this is as an opportunity to organize your thoughts and not to reproduce the procedure in the handout. Perhaps the easiest way to collect your data and observations is to paraphrase the procedure as you go through t ...
... chart (or any other device to jog your memory) of the procedure to be followed. View this is as an opportunity to organize your thoughts and not to reproduce the procedure in the handout. Perhaps the easiest way to collect your data and observations is to paraphrase the procedure as you go through t ...
Analytical Chemistry
... (concentration or composition) of various substances in samples. There are many methods of determining these amounts, all based on chemical or physical ...
... (concentration or composition) of various substances in samples. There are many methods of determining these amounts, all based on chemical or physical ...
Exercises Chem Eqm
... 7.1(a) K = 2.85 x 10-6; (b) ∆rGo = +240 kJ mol-1; (c) ∆rG = 0 7.4(a) Mole fractions A: 0.087, B: 0.370, C: 0.196, D: 0.348, Total: 1.001; (b) Kx – 0.33; (c) p = 0.33; (d) ∆rGo = + 2.8 x 103 J mol-1. 7.6(a) ∆rHo = +2.77 kJ mol-1, ∆rSo = -16.5 J K-1 mol-1 7.9(a) χB = 0.904, χI = 0.096 7.11(a) ∆rGo = – ...
... 7.1(a) K = 2.85 x 10-6; (b) ∆rGo = +240 kJ mol-1; (c) ∆rG = 0 7.4(a) Mole fractions A: 0.087, B: 0.370, C: 0.196, D: 0.348, Total: 1.001; (b) Kx – 0.33; (c) p = 0.33; (d) ∆rGo = + 2.8 x 103 J mol-1. 7.6(a) ∆rHo = +2.77 kJ mol-1, ∆rSo = -16.5 J K-1 mol-1 7.9(a) χB = 0.904, χI = 0.096 7.11(a) ∆rGo = – ...
Yellow nanosecond sum-frequency generating optical
... copper vapour lasers at 578 nm and dye lasers operating at 585 nm and 595 nm. These lasers are both bulky and inefficient and it would be attractive to develop a solid-state alternative to these lasers. One path that has been followed for the generation of yellow light is second harmonic generation ...
... copper vapour lasers at 578 nm and dye lasers operating at 585 nm and 595 nm. These lasers are both bulky and inefficient and it would be attractive to develop a solid-state alternative to these lasers. One path that has been followed for the generation of yellow light is second harmonic generation ...
NON-LINEAR MATERIALS Definition
... absorption and scattering when the light pulse propagates through the fibre. It is, now-a-days, possible to fabricate fibres which amplify the light signal propagating through it. They are called fibre amplifiers. By pumping the atoms inside the fibre by sending a pump beam, population inversion is ...
... absorption and scattering when the light pulse propagates through the fibre. It is, now-a-days, possible to fabricate fibres which amplify the light signal propagating through it. They are called fibre amplifiers. By pumping the atoms inside the fibre by sending a pump beam, population inversion is ...
AP Chemistry - Partners4results
... AP Chemistry Free Response 3. A solution is made that is 0.24M HC2H3O2, acetic acid, which has a Ka value of 1.8x10-5. Determine the pH of this solution. ...
... AP Chemistry Free Response 3. A solution is made that is 0.24M HC2H3O2, acetic acid, which has a Ka value of 1.8x10-5. Determine the pH of this solution. ...
Experimental study of Bloch vector analysis in nonlinear, finite
... quadratic nonlinearity is assumed to be in the metal layers. We measured the reflected SH signal at 400 nm for different polarization states of the fundamental input beam, intensities, and incident angles. The fundamental beam was provided by the output of a femtosecond Ti:sapphire laser (λ = 800 nm ...
... quadratic nonlinearity is assumed to be in the metal layers. We measured the reflected SH signal at 400 nm for different polarization states of the fundamental input beam, intensities, and incident angles. The fundamental beam was provided by the output of a femtosecond Ti:sapphire laser (λ = 800 nm ...
H. F. Ghaemi - Department of Physics | Oregon State
... We identify the transmission minima as the result of Wood’s anomaly,11 which was observed in diffraction gratings and occurs when a diffracted order becomes tangent to the plane of the grating. When the order disappears, the light intensity is redistributed among the remaining orders; it has been su ...
... We identify the transmission minima as the result of Wood’s anomaly,11 which was observed in diffraction gratings and occurs when a diffracted order becomes tangent to the plane of the grating. When the order disappears, the light intensity is redistributed among the remaining orders; it has been su ...
ANSWERS - AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice – Torque
... Step the two pulses through each other a little bit at a time and use superposition to see how the amplitudes add. At first the amplitude jumps up rapidly, then the amplitude moves down as the rightmost negative pulse continues to propagate. At the very end of their passing the amplitude would be al ...
... Step the two pulses through each other a little bit at a time and use superposition to see how the amplitudes add. At first the amplitude jumps up rapidly, then the amplitude moves down as the rightmost negative pulse continues to propagate. At the very end of their passing the amplitude would be al ...
Fiber Optics: How Fused Fiber Optic Couplers Work
... Up to this point we have tacitly assumed that a single transfer of energy has occurred from one fiber to the other. In reality, energy transfers back and forth between the two fibers many times over the coupling region (also called the Interaction Length). The transfer rate is a function of waveleng ...
... Up to this point we have tacitly assumed that a single transfer of energy has occurred from one fiber to the other. In reality, energy transfers back and forth between the two fibers many times over the coupling region (also called the Interaction Length). The transfer rate is a function of waveleng ...
FIB – an easy tool for fabrication of high quality plasmonic structures
... electrons propagating at metal-dielectric interfaces. This dynamic effect results in formation of the electromagnetic near-field zone which can be detected using Scanning ...
... electrons propagating at metal-dielectric interfaces. This dynamic effect results in formation of the electromagnetic near-field zone which can be detected using Scanning ...
Optical Trapping: Laser Tweezers
... I. Repeat steps F and G for at least two other power settings. The exact power in the trap can’t be measured accurately but you can get a scale of the power by using the angle of the polarizer. Find the angle of minimum power, then turn 90° to get the maximum. Assume this power is 30 mW. The relativ ...
... I. Repeat steps F and G for at least two other power settings. The exact power in the trap can’t be measured accurately but you can get a scale of the power by using the angle of the polarizer. Find the angle of minimum power, then turn 90° to get the maximum. Assume this power is 30 mW. The relativ ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.