Orbital Dynamics of the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna
... Adjust mirrors 10 and 12B so that the laser passes through the pinholes of both targets. Due to the design of the Newport cubes, mirror 12A has to be assumed fixed and cannot be used for alignment. The periscope was initially aligned independent of the rest of the system, and mirror 10 and 12B are u ...
... Adjust mirrors 10 and 12B so that the laser passes through the pinholes of both targets. Due to the design of the Newport cubes, mirror 12A has to be assumed fixed and cannot be used for alignment. The periscope was initially aligned independent of the rest of the system, and mirror 10 and 12B are u ...
Optics-Light Lab - University of Michigan SharePoint Portal
... Reflected waves are redirected according to the law of reflection: the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. The angles of incidence and reflection are defined with respect to the direction normal (perpendicular) to the mirror surface as shown below. The law of reflection holds for ...
... Reflected waves are redirected according to the law of reflection: the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. The angles of incidence and reflection are defined with respect to the direction normal (perpendicular) to the mirror surface as shown below. The law of reflection holds for ...
Section 4.8: Acid-Base Reactions
... reagent (the titrant), that is required to react completely with an exact amount of another reagent, is measured precisely. The method presumes that the titration reaction goes to completion. In most titrations the concentration of titrant is known, in which case the exact amount of analyte, the sub ...
... reagent (the titrant), that is required to react completely with an exact amount of another reagent, is measured precisely. The method presumes that the titration reaction goes to completion. In most titrations the concentration of titrant is known, in which case the exact amount of analyte, the sub ...
Міністерство охорони здоров`я України
... 1) true solutions (particle size is less than 10-9 m), which can be ionic and molecular depending on whether the solute dissociates on ions or molecules or stays in molecular state; b) colloidal solutions (particle size is from 10 -7 to 10-9 m) are heterogeneous and have interface between phases - s ...
... 1) true solutions (particle size is less than 10-9 m), which can be ionic and molecular depending on whether the solute dissociates on ions or molecules or stays in molecular state; b) colloidal solutions (particle size is from 10 -7 to 10-9 m) are heterogeneous and have interface between phases - s ...
Photonic crystal slot nanobeam slow light
... was designed. In our simulation, the slot modes of the cavity infiltrated with distilled water 共n = 1.333兲 and sugar/water solution 共n = 1.3417兲 are at 1416.5 nm and 1422.8 nm respectively, with Q factors of 2000. Because the structure is finite, losses occur near the two ends. To decrease these los ...
... was designed. In our simulation, the slot modes of the cavity infiltrated with distilled water 共n = 1.333兲 and sugar/water solution 共n = 1.3417兲 are at 1416.5 nm and 1422.8 nm respectively, with Q factors of 2000. Because the structure is finite, losses occur near the two ends. To decrease these los ...
Principles of remote sensing of atmospheric parameters
... of the distribution of the emitting gases and of temperature throughout the atmosphere, measurements of radiance contain some information on both these quantities. These lectures will start with an introduction to the basic radiometric quantities and laws to be used, then will derive and discuss the ...
... of the distribution of the emitting gases and of temperature throughout the atmosphere, measurements of radiance contain some information on both these quantities. These lectures will start with an introduction to the basic radiometric quantities and laws to be used, then will derive and discuss the ...
Materials and Waves
... Change in kinetic energy: Ek = 1/2mv2 - 1/2mu2 Power - The rate at which work is done. Units: ...
... Change in kinetic energy: Ek = 1/2mv2 - 1/2mu2 Power - The rate at which work is done. Units: ...
Slide 1
... junction. As in other diodes, current flows easily from the p-side, or anode, to the n-side, or cathode, but not in the reverse direction. Charge-carriers—electrons and holes—flow into the junction from electrodes with different voltages. When an electron meets a hole, it falls into a lower energy l ...
... junction. As in other diodes, current flows easily from the p-side, or anode, to the n-side, or cathode, but not in the reverse direction. Charge-carriers—electrons and holes—flow into the junction from electrodes with different voltages. When an electron meets a hole, it falls into a lower energy l ...
Proposal for a Magneto-optical Beam Splitter for Atoms.
... The momentum distribution in the adiabatic limit was calculated by considering the eigenvalue potential as a phase grating (i.e. the momentum distribution is given by the Fourier transform of exp UJ).2 (z, t) dt], where ).2 is the triangular eigenvalue). The calculation assumes that the change in th ...
... The momentum distribution in the adiabatic limit was calculated by considering the eigenvalue potential as a phase grating (i.e. the momentum distribution is given by the Fourier transform of exp UJ).2 (z, t) dt], where ).2 is the triangular eigenvalue). The calculation assumes that the change in th ...
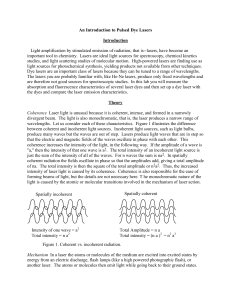
An Introduction to Pulsed Dye Lasers Introduction Light amplification
... is called phosphorescence. Molecular fluorescence is responsible for dye laser emission. The wavelength of laser emission is limited by the range of fluorescence wavelengths. To choose a dye, we then pick a dye with its fluorescence emission spectrum near the desired laser wavelength. We must also c ...
... is called phosphorescence. Molecular fluorescence is responsible for dye laser emission. The wavelength of laser emission is limited by the range of fluorescence wavelengths. To choose a dye, we then pick a dye with its fluorescence emission spectrum near the desired laser wavelength. We must also c ...
Physical Setting/Chemistry Examination
... 16 A large sample of solid calcium sulfate is crushed into smaller pieces for testing. Which two physical properties are the same for both the large sample and one of the smaller pieces? (1) mass and density (2) mass and volume (3) solubility and density (4) solubility and volume ...
... 16 A large sample of solid calcium sulfate is crushed into smaller pieces for testing. Which two physical properties are the same for both the large sample and one of the smaller pieces? (1) mass and density (2) mass and volume (3) solubility and density (4) solubility and volume ...
Problem Sheet
... R1 R2 (the lens-maker’s formula) making clear any assumptions or approximations. 6. If such a lens has n = 1.60, by what factor does the focal length of the lens change when using it in water (n = 1.33) instead of air? 7. Consider a light source placed at a fixed distance s from a screen, such that ...
... R1 R2 (the lens-maker’s formula) making clear any assumptions or approximations. 6. If such a lens has n = 1.60, by what factor does the focal length of the lens change when using it in water (n = 1.33) instead of air? 7. Consider a light source placed at a fixed distance s from a screen, such that ...
Lecture 5
... In an effort to make a relatively inexpensive aligner, capable of producing very small features an optical source of a simple contact printer is replaced with ArF laser. – list 2 problems that the engineer is likely to encounter in trying to use this device, assume yield is unimportant – assume the ...
... In an effort to make a relatively inexpensive aligner, capable of producing very small features an optical source of a simple contact printer is replaced with ArF laser. – list 2 problems that the engineer is likely to encounter in trying to use this device, assume yield is unimportant – assume the ...
KEMS448 Physical Chemistry Advanced Laboratory Work
... where χ is the mole fraction of the solvent (or solute) and p∗ is the pure solvent’s (or solute’s) vapour pressure. Because it is assumed that the solute is non-vaporizable, the latter term in equation (1) is zero. In an ideal solution there are no attractive forces between the solvent and the solut ...
... where χ is the mole fraction of the solvent (or solute) and p∗ is the pure solvent’s (or solute’s) vapour pressure. Because it is assumed that the solute is non-vaporizable, the latter term in equation (1) is zero. In an ideal solution there are no attractive forces between the solvent and the solut ...
1 Macleod ‐ Thin Film Optics
... somewhere else. Somewhere else can often be the image plane, where it causes ghost images and veiling glare. Most simple optical surfaces, therefore, are treated with a antireflection coating. The least complex is a quarterwave of magnesium fluoride that reduces the reflectance of glass as shown. ...
... somewhere else. Somewhere else can often be the image plane, where it causes ghost images and veiling glare. Most simple optical surfaces, therefore, are treated with a antireflection coating. The least complex is a quarterwave of magnesium fluoride that reduces the reflectance of glass as shown. ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.