Introductory Chemistry I
... 4. The maximum number of electrons that can occupy the 3d orbitals is a. 5 b. 6 c. 10 d. 14 e. 18 5. Let’s say that you are examining the outermost electrons in a ground-state germanium atom. Which of the following sets of values for the four quantum numbers (n, l, ml, and ms) could you use to descr ...
... 4. The maximum number of electrons that can occupy the 3d orbitals is a. 5 b. 6 c. 10 d. 14 e. 18 5. Let’s say that you are examining the outermost electrons in a ground-state germanium atom. Which of the following sets of values for the four quantum numbers (n, l, ml, and ms) could you use to descr ...
Exam Review Chapter 18-Equilibrium
... 10. Which of the following is true concerning the impact of increasing temperature on reaction rates? a. The number of collisions between reactant atoms is increased. b. The energy of each reactant atom is increased. c. The percentage of collisions with sufficient energy to cross the activation ener ...
... 10. Which of the following is true concerning the impact of increasing temperature on reaction rates? a. The number of collisions between reactant atoms is increased. b. The energy of each reactant atom is increased. c. The percentage of collisions with sufficient energy to cross the activation ener ...
Michelson Interferometer
... The experimental arrangement is shown in Fig 3. The orientation of M2 can be adjusted for alignment with M1 and the path length in the reflective arm can be altered by moving M1 using a micrometer screw and lever arm. Note that the interferometer includes an extra component which is not shown in Fig ...
... The experimental arrangement is shown in Fig 3. The orientation of M2 can be adjusted for alignment with M1 and the path length in the reflective arm can be altered by moving M1 using a micrometer screw and lever arm. Note that the interferometer includes an extra component which is not shown in Fig ...
Subject: Precision Optics II Grade: 10
... Optics is the science of controlling light. Simple rays are used by engineers and lens designers to illustrate the path of light through an optic. The performance of a lens (system) depends on each lens’ shape, orientation, glass type, and alignment within the system. Real lens systems are d ...
... Optics is the science of controlling light. Simple rays are used by engineers and lens designers to illustrate the path of light through an optic. The performance of a lens (system) depends on each lens’ shape, orientation, glass type, and alignment within the system. Real lens systems are d ...
Effective Charge Transfer Distances in Cyanide
... spectra shown for 2-4 were scaled to a field strength of 1 MV‚cm-1 by using the F4 and F2 field dependencies of the signals, respectively. All spectra were obtained at χ ) 90°, except for 4, where χ ) 65° for better comparison with the results in ref 17. Table 1 lists the results of the simultaneous ...
... spectra shown for 2-4 were scaled to a field strength of 1 MV‚cm-1 by using the F4 and F2 field dependencies of the signals, respectively. All spectra were obtained at χ ) 90°, except for 4, where χ ) 65° for better comparison with the results in ref 17. Table 1 lists the results of the simultaneous ...
Understanding the reactivity of photoinitiating systems for
... After formation of the radicals, the initiation process must occur between one initiating radical and one monomer unit. It is well known that the large variety of radicals that can be formed by light absorption behave in very different ways. For instance, aminoalkyl radicals are known to react at hi ...
... After formation of the radicals, the initiation process must occur between one initiating radical and one monomer unit. It is well known that the large variety of radicals that can be formed by light absorption behave in very different ways. For instance, aminoalkyl radicals are known to react at hi ...
Atomic spectra
... particular manner. All forms of electromagnetic radiation interact with matter in the process of emission and absorption. The radiation propagates in a wavelike fashion but in an interaction the radiation behaves as a concentration of energy (photons) moving at the speed of light. Each photon carrie ...
... particular manner. All forms of electromagnetic radiation interact with matter in the process of emission and absorption. The radiation propagates in a wavelike fashion but in an interaction the radiation behaves as a concentration of energy (photons) moving at the speed of light. Each photon carrie ...
1 - TAMU Chemistry
... f) The orientation of ethylene in Fe(C0)4(YJ 2 -CH2 =CH2): Cli)face on and parallel to the x/y plane; ii) face on and perpendicular to the x/y plane; iii) side on and parallel to the z axis; iv) side on and perpendicular to the z-axis. (if you don't understand "face on" or "side on", ask.) g) The MC ...
... f) The orientation of ethylene in Fe(C0)4(YJ 2 -CH2 =CH2): Cli)face on and parallel to the x/y plane; ii) face on and perpendicular to the x/y plane; iii) side on and parallel to the z axis; iv) side on and perpendicular to the z-axis. (if you don't understand "face on" or "side on", ask.) g) The MC ...
112 ex i lec outline
... light shines on metals, electrons could be ejected from the surface of the metals. For each metal there is a minimum frequency of light required to cause an electron to be released. Planck’s idea of energy quanta with the notion that light could be described not only as having wave-like properties b ...
... light shines on metals, electrons could be ejected from the surface of the metals. For each metal there is a minimum frequency of light required to cause an electron to be released. Planck’s idea of energy quanta with the notion that light could be described not only as having wave-like properties b ...
Miniaturized modules for light sheet microscopy with low chromatic
... attained when using the relation AN = sinα ࣈ tanα = A/2f’ for small angles. The resulting beam waist d = λ/AN = 5.9 μm is defined by the thinnest line described by the distance between the first zeros of the diffraction function of a slit. The depth of focus L = nλ/AN ² considered in physical optics ...
... attained when using the relation AN = sinα ࣈ tanα = A/2f’ for small angles. The resulting beam waist d = λ/AN = 5.9 μm is defined by the thinnest line described by the distance between the first zeros of the diffraction function of a slit. The depth of focus L = nλ/AN ² considered in physical optics ...
Forces, light and waves
... When the particle index of refraction is smaller than that of the medium (bubble), the deflection of light tends to expell the particle from maximum intensity region (should also be observed with reflective particles) ...
... When the particle index of refraction is smaller than that of the medium (bubble), the deflection of light tends to expell the particle from maximum intensity region (should also be observed with reflective particles) ...
Magneto-Optic Kerr Effect
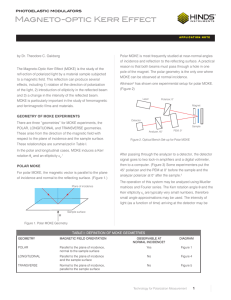
... If very fast response is required, a PEM could be used as an optical chopper to modulate the incident laser beam. AC ...
... If very fast response is required, a PEM could be used as an optical chopper to modulate the incident laser beam. AC ...
2008 local exam - American Chemical Society
... added slowly to a solution that is 0.10 M with respect to both Ca(NO3)2 and Mg(NO3)2? (A) The initial precipitate will contain CaF2 only. (B) The initial precipitate will contain MgF2 only. (C) The initial precipitate will contain both CaF2 and MgF2 with more CaF2. (D) The initial precipitate will c ...
... added slowly to a solution that is 0.10 M with respect to both Ca(NO3)2 and Mg(NO3)2? (A) The initial precipitate will contain CaF2 only. (B) The initial precipitate will contain MgF2 only. (C) The initial precipitate will contain both CaF2 and MgF2 with more CaF2. (D) The initial precipitate will c ...
Enthalpy of Neutralization
... Calorimetry will be employed to determine the amount of heat lost by the reaction and gained by the salt water solution. A calorimeter is simply a container used to measure the heat change. Coffee Cup Calorimetry just means that we will be measuring heat at constant pressure, H. The heat lost by th ...
... Calorimetry will be employed to determine the amount of heat lost by the reaction and gained by the salt water solution. A calorimeter is simply a container used to measure the heat change. Coffee Cup Calorimetry just means that we will be measuring heat at constant pressure, H. The heat lost by th ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.