Phoronida - Paleopolis
... Phoronids secrete characteristic rigid tubes consisting of layers of chitin to which adhere particles of sediment and debris from the animal’s immediate environment. Phoronids occur singly, vertically embedded in soft sediment (sand, mud, or fine gravel) or form tangled masses of many individuals bu ...
... Phoronids secrete characteristic rigid tubes consisting of layers of chitin to which adhere particles of sediment and debris from the animal’s immediate environment. Phoronids occur singly, vertically embedded in soft sediment (sand, mud, or fine gravel) or form tangled masses of many individuals bu ...
Introduction to Invertebrates
... swimmers and surfers who accidentally brush up against them in the water. ...
... swimmers and surfers who accidentally brush up against them in the water. ...
Intro to Invertebrates
... The ocean is home to many different types of organisms, including phytoplankton, zooplankton, fish. Phytoplankton, tiny photosynthetic organisms that float in the water, make their own food from the energy of the sun. Small water animals, known as zooplankton, and larger animals, such as fish, use p ...
... The ocean is home to many different types of organisms, including phytoplankton, zooplankton, fish. Phytoplankton, tiny photosynthetic organisms that float in the water, make their own food from the energy of the sun. Small water animals, known as zooplankton, and larger animals, such as fish, use p ...
Phylum Cnidaria – Cnidarians - Marine Benthic Fauna of Chilean
... The exclusively aquatic phylum Cnidaria is a very diverse group with more than 11,000 species worldwide. Morphologically simple, with relatively few cell types, cnidarians have reached a remarkable diversity through modifications mainly in colonial organization and life histories. They can be found ...
... The exclusively aquatic phylum Cnidaria is a very diverse group with more than 11,000 species worldwide. Morphologically simple, with relatively few cell types, cnidarians have reached a remarkable diversity through modifications mainly in colonial organization and life histories. They can be found ...
Animal classification
... When you look around, you will observe different animals with different structures and forms. As over a million species of animals have been described till now, the need for classification becomes all the more important. The classification also helps in assigning a systematic position to newly descr ...
... When you look around, you will observe different animals with different structures and forms. As over a million species of animals have been described till now, the need for classification becomes all the more important. The classification also helps in assigning a systematic position to newly descr ...
5 7.2 A typical cell of any organ- ism contains genetic instructions
... Movement All animals move in some way at some point in their lives. Most animals move freely from place to place throughout their lives-for example, by swimming, walking, or hopping. Other animals, such as oysters and barnacles, move from place to place only during the earliest stage of their lives. ...
... Movement All animals move in some way at some point in their lives. Most animals move freely from place to place throughout their lives-for example, by swimming, walking, or hopping. Other animals, such as oysters and barnacles, move from place to place only during the earliest stage of their lives. ...
unit 1: introduction to biology
... deliver oxygen directly to cells. (e.g., insects) 5. Metamorphosis metamorphosis is drastic change in form and physiology of an arthropod animal, that occurs as an immature stage becomes an adult the immature, larval stage eats food and lives in environments different from the adult this reduc ...
... deliver oxygen directly to cells. (e.g., insects) 5. Metamorphosis metamorphosis is drastic change in form and physiology of an arthropod animal, that occurs as an immature stage becomes an adult the immature, larval stage eats food and lives in environments different from the adult this reduc ...
Practice 3 exam with answers
... e) have a solid body without a cavity 40. _________ is a process that rearranges the developing embryo to form germ layers. *a) Gastrulation b) Cleavage c) Mitosis d) Blastulation e) Blastopore 41. __________ is an important developmental process, when a single-cell zygote undergoes mitotic cell div ...
... e) have a solid body without a cavity 40. _________ is a process that rearranges the developing embryo to form germ layers. *a) Gastrulation b) Cleavage c) Mitosis d) Blastulation e) Blastopore 41. __________ is an important developmental process, when a single-cell zygote undergoes mitotic cell div ...
Development - Iowa State University
... 59. In animals, bilateral symmetry is correlated with _____. a) an ability to attach to a host organism b) the presence of a skeleton c) adaptation to terrestrial environments d) cephalization e) an ability to swim 60. In a parasitic life cycle, sexual reproduction occurs ___ . a) in the intermediat ...
... 59. In animals, bilateral symmetry is correlated with _____. a) an ability to attach to a host organism b) the presence of a skeleton c) adaptation to terrestrial environments d) cephalization e) an ability to swim 60. In a parasitic life cycle, sexual reproduction occurs ___ . a) in the intermediat ...
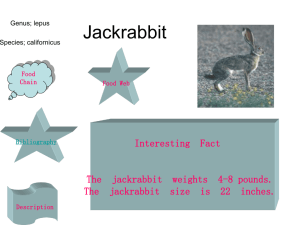
Jackrabbit - Gulf Coast Consortia
... Description The jackrabbit length is about 22 inches. It weighs about 4 – 8 pounds. The jackrabbit predators are hawks and snakes. It eats plants, grasses and leaves. Jackrabbit have 4 legs . Its color is black , brown white and gray. Jackrabbit have only 2 teeth. ...
... Description The jackrabbit length is about 22 inches. It weighs about 4 – 8 pounds. The jackrabbit predators are hawks and snakes. It eats plants, grasses and leaves. Jackrabbit have 4 legs . Its color is black , brown white and gray. Jackrabbit have only 2 teeth. ...
flatworm
... This type of system is called integumentary exchange. However, flatworms do have a bilateral nervous system; they are the simplest animals to have one. Two cordlike nerves branch repeatedly in an array resembling a ladder. The head end of some species even has a collection of ganglia acting as a rud ...
... This type of system is called integumentary exchange. However, flatworms do have a bilateral nervous system; they are the simplest animals to have one. Two cordlike nerves branch repeatedly in an array resembling a ladder. The head end of some species even has a collection of ganglia acting as a rud ...
Teachers Fact Sheet No 5 Cave Biology
... move freely in and out of the cave. They are cave visitors that seek out such a habitat from choice, and never complete their entire life cycle in the cave. The largest is the Tasmanian cave spider, which may have a leg span of up to 14cm and a web up to 1m across. It also occurs in other dark, damp ...
... move freely in and out of the cave. They are cave visitors that seek out such a habitat from choice, and never complete their entire life cycle in the cave. The largest is the Tasmanian cave spider, which may have a leg span of up to 14cm and a web up to 1m across. It also occurs in other dark, damp ...
Chapter 32
... • Many animals have at least one larval stage • A larva is sexually immature and morphologically distinct from the adult; it eventually undergoes metamorphosis • A juvenile resembles an adult, but is not yet sexually mature ...
... • Many animals have at least one larval stage • A larva is sexually immature and morphologically distinct from the adult; it eventually undergoes metamorphosis • A juvenile resembles an adult, but is not yet sexually mature ...
Animal Diversity
... • Many animals have at least one larval stage • A larva is sexually immature and morphologically distinct from the adult; it eventually undergoes metamorphosis • A juvenile resembles an adult, but is not yet sexually mature ...
... • Many animals have at least one larval stage • A larva is sexually immature and morphologically distinct from the adult; it eventually undergoes metamorphosis • A juvenile resembles an adult, but is not yet sexually mature ...
Overview of Invertebrates
... Ancestors of modern roundworms were the first animals to evolve a complete digestive system. With a separate mouth and anus, food could move through the body in just one direction. This made digestion more efficient. An animal could keep eating while digesting food and getting rid of waste. Differen ...
... Ancestors of modern roundworms were the first animals to evolve a complete digestive system. With a separate mouth and anus, food could move through the body in just one direction. This made digestion more efficient. An animal could keep eating while digesting food and getting rid of waste. Differen ...
Chapter 26: Sponges, Cnidarians, and Unsegmented Worms
... These food fragments are taken up by _________________________________________ in the gastroderm that digests them further The nutrients are then transported throughout the body by _________________________ Any materials that cannot be digested are passed back out through the _________________ ...
... These food fragments are taken up by _________________________________________ in the gastroderm that digests them further The nutrients are then transported throughout the body by _________________________ Any materials that cannot be digested are passed back out through the _________________ ...
Animals with Bilateral Symmetry
... polyps in various stages of tentacle extension. At the lower right, areas where the coral has died expose the calcium carbonate skeleton that supports the polyps and forms the reef. A strikingly patterned crab (an arthropod) sits atop the coral, holding tiny white anemones in its claws. Their stingi ...
... polyps in various stages of tentacle extension. At the lower right, areas where the coral has died expose the calcium carbonate skeleton that supports the polyps and forms the reef. A strikingly patterned crab (an arthropod) sits atop the coral, holding tiny white anemones in its claws. Their stingi ...
In the Wild - The Maryland Zoo in Baltimore
... o Grab prey with their teeth and wrap coils of their body around the prey and squeeze – do not crush the prey and break bones but rather squeeze tightly so that the prey cannot breathe and suffocates o Can unhinge their jaw to swallow the prey whole utilizing rhythmic muscular contractions that pull ...
... o Grab prey with their teeth and wrap coils of their body around the prey and squeeze – do not crush the prey and break bones but rather squeeze tightly so that the prey cannot breathe and suffocates o Can unhinge their jaw to swallow the prey whole utilizing rhythmic muscular contractions that pull ...
Overview of Invertebrates
... Ancestors of modern roundworms were the first animals to evolve a complete digestive system. With a separate mouth and anus, food could move through the body in just one direction. This made digestion more efficient. An animal could keep eating while digesting food and getting rid of waste. Differen ...
... Ancestors of modern roundworms were the first animals to evolve a complete digestive system. With a separate mouth and anus, food could move through the body in just one direction. This made digestion more efficient. An animal could keep eating while digesting food and getting rid of waste. Differen ...
- Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute
... When the female is ready to deposit the eggs in protected areas under rocks or in discarded shells, the female uses the arms to wipe the stored spermatophores onto each egg. Cuttlefish eggs are individually enclosed in a tough protective external coating, often pigmented black from the ink-sac secre ...
... When the female is ready to deposit the eggs in protected areas under rocks or in discarded shells, the female uses the arms to wipe the stored spermatophores onto each egg. Cuttlefish eggs are individually enclosed in a tough protective external coating, often pigmented black from the ink-sac secre ...
Ch 17 (30 MCQ questions)
... 25) Which of the following do we know to be true about prototype and exemplarbased models of social categorization? (Please highlight all true answers.) a) In a prototype model, the more features an instance shares with other category members, the more quickly it is identified as a member. b) At any ...
... 25) Which of the following do we know to be true about prototype and exemplarbased models of social categorization? (Please highlight all true answers.) a) In a prototype model, the more features an instance shares with other category members, the more quickly it is identified as a member. b) At any ...
Goniopsis cruentata (Mangrove Root Crab)
... to the recycling of nutrients. They are detritivores, their diet consists of dead mangrove leaves and crustacean corpses, including those of their own species. G. cruentata have one of the most important functions in the mangrove; they utilizes particulate organic matter from microbial biodegradatio ...
... to the recycling of nutrients. They are detritivores, their diet consists of dead mangrove leaves and crustacean corpses, including those of their own species. G. cruentata have one of the most important functions in the mangrove; they utilizes particulate organic matter from microbial biodegradatio ...
ch 32 animal diversity
... • Many animals have at least one larval stage • A larva is sexually immature and morphologically distinct from the adult; it eventually undergoes metamorphosis • A juvenile resembles an adult, but is not yet sexually mature ...
... • Many animals have at least one larval stage • A larva is sexually immature and morphologically distinct from the adult; it eventually undergoes metamorphosis • A juvenile resembles an adult, but is not yet sexually mature ...