Dispatch Vision: How to Train Visual Cortex to Predict Reward Time
... only early visual representations but also rapid object recognition, a key function of the primate visual system [6]. In recent years, the feedforward view of visual processing has undergone significant revision, with increasing appreciation for the role of feedback from higher cortical centers, as ...
... only early visual representations but also rapid object recognition, a key function of the primate visual system [6]. In recent years, the feedforward view of visual processing has undergone significant revision, with increasing appreciation for the role of feedback from higher cortical centers, as ...
The Problem of Consciousness by Francis Crick and
... as something immaterial, separate from the brain but interacting with it in some way. A few neuroscientists, such as the late Sir John Eccles, have asserted that the soul is distinct from the body. But most neuroscientists now believe that all aspects of mind, including its most puzzling attribute— ...
... as something immaterial, separate from the brain but interacting with it in some way. A few neuroscientists, such as the late Sir John Eccles, have asserted that the soul is distinct from the body. But most neuroscientists now believe that all aspects of mind, including its most puzzling attribute— ...
phys chapter 51 [3-20
... Concerned with recognizing letters, reading, determining texture of surfaces, determining detailed color of objects, and deciphering what object is and what it means Neuronal Patterns of Stimulation During Analysis of Visual Image Areas of max excitation occur along sharp borders of visual pattern ...
... Concerned with recognizing letters, reading, determining texture of surfaces, determining detailed color of objects, and deciphering what object is and what it means Neuronal Patterns of Stimulation During Analysis of Visual Image Areas of max excitation occur along sharp borders of visual pattern ...
PDF
... of neuronal systems. For example, the inferior temporal cortex processes sensory information about shape and color, but is equally involved in storage of the same types of stimulus features [64]. Although psychology has traditionally divided the mind into separate functions, such as perception, memo ...
... of neuronal systems. For example, the inferior temporal cortex processes sensory information about shape and color, but is equally involved in storage of the same types of stimulus features [64]. Although psychology has traditionally divided the mind into separate functions, such as perception, memo ...
Interactions between Motivation, Emotion and Attention: From
... (Huang and Weng, 2002; Canamero, 2003), it is seldom discussed in relation to stimulus selection. However, a robot with multiple goals and motives must be able to learn what objects are useful for each of its activities. This is even more important for a developing system where object representation ...
... (Huang and Weng, 2002; Canamero, 2003), it is seldom discussed in relation to stimulus selection. However, a robot with multiple goals and motives must be able to learn what objects are useful for each of its activities. This is even more important for a developing system where object representation ...
Visual behaviour mediated by retinal projections directed to the
... adding them last to this minimal adequate model. When there was signi®cant overdispersion using Poisson errors, we re-scaled the model using Pearson's x2/d.f. (where d.f. is degrees of freedom)22. Means 6 standard errors are reported. We assumed that foraging effort was proportional to percentage ti ...
... adding them last to this minimal adequate model. When there was signi®cant overdispersion using Poisson errors, we re-scaled the model using Pearson's x2/d.f. (where d.f. is degrees of freedom)22. Means 6 standard errors are reported. We assumed that foraging effort was proportional to percentage ti ...
Interactions between Motivation, Emotion and Attention: From
... (Huang and Weng, 2002; Canamero, 2003), it is seldom discussed in relation to stimulus selection. However, a robot with multiple goals and motives must be able to learn what objects are useful for each of its activities. This is even more important for a developing system where object representation ...
... (Huang and Weng, 2002; Canamero, 2003), it is seldom discussed in relation to stimulus selection. However, a robot with multiple goals and motives must be able to learn what objects are useful for each of its activities. This is even more important for a developing system where object representation ...
Serre-Poggio_ACM_R2_finalSubmission
... local afferent units with selectivities for different imagefeatures (for instance edges at different orientations). Complex units on the other hand increase the tolerance of the representation with respect to 2D transformations by pooling over afferent units with similar selectivity but slightly dif ...
... local afferent units with selectivities for different imagefeatures (for instance edges at different orientations). Complex units on the other hand increase the tolerance of the representation with respect to 2D transformations by pooling over afferent units with similar selectivity but slightly dif ...
Relative timing: from behaviour to neurons
... SOA is positive when stimulus A is presented first and negative when stimulus B is presented first. The single-headed arrow (green) corresponds to the point of subjective simultaneity (PSS), the SOA that corresponds to 50% on the ordinate. The double-headed arrow (blue) indicates the just notable di ...
... SOA is positive when stimulus A is presented first and negative when stimulus B is presented first. The single-headed arrow (green) corresponds to the point of subjective simultaneity (PSS), the SOA that corresponds to 50% on the ordinate. The double-headed arrow (blue) indicates the just notable di ...
View PDF
... distribution of voxel activations for a single participant, for each stimulus, is shown in Fig. 3. Highest activations were observed when HCC came into sight (average: 1190) followed by RTC (average: 1050), HCF (average: 796) and RTX (average: 475), in order as shown in box plot. The results also s ...
... distribution of voxel activations for a single participant, for each stimulus, is shown in Fig. 3. Highest activations were observed when HCC came into sight (average: 1190) followed by RTC (average: 1050), HCF (average: 796) and RTX (average: 475), in order as shown in box plot. The results also s ...
`What` and `where` in the human brain
... for the expansion/contraction of the image of any object moving in depth 125,261, and whereas such motion selectivity has also been reported for parietal neurons, these neurons demonstrate even more complex spatial properties 127,281. Thus, much of the neural mechanism for both object vision and spa ...
... for the expansion/contraction of the image of any object moving in depth 125,261, and whereas such motion selectivity has also been reported for parietal neurons, these neurons demonstrate even more complex spatial properties 127,281. Thus, much of the neural mechanism for both object vision and spa ...
Partial Position Transfer in Categorical Perceptual Learning Alexander Gerganov ()
... Inferotemporal cortex or later. If there is no transfer at all, probably the learning occurred at a neural level comprising neurons with smaller receptive fields than the distance between the training and transfer locations (see figure 3), implicating an earlier site of plasticity. There are many st ...
... Inferotemporal cortex or later. If there is no transfer at all, probably the learning occurred at a neural level comprising neurons with smaller receptive fields than the distance between the training and transfer locations (see figure 3), implicating an earlier site of plasticity. There are many st ...
Gaze direction controls response gain in primary visual
... animals, were performed according to the Public Health Service policy on the use of laboratory animals. Two monkeys (Macaca mulatta) were placed in complete darkness, with their head ®xed, and trained to ®xate on a small bright target (12 min of arc) on a video screen. Eye position was monitored usi ...
... animals, were performed according to the Public Health Service policy on the use of laboratory animals. Two monkeys (Macaca mulatta) were placed in complete darkness, with their head ®xed, and trained to ®xate on a small bright target (12 min of arc) on a video screen. Eye position was monitored usi ...
Making Sense of Internal Logic: Theory and a Case Study
... In order to formulate an e ective interface, we have searched a suÆciently simple yet meaningful cognitive experiment. As one candidate for such an experiment, we considered the type recently carried out by Sakagami and Niki [4] and Sakagami and Tsutsui [5]. They performed a set of experiments inves ...
... In order to formulate an e ective interface, we have searched a suÆciently simple yet meaningful cognitive experiment. As one candidate for such an experiment, we considered the type recently carried out by Sakagami and Niki [4] and Sakagami and Tsutsui [5]. They performed a set of experiments inves ...
Mechanisms of Visual Attention in the Human Cortex
... paired stimuli was reduced compared with that elicited by the single good stimulus. This result indicates that two stimuli present at the same time within a neuron’s RF are not processed independently, but rather that they interact with each other in a mutually suppressive way. This sensory suppress ...
... paired stimuli was reduced compared with that elicited by the single good stimulus. This result indicates that two stimuli present at the same time within a neuron’s RF are not processed independently, but rather that they interact with each other in a mutually suppressive way. This sensory suppress ...
On the importance of the transient visual response in the superior
... required to stimulate immediate action, either towards stimuli of interest (e.g. prey) or away from perilous stimuli (e.g. large looming things). The SC mediates these two fast responses through access to different motor output channels [4,5]. Unlike other parts of the visual orienting network (see ...
... required to stimulate immediate action, either towards stimuli of interest (e.g. prey) or away from perilous stimuli (e.g. large looming things). The SC mediates these two fast responses through access to different motor output channels [4,5]. Unlike other parts of the visual orienting network (see ...
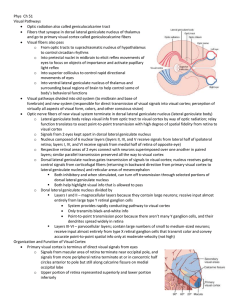
Optometric Management Of A Patient With Parietal Lobe Injury
... processing, tactile recognition, proprioception, kinesthesia, and visual guidance to motor actions.16,17 However, the evident redundancy of function in the brain may relate to the varied responses to the severity of the symptom manifestation. Inferior Parietal Lobule The inferior parietal lobule is ...
... processing, tactile recognition, proprioception, kinesthesia, and visual guidance to motor actions.16,17 However, the evident redundancy of function in the brain may relate to the varied responses to the severity of the symptom manifestation. Inferior Parietal Lobule The inferior parietal lobule is ...
Representation of naturalistic image structure in the primate visual
... some randomization in their location, size, color, orientation, etc; for example, an image of leaves, or pebbles, or tree bark (Fig. 1a). Lettvin (1976), offered this insight: “Let us say that to the extent that visible objects are different and far apart, they are forms. To the extent that they are ...
... some randomization in their location, size, color, orientation, etc; for example, an image of leaves, or pebbles, or tree bark (Fig. 1a). Lettvin (1976), offered this insight: “Let us say that to the extent that visible objects are different and far apart, they are forms. To the extent that they are ...
Chapter 21: Attention - Biology Courses Server
... • More mental energy to one location – Enhanced sensitivity & reaction time ...
... • More mental energy to one location – Enhanced sensitivity & reaction time ...
Human Lateral Geniculate Nucleus and Visual Cortex Respond to
... During a second procedure, subjects looked at static grayscale faces of men and women depicting five emotional expressions.8 The digitized size-, brightness-, and contrastadjusted images were presented on the computer screen with a visual angle of 4 ⫻ 5 degrees. They were presented during 400 millis ...
... During a second procedure, subjects looked at static grayscale faces of men and women depicting five emotional expressions.8 The digitized size-, brightness-, and contrastadjusted images were presented on the computer screen with a visual angle of 4 ⫻ 5 degrees. They were presented during 400 millis ...
Vigabatrin: The Problem of Monitoring for Peripheral Vision Loss in
... Vigabatrin has been used around the world to treat epilepsy since the early 1990’s and has recently been approved for use in the United States. Vigabatrin is approved for the management of refractory, complex partial seizures in adults who have failed a number of other anti-epileptic drugs. However ...
... Vigabatrin has been used around the world to treat epilepsy since the early 1990’s and has recently been approved for use in the United States. Vigabatrin is approved for the management of refractory, complex partial seizures in adults who have failed a number of other anti-epileptic drugs. However ...
CATEGORIES IN THE PIGEON BRAIN - Ruhr-Universität
... peri-peck time histograms for peaks of spiking activity near time point 0. Materials, recording, and spike sorting procedure have been described in greater detail by Starosta et al. (2013, 2014). Data Analysis To analyze our data, we used custom-written Matlab code. For each pigeon, we constructed a ...
... peri-peck time histograms for peaks of spiking activity near time point 0. Materials, recording, and spike sorting procedure have been described in greater detail by Starosta et al. (2013, 2014). Data Analysis To analyze our data, we used custom-written Matlab code. For each pigeon, we constructed a ...
mechanisms of visual attention in the human cortex
... paired stimuli was reduced compared with that elicited by the single good stimulus. This result indicates that two stimuli present at the same time within a neuron’s RF are not processed independently, but rather that they interact with each other in a mutually suppressive way. This sensory suppress ...
... paired stimuli was reduced compared with that elicited by the single good stimulus. This result indicates that two stimuli present at the same time within a neuron’s RF are not processed independently, but rather that they interact with each other in a mutually suppressive way. This sensory suppress ...
test prep
... 46. Which of the following is true? A) The absolute threshold for any stimulus is a constant. B) The absolute threshold for any stimulus varies somewhat. C) The absolute threshold is defined as the minimum amount of stimulation necessary for a stimulus to be detected 75 percent of the time. D) The a ...
... 46. Which of the following is true? A) The absolute threshold for any stimulus is a constant. B) The absolute threshold for any stimulus varies somewhat. C) The absolute threshold is defined as the minimum amount of stimulation necessary for a stimulus to be detected 75 percent of the time. D) The a ...
The Physiology of the Senses Lecture 5
... The “dominant” side (usually the left) excels in sequential or serial tasks such as language (reading, writing, speaking, signing) and mathematics (algebra A=B, B=C, therefore A=C). The “non-dominant” side (usually the right) excels in tasks requiring parallel processing such as face recognition and ...
... The “dominant” side (usually the left) excels in sequential or serial tasks such as language (reading, writing, speaking, signing) and mathematics (algebra A=B, B=C, therefore A=C). The “non-dominant” side (usually the right) excels in tasks requiring parallel processing such as face recognition and ...
Visual N1
The visual N1 is a visual evoked potential, a type of event-related electrical potential (ERP), that is produced in the brain and recorded on the scalp. The N1 is so named to reflect the polarity and typical timing of the component. The ""N"" indicates that the polarity of the component is negative with respect to an average mastoid reference. The ""1"" originally indicated that it was the first negative-going component, but it now better indexes the typical peak of this component, which is around 150 to 200 milliseconds post-stimulus. The N1 deflection may be detected at most recording sites, including the occipital, parietal, central, and frontal electrode sites. Although, the visual N1 is widely distributed over the entire scalp, it peaks earlier over frontal than posterior regions of the scalp, suggestive of distinct neural and/or cognitive correlates. The N1 is elicited by visual stimuli, and is part of the visual evoked potential – a series of voltage deflections observed in response to visual onsets, offsets, and changes. Both the right and left hemispheres generate an N1, but the laterality of the N1 depends on whether a stimulus is presented centrally, laterally, or bilaterally. When a stimulus is presented centrally, the N1 is bilateral. When presented laterally, the N1 is larger, earlier, and contralateral to the visual field of the stimulus. When two visual stimuli are presented, one in each visual field, the N1 is bilateral. In the latter case, the N1’s asymmetrical skewedness is modulated by attention. Additionally, its amplitude is influenced by selective attention, and thus it has been used to study a variety of attentional processes.