Chapter Three: Phylum Cnidaria
... The Cnidarians are a group of fairly simple animals who all have one thing in common, they have stinging cells. They are all aquatic and can be found mainly in salt water although there are a few freshwater species. They include the jellyfishes, anemones, corals and hydras. What do Cnidarians look l ...
... The Cnidarians are a group of fairly simple animals who all have one thing in common, they have stinging cells. They are all aquatic and can be found mainly in salt water although there are a few freshwater species. They include the jellyfishes, anemones, corals and hydras. What do Cnidarians look l ...
Katie Perryman
... in the genus Chateophractus (Redford and Eisenberg 1992). Like other armadillos it is covered in armor. The armor develops from skin and is made up of hard bony plates called scutes (MacDonald 2001). The carapace (armor) protects the shoulders, back, sides, and rump (Nowak 1999). The central portion ...
... in the genus Chateophractus (Redford and Eisenberg 1992). Like other armadillos it is covered in armor. The armor develops from skin and is made up of hard bony plates called scutes (MacDonald 2001). The carapace (armor) protects the shoulders, back, sides, and rump (Nowak 1999). The central portion ...
EPS/OEB 56 – Geobiology and the History of Life Lab 8: Paleozoic
... Goal: The goal of this section of the lab is to grapple with the problems of interpreting Ediacaran macrofossils. What features, if any, support their interpretation as animals? If animals, where do they fall on the metazoan tree? Introduction: The so-called Ediacaran biota records some of the first ...
... Goal: The goal of this section of the lab is to grapple with the problems of interpreting Ediacaran macrofossils. What features, if any, support their interpretation as animals? If animals, where do they fall on the metazoan tree? Introduction: The so-called Ediacaran biota records some of the first ...
Today:
... Most sponges are hermaphrodites; eggs are retained in the mesophyl while sperm are released into the ...
... Most sponges are hermaphrodites; eggs are retained in the mesophyl while sperm are released into the ...
Jellyfish Dream - Tennessee Aquarium
... mesoglea - The jellylike material that is in the middle of the three layers of the jellyfish body. It is thin in polyps and thick in medusa. tentacle - Long feelers surrounding the mouth of the polyp, which capture food and draw it back to the mouth. nematocyst -The minute stinging structures on the ...
... mesoglea - The jellylike material that is in the middle of the three layers of the jellyfish body. It is thin in polyps and thick in medusa. tentacle - Long feelers surrounding the mouth of the polyp, which capture food and draw it back to the mouth. nematocyst -The minute stinging structures on the ...
from mesoderm - HCC Learning Web
... • Many animals have at least one larval stage • A larva is sexually immature and morphologically distinct from the adult; it eventually undergoes metamorphosis • A juvenile resembles an adult, but is not yet sexually mature ...
... • Many animals have at least one larval stage • A larva is sexually immature and morphologically distinct from the adult; it eventually undergoes metamorphosis • A juvenile resembles an adult, but is not yet sexually mature ...
CHAPTER 4 copy - WordPress.com
... of prey. Level of organization – tissue level of organisation and diploblastic. Body Cavity – Absent, central gastro-vascular cavity present with a single opening, hypostome. Digestion – both extracellular and intracellular. Skeleton – Some of the cnidarians – corals have a skeleton composed of calc ...
... of prey. Level of organization – tissue level of organisation and diploblastic. Body Cavity – Absent, central gastro-vascular cavity present with a single opening, hypostome. Digestion – both extracellular and intracellular. Skeleton – Some of the cnidarians – corals have a skeleton composed of calc ...
Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Question Bank
... a) gills b) book gills c) book lungs d) tracheal system 38. Sensory structures found in arthropods are a) Anternnae b) Eye (simple & compound) c) statocysts 39. 1) Honey bee or apis 2) Bombyx or silkworm 40. Vectors are those animals which carries diseases causing germs in them example : mosquito (a ...
... a) gills b) book gills c) book lungs d) tracheal system 38. Sensory structures found in arthropods are a) Anternnae b) Eye (simple & compound) c) statocysts 39. 1) Honey bee or apis 2) Bombyx or silkworm 40. Vectors are those animals which carries diseases causing germs in them example : mosquito (a ...
Correlates between morphology, diet and foraging mode in the
... ern Iberian Peninsula. The goal is to seek for correlates between morphology, diet and foraging mode in this snake. At first we analysed certain morphological traits of the species, such as teeth number and tail breakage. Teeth features in snakes are closely related to diet (Cundall, 1987) and we tr ...
... ern Iberian Peninsula. The goal is to seek for correlates between morphology, diet and foraging mode in this snake. At first we analysed certain morphological traits of the species, such as teeth number and tail breakage. Teeth features in snakes are closely related to diet (Cundall, 1987) and we tr ...
Chapter 25: What is an animal?
... is stored as fat or glycogen, a polysaccharide, and used when other food is not available. Examine the digestive tracts of a flatworm and an earthworm in Figure 25.3. Notice that there is only one opening to the flatworm’s digestive tract, a pharynx. An earthworm has a digestive tract with two openi ...
... is stored as fat or glycogen, a polysaccharide, and used when other food is not available. Examine the digestive tracts of a flatworm and an earthworm in Figure 25.3. Notice that there is only one opening to the flatworm’s digestive tract, a pharynx. An earthworm has a digestive tract with two openi ...
Predation in suspended and forest floor soils
... Europe, and many of our inferences about their trophic functions come from their better known plantinhabiting relatives. Unlike soil systems, where several to many families of predatory Mesostigmata commonly coexist, vegetation is dominated by members of a single family, the Phytoseiidae. Most phyto ...
... Europe, and many of our inferences about their trophic functions come from their better known plantinhabiting relatives. Unlike soil systems, where several to many families of predatory Mesostigmata commonly coexist, vegetation is dominated by members of a single family, the Phytoseiidae. Most phyto ...
Chapter 13 - Angelo State University
... Pelagic cnidarians in which the medusa is the dominant and conspicuous form. Often seen in coastal waters and usually feared by local swimmers. Only about 200 species, but very abundant, so play important ecological role. Found everywhere in oceans, extending to depths of 3000 m or more. ...
... Pelagic cnidarians in which the medusa is the dominant and conspicuous form. Often seen in coastal waters and usually feared by local swimmers. Only about 200 species, but very abundant, so play important ecological role. Found everywhere in oceans, extending to depths of 3000 m or more. ...
EASTErN INdIgO SNAkE
... snakes are a glossy, bluish-black color, which is where the “indigo” portion of its name originates. The chin, throat and sides of the face may be lighter in color, sometimes even reddish. Indigo snakes are harmless and generally calm. However, if threatened, indigo snakes may flatten their necks, ...
... snakes are a glossy, bluish-black color, which is where the “indigo” portion of its name originates. The chin, throat and sides of the face may be lighter in color, sometimes even reddish. Indigo snakes are harmless and generally calm. However, if threatened, indigo snakes may flatten their necks, ...
amphibians
... WHY DO MOST AMPHIBIANS LIVE NEAR WATER? The moist skin of most amphibians is not waterproof, so they live in damp places to keep from drying out. Many amphibians lay their soft, jelly-covered eggs in water, which is known as spawning. Their young, called TADPOLES, grow up in the water and come onto ...
... WHY DO MOST AMPHIBIANS LIVE NEAR WATER? The moist skin of most amphibians is not waterproof, so they live in damp places to keep from drying out. Many amphibians lay their soft, jelly-covered eggs in water, which is known as spawning. Their young, called TADPOLES, grow up in the water and come onto ...
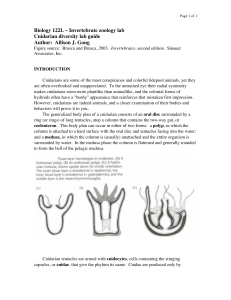
Biology 122L – Invertebrate zoology lab Cnidarian diversity lab
... stages of the moon jelly, Aurelia sp. The scyphistoma of Aurelia is a small funnelshaped polyp, usually 3-10 mm long, attached at its basal end by a few stolons. Unlike hydroid polyps, scyphistomae do not have a protective coating of periderm and can "walk" around a bit by selectively detaching and ...
... stages of the moon jelly, Aurelia sp. The scyphistoma of Aurelia is a small funnelshaped polyp, usually 3-10 mm long, attached at its basal end by a few stolons. Unlike hydroid polyps, scyphistomae do not have a protective coating of periderm and can "walk" around a bit by selectively detaching and ...
animal kingdom
... When you look around, you will observe different animals with different structures and forms. As over a million species of animals have been described till now, the need for classification becomes all the more important. The classification also helps in assigning a systematic position to newly descr ...
... When you look around, you will observe different animals with different structures and forms. As over a million species of animals have been described till now, the need for classification becomes all the more important. The classification also helps in assigning a systematic position to newly descr ...
Bio. Unit 10 Invertebrates Test
... a. specialization b. ganglia formation c. nerve net formation d. eye formation _____ 25. The invertebrate, listed below, that does not exhibit cephalization. a. planaria b. Giant squid c. monarch butterfly d. glass sponge _____ 26. Invertebrates have one of three main kinds of skeletons, exoskeleton ...
... a. specialization b. ganglia formation c. nerve net formation d. eye formation _____ 25. The invertebrate, listed below, that does not exhibit cephalization. a. planaria b. Giant squid c. monarch butterfly d. glass sponge _____ 26. Invertebrates have one of three main kinds of skeletons, exoskeleton ...
Reptiles - walker2011
... Most lizards have four limbs Snakes have no limbs and lack the bones to support limbs ...
... Most lizards have four limbs Snakes have no limbs and lack the bones to support limbs ...
Document
... b. segmentation c. pseudocoelom d. closed circulatory system e. all of the above are characteristics of Annelida 2. Which phylum is characterized by animals that have a segmented body? a. Cnidaria b. Platyhelminthes c. Porifera d. Arthropoda e. Mollusca 3. Which of the following characteristics is r ...
... b. segmentation c. pseudocoelom d. closed circulatory system e. all of the above are characteristics of Annelida 2. Which phylum is characterized by animals that have a segmented body? a. Cnidaria b. Platyhelminthes c. Porifera d. Arthropoda e. Mollusca 3. Which of the following characteristics is r ...
Butterfly Gardening - Manitoba Nature Summit
... Discuss the four stages of a butterfly’s lifecycle. Use student suggestions to give every stage a phrase and an action. For example, the caterpillar could be shown by pretending to eat. All students are given the role of an egg to start the game and must repeat the egg phrase and action until they f ...
... Discuss the four stages of a butterfly’s lifecycle. Use student suggestions to give every stage a phrase and an action. For example, the caterpillar could be shown by pretending to eat. All students are given the role of an egg to start the game and must repeat the egg phrase and action until they f ...
BIOL 2015 – Evolution and Diversity
... They have evolved a pump-like mechanism to move nutrients suspended in water past the individual cells that make up their body. As nutrients pass these cells they are taken up via endocytosis and digested within the each cell. Most animals move about in search of food and have a gut within which ...
... They have evolved a pump-like mechanism to move nutrients suspended in water past the individual cells that make up their body. As nutrients pass these cells they are taken up via endocytosis and digested within the each cell. Most animals move about in search of food and have a gut within which ...