A Laser Coupler for DVD/CD Playback
... A new optical integrated device called the 2BLC, which has two-wavelength light emission/detection functions, has been developed. It has been especially designed for use in PlayStation 2 with many hard requirements, such as including two-wavelength functions in one integrated-device, being of small ...
... A new optical integrated device called the 2BLC, which has two-wavelength light emission/detection functions, has been developed. It has been especially designed for use in PlayStation 2 with many hard requirements, such as including two-wavelength functions in one integrated-device, being of small ...
High power, continuous-wave ytterbium-doped fiber - HAL
... cooling where the laser wavelength has to be specifically adjusted, metrology or medical treatments. There is also an increasing attention of such sources for parametric applications as for instance frequency conversion, including Raman or optical parametric amplifiers [1–3]. To this purpose, rare e ...
... cooling where the laser wavelength has to be specifically adjusted, metrology or medical treatments. There is also an increasing attention of such sources for parametric applications as for instance frequency conversion, including Raman or optical parametric amplifiers [1–3]. To this purpose, rare e ...
THE BASIC PRINCIPLES OF LASER TECHNOLOGY, USES AND
... A laser diode, also known as a semiconductor laser, is a light-emitting diode that uses stimulated emission to form a coherent light output. Typically, laser diodes are small, compact electronic devices that can be placed into housings and have a small window on the end where the laser light is emit ...
... A laser diode, also known as a semiconductor laser, is a light-emitting diode that uses stimulated emission to form a coherent light output. Typically, laser diodes are small, compact electronic devices that can be placed into housings and have a small window on the end where the laser light is emit ...
en_20160128_lzh_pm_hymnos_final
... fiber amplifiers“, the scientists will be working on increasing the laser power of continuous and pulsed systems for the next three years. Presently, the maximum usable output power of high power fiber systems is limited by the so-called transverse mode instability (TMI). Here, the laser beam profil ...
... fiber amplifiers“, the scientists will be working on increasing the laser power of continuous and pulsed systems for the next three years. Presently, the maximum usable output power of high power fiber systems is limited by the so-called transverse mode instability (TMI). Here, the laser beam profil ...
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... a. Pre-requisite(s): PHYS 132 (University Physics II) or PHYS 122 (College Physics II) or permission of instructor b. Co-requisite(s): None ...
... a. Pre-requisite(s): PHYS 132 (University Physics II) or PHYS 122 (College Physics II) or permission of instructor b. Co-requisite(s): None ...
NEWS RELEASE Redfern Integrated Optics, Inc. Expands Product
... CEO of RIO “The design guarantees no performance degradation as compared to an ORIONTM module of the RIN, linewidth and phase noise over the operating case temperature of 0-70C.” The high-power RIO GRANDE, ideal for sensing, LIDAR, high-resolution metrology and general research and development appli ...
... CEO of RIO “The design guarantees no performance degradation as compared to an ORIONTM module of the RIN, linewidth and phase noise over the operating case temperature of 0-70C.” The high-power RIO GRANDE, ideal for sensing, LIDAR, high-resolution metrology and general research and development appli ...
Optical Filters for Laser-based Fluorescence Microscopes
... substrate with ultra-low autofluorescence, such as fused silica, should be used. Note that since the excitation light and the emission signal intensity levels differ by many orders of magnitude (typically a factor of 106) the requirement for the emission filter autofluorescence is not as stringent a ...
... substrate with ultra-low autofluorescence, such as fused silica, should be used. Note that since the excitation light and the emission signal intensity levels differ by many orders of magnitude (typically a factor of 106) the requirement for the emission filter autofluorescence is not as stringent a ...
Ultralow threshold laser using a single quantum dot and a
... To determine whether our device is capable of exhibiting laser action, we cannot use the conventional, macroscopic definition of threshold, that the gain of the optical mode equals the cavity losses. Instead, we follow the alternative definition given by Björk, Karlsson, and Yamamoto, that the mean ...
... To determine whether our device is capable of exhibiting laser action, we cannot use the conventional, macroscopic definition of threshold, that the gain of the optical mode equals the cavity losses. Instead, we follow the alternative definition given by Björk, Karlsson, and Yamamoto, that the mean ...
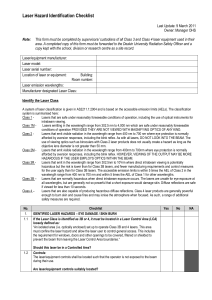
Laser Hazard Identification Checklist
... Class 3R Lasers that emit in the wavelength range from 302.5nm to 106nm where direct intrabeam viewing is potentially hazardous but the risk is lower than for Class 3B lasers, and fewer manufacturing requirements and control measures for the user apply than for Class 3B lasers. The accessible emissi ...
... Class 3R Lasers that emit in the wavelength range from 302.5nm to 106nm where direct intrabeam viewing is potentially hazardous but the risk is lower than for Class 3B lasers, and fewer manufacturing requirements and control measures for the user apply than for Class 3B lasers. The accessible emissi ...
Introduction The acronym LASER, which stands for light
... of (equal) mirror reflectance R. In a resonator containing an active medium, as γ − α increases from zero and we have an infinite amplitude transmitted wave for a finite amplitude incident wave. In other words, a finite amplitude transmitted wave for zero incident wave—oscillation. The threshold gai ...
... of (equal) mirror reflectance R. In a resonator containing an active medium, as γ − α increases from zero and we have an infinite amplitude transmitted wave for a finite amplitude incident wave. In other words, a finite amplitude transmitted wave for zero incident wave—oscillation. The threshold gai ...
Lab 5 - College of Science | Oregon State University
... the rotation axis lies on the reflecting surface, which is important so that the laser beam remains on the glass surface as the sample is rotated, especially at high angles. A schematic for the general layout to be used in these experiments is shown in the above figure. Position the glass reflector ...
... the rotation axis lies on the reflecting surface, which is important so that the laser beam remains on the glass surface as the sample is rotated, especially at high angles. A schematic for the general layout to be used in these experiments is shown in the above figure. Position the glass reflector ...
Long Haul Fiber Optic Transmission Systems : Modeling and
... • To introduce the basic physics of photonic devices and apply it for the design of optical transmission systems and networks. • To simulate the various photonic components and also to do system level simulations. • To study different noise processes in photonic circuits and understand their impact ...
... • To introduce the basic physics of photonic devices and apply it for the design of optical transmission systems and networks. • To simulate the various photonic components and also to do system level simulations. • To study different noise processes in photonic circuits and understand their impact ...
- Welcome to UC Santa Barbara
... Due to high intensity, fs pulses can not be amplified as is. Recipe for the amplification: Chirped pulse amplifier (CPA) • Stretch the pulse in time, thus reducing the peak power (I = J / tpulse !) (typically the pulse is stretched up to hundreds of ps) • Amplify the stretched pulse • Compress the p ...
... Due to high intensity, fs pulses can not be amplified as is. Recipe for the amplification: Chirped pulse amplifier (CPA) • Stretch the pulse in time, thus reducing the peak power (I = J / tpulse !) (typically the pulse is stretched up to hundreds of ps) • Amplify the stretched pulse • Compress the p ...
femtosecond laser - UCSB - Optical Characterization Lab
... Due to high intensity, fs pulses can not be amplified as is. Recipe for the amplification: Chirped pulse amplifier (CPA) • Stretch the pulse in time, thus reducing the peak power (I = J / tpulse !) (typically the pulse is stretched up to hundreds of ps) • Amplify the stretched pulse • Compress the p ...
... Due to high intensity, fs pulses can not be amplified as is. Recipe for the amplification: Chirped pulse amplifier (CPA) • Stretch the pulse in time, thus reducing the peak power (I = J / tpulse !) (typically the pulse is stretched up to hundreds of ps) • Amplify the stretched pulse • Compress the p ...
Laser Tweezers
... noticed that some of the particles in his sample began to "stick" to the laser beam and follow it around as the laser tracked across the field of view. After further investigation, it was clear that for some reason the laser beam was in fact acting like a pair of microscopic tweezers, squeezing part ...
... noticed that some of the particles in his sample began to "stick" to the laser beam and follow it around as the laser tracked across the field of view. After further investigation, it was clear that for some reason the laser beam was in fact acting like a pair of microscopic tweezers, squeezing part ...
XIII. GRAVITATION RESEARCH Academic and Research Staff Prof
... IN AN ATOMIC BEAM OF RUBIDIUM In connection with our program on laser frequency stabilization, concerning the use ...
... IN AN ATOMIC BEAM OF RUBIDIUM In connection with our program on laser frequency stabilization, concerning the use ...
Ultimate temperature for laser cooling of two
... Fig.3 - Time evolution of the kinetic energy in the z-direction for the one-dimensional cooling. think of alternating the laser among the three directions (r,yandz). We have performed calculations concerning this situation and the results show that for cooling times (time that the laser spends in a ...
... Fig.3 - Time evolution of the kinetic energy in the z-direction for the one-dimensional cooling. think of alternating the laser among the three directions (r,yandz). We have performed calculations concerning this situation and the results show that for cooling times (time that the laser spends in a ...
Loss measurements on semiconductor lasers by
... loss/gain is related to the ratio between the Fourier coefficients of adjacent harmonics. On the other hand, the width of the individual harmonic peaks is also inversely proportional to the spectral bandwidth of the light emission.7,8 Therefore, by using the propagation loss/gain as a fitting parame ...
... loss/gain is related to the ratio between the Fourier coefficients of adjacent harmonics. On the other hand, the width of the individual harmonic peaks is also inversely proportional to the spectral bandwidth of the light emission.7,8 Therefore, by using the propagation loss/gain as a fitting parame ...
Monolithic, unidirectional single
... subtracts from the polarization rotation that is due to the nonplanar design, whereas for the other direction, rotation is increased. Nonnormal incidence on the output coupler face serves as the polarizer in this resonator. The P polarization is more strongly transmitted at the output coupler face, ...
... subtracts from the polarization rotation that is due to the nonplanar design, whereas for the other direction, rotation is increased. Nonnormal incidence on the output coupler face serves as the polarizer in this resonator. The P polarization is more strongly transmitted at the output coupler face, ...
Yellow nanosecond sum-frequency generating optical
... parametric oscillation and sum-frequency generation was phase matched in a single crystal containing two different poling periods. We furthermore present observations of secondary optical parametric oscillators pumped by the circulating signal wave and the generated yellow light. 2. Experimental set ...
... parametric oscillation and sum-frequency generation was phase matched in a single crystal containing two different poling periods. We furthermore present observations of secondary optical parametric oscillators pumped by the circulating signal wave and the generated yellow light. 2. Experimental set ...
WINDOWS During the Apollo (manned lunar exploration) space
... were charted, phenomena were observed and records were maintained. The accuracy and validity of the data were, among other things, dependent on the windows’ ability to transmit images from outside the spacecraft to the inside for photographic recording without significant distortion. These windows a ...
... were charted, phenomena were observed and records were maintained. The accuracy and validity of the data were, among other things, dependent on the windows’ ability to transmit images from outside the spacecraft to the inside for photographic recording without significant distortion. These windows a ...
Photonic Devices I Purpose of the Lab
... 1) Connect the DFB laser to the OSA. 2) The settings of the OSA may need to be changed to make the graph look nicer. It is recommended that the number of sampling points be set to 250. This can be done by pressing SETUP, followed by SAMPLING POINTS and then typing in 250 and pressing nm/ENTER. Try t ...
... 1) Connect the DFB laser to the OSA. 2) The settings of the OSA may need to be changed to make the graph look nicer. It is recommended that the number of sampling points be set to 250. This can be done by pressing SETUP, followed by SAMPLING POINTS and then typing in 250 and pressing nm/ENTER. Try t ...
Temporal Integrated Detection and Applications of FS-Pulse Scattering S. Bakic
... the theoretical and numerical description of the scattering process [1], whereas the applications mainly focus on the inelastic scattering after stimulation with laser light. Up to now, the special characteristics of short pulse elastic scattering, with pulse lengths shorter than the object’s extent ...
... the theoretical and numerical description of the scattering process [1], whereas the applications mainly focus on the inelastic scattering after stimulation with laser light. Up to now, the special characteristics of short pulse elastic scattering, with pulse lengths shorter than the object’s extent ...
13 Int. Symp on Appl. Laser ...
... the theoretical and numerical description of the scattering process [1], whereas the applications mainly focus on the inelastic scattering after stimulation with laser light. Up to now, the special characteristics of short pulse elastic scattering, with pulse lengths shorter than the object’s extent ...
... the theoretical and numerical description of the scattering process [1], whereas the applications mainly focus on the inelastic scattering after stimulation with laser light. Up to now, the special characteristics of short pulse elastic scattering, with pulse lengths shorter than the object’s extent ...
OSA journals template (MSWORD)
... parametric oscillation and sum-frequency generation was phase matched in a single crystal containing two different poling periods. We furthermore present observations of secondary optical parametric oscillators pumped by the circulating signal wave and the generated yellow light. 2. Experimental set ...
... parametric oscillation and sum-frequency generation was phase matched in a single crystal containing two different poling periods. We furthermore present observations of secondary optical parametric oscillators pumped by the circulating signal wave and the generated yellow light. 2. Experimental set ...
Laser

A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The term ""laser"" originated as an acronym for ""light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation"". The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore H. Maiman at Hughes Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles Hard Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light coherently. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling applications such as laser cutting and lithography. Spatial coherence also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimation), enabling applications such as laser pointers. Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which allows them to emit light with a very narrow spectrum, i.e., they can emit a single color of light. Temporal coherence can be used to produce pulses of light as short as a femtosecond.Among their many applications, lasers are used in optical disk drives, laser printers, and barcode scanners; fiber-optic and free-space optical communication; laser surgery and skin treatments; cutting and welding materials; military and law enforcement devices for marking targets and measuring range and speed; and laser lighting displays in entertainment.