
Why do scientists grow crystals? - Bryn Mawr School Faculty Web
... Substances grown in crystals are extremely pure. These are insulin crystals, grown to purify the insulin used by diabetics ...
... Substances grown in crystals are extremely pure. These are insulin crystals, grown to purify the insulin used by diabetics ...
Electron Diffraction
... end of the electron tube. The potentials G1 and G4 can be used to focus the electron beam but the electrons accumulate most (and for ease of calculation we assume all) of their kinetic energy while crossing G3. The wiring of the setup is depicted in figure 2. The diffraction reflexes are casted onto ...
... end of the electron tube. The potentials G1 and G4 can be used to focus the electron beam but the electrons accumulate most (and for ease of calculation we assume all) of their kinetic energy while crossing G3. The wiring of the setup is depicted in figure 2. The diffraction reflexes are casted onto ...
MLSystems Lab 1 - Fourier v4 - RIT
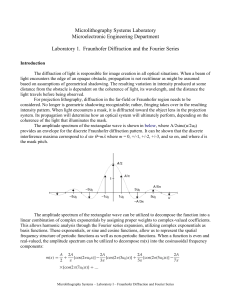
... These discrete coefficients are the diffraction orders of the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern that are produced when a diffraction grating is illuminated by coherent illumination. These coefficients, represented as terms in the harmonic decomposition of m(x) correspond to the discrete orders seen in ...
... These discrete coefficients are the diffraction orders of the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern that are produced when a diffraction grating is illuminated by coherent illumination. These coefficients, represented as terms in the harmonic decomposition of m(x) correspond to the discrete orders seen in ...
Nuclear atom 1 - schoolphysics
... 5. What is approximate size of the nucleus compared with the atom? 6. What three properties of the nucleus can be deduced from the Rutherford scattering experiment. Explain your answer. 7. What is the distance of closest approach of an alpha particle with an energy of 8x10-13 J to a gold nucleus (ch ...
... 5. What is approximate size of the nucleus compared with the atom? 6. What three properties of the nucleus can be deduced from the Rutherford scattering experiment. Explain your answer. 7. What is the distance of closest approach of an alpha particle with an energy of 8x10-13 J to a gold nucleus (ch ...
Interference
... fields add according to the superposition principle. If the two waves are in phase, they add constructively to produce a new wave with greater amplitude. If the two waves are 180° out of phase and have the same amplitude, they add destructively - the combined amplitude is zero. The result of adding ...
... fields add according to the superposition principle. If the two waves are in phase, they add constructively to produce a new wave with greater amplitude. If the two waves are 180° out of phase and have the same amplitude, they add destructively - the combined amplitude is zero. The result of adding ...
nano3-microscopy
... Electron microscopes, diffraction, Transmission electron microscopes, Scanning electron microscopes, ...
... Electron microscopes, diffraction, Transmission electron microscopes, Scanning electron microscopes, ...
Diffraction Basics
... X-ray diffraction can be envisioned as an equivalent process to what happens when you shine light through a grating - Formulism obeys the same laws as “slit experiments” ...
... X-ray diffraction can be envisioned as an equivalent process to what happens when you shine light through a grating - Formulism obeys the same laws as “slit experiments” ...
n 1n d
... • Photopolymerization-induced phase separation of the constituent components in H-PDLCs causes a huge variation of refractive index for light as well as for neutrons. • H-PDLC transmission gratings with the thickness of only few tens of micrometers act as extremely efficient gratings for neutrons. • ...
... • Photopolymerization-induced phase separation of the constituent components in H-PDLCs causes a huge variation of refractive index for light as well as for neutrons. • H-PDLC transmission gratings with the thickness of only few tens of micrometers act as extremely efficient gratings for neutrons. • ...
Example
... of diameter around 2 mm. Diffraction therefore limits the ability to resolve distance objects. Applying Rayleigh’s criterion, two “dots” (as shown) cannot be resolved if (=D/L) is less than R = 1.22 /d, where d is the diameter of the pupil. Note: the index of refraction inside the eye is simila ...
... of diameter around 2 mm. Diffraction therefore limits the ability to resolve distance objects. Applying Rayleigh’s criterion, two “dots” (as shown) cannot be resolved if (=D/L) is less than R = 1.22 /d, where d is the diameter of the pupil. Note: the index of refraction inside the eye is simila ...
2.2.3.- X-ray diffraction
... which took into account the possibility of having more than one reflection inside the material before the beam emerged from it [38]. If one assumes that the incident x-ray beam is perfectly collimated and monochromatic (with a single wavelength λ) and makes an incident angle θ with respect to the re ...
... which took into account the possibility of having more than one reflection inside the material before the beam emerged from it [38]. If one assumes that the incident x-ray beam is perfectly collimated and monochromatic (with a single wavelength λ) and makes an incident angle θ with respect to the re ...
Diffraction grating has periodic structure that splits and diffracts light
... Ordinary pressed CD and DVD media are every-day examples of diffraction gratings and can be used to demonstrate the effect by reflecting sunlight off them onto a white wall. (see ). This is a side effect of their manufacture, as one surface of a CD has many small pits in the plastic, arranged in a s ...
... Ordinary pressed CD and DVD media are every-day examples of diffraction gratings and can be used to demonstrate the effect by reflecting sunlight off them onto a white wall. (see ). This is a side effect of their manufacture, as one surface of a CD has many small pits in the plastic, arranged in a s ...
Chapter 10: Simple Harmonic Motion
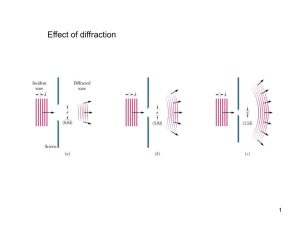
... expect that a plane wave (light beam) would produce a bright spot the same size as the open However, what we actually see is a series of light and dark fringes similar the double-slit interference ...
... expect that a plane wave (light beam) would produce a bright spot the same size as the open However, what we actually see is a series of light and dark fringes similar the double-slit interference ...
Nanoscopy with focused light
... Throughout the 20th century it was widely accepted that a light microscope relying on conventional optical lenses cannot discern details that are much finer than about half the wavelength of light (200-400 nm), due to diffraction. However, in the 1990s, the viability to overcome the diffraction barr ...
... Throughout the 20th century it was widely accepted that a light microscope relying on conventional optical lenses cannot discern details that are much finer than about half the wavelength of light (200-400 nm), due to diffraction. However, in the 1990s, the viability to overcome the diffraction barr ...
Scalar Diffraction Theory and Basic Fourier Optics [Hecht 10.2.410.2.6, 10.2.8, 11.211.3 or Fowles Ch. 5]
... This is a standard integral. Its value is π J1 ( ρ ) / ρ where J1 is the Bessel function of the first kind, order one. The ratio J1 ( ρ ) / ρ → 12 as ρ → 0 . The irradiance/intensity distribution is therefore given by ...
... This is a standard integral. Its value is π J1 ( ρ ) / ρ where J1 is the Bessel function of the first kind, order one. The ratio J1 ( ρ ) / ρ → 12 as ρ → 0 . The irradiance/intensity distribution is therefore given by ...
$doc.title
... ⎣ ρ ⎦ The diffraction pattern is circularly symmetric and consists of a bright central disk surrounded by concentric circular bands of rapidly diminishing intensity. The bright central area is know as the Airy disk. It extends to the first dark ring whose size is given by the first zero of the Besse ...
... ⎣ ρ ⎦ The diffraction pattern is circularly symmetric and consists of a bright central disk surrounded by concentric circular bands of rapidly diminishing intensity. The bright central area is know as the Airy disk. It extends to the first dark ring whose size is given by the first zero of the Besse ...
Powder diffraction

Powder diffraction is a scientific technique using X-ray, neutron, or electron diffraction on powder or microcrystalline samples for structural characterization of materials.









![Scalar Diffraction Theory and Basic Fourier Optics [Hecht 10.2.410.2.6, 10.2.8, 11.211.3 or Fowles Ch. 5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008906603_1-55857b6efe7c28604e1ff5a68faa71b2-300x300.png)
