Stellar Evolution - Harnett County High Schools Wiki
... When all the hydrogen in a star’s core is gone, star has a helium center and the outer layers have mostly hydrogen gas Some hydrogen will continue to undergo reactions in the outermost layer of the helium core; energy produced in this layer forces out layers of the star to expand and cool The star h ...
... When all the hydrogen in a star’s core is gone, star has a helium center and the outer layers have mostly hydrogen gas Some hydrogen will continue to undergo reactions in the outermost layer of the helium core; energy produced in this layer forces out layers of the star to expand and cool The star h ...
LIGHT
... However, if a light wave is incident upon the interface of a more dense medium at some angle other than 90 degrees, the wave will slow down and change directions. It will also speed up again and change directions again when it leaves the new medium. This change in direction is called Refraction. ...
... However, if a light wave is incident upon the interface of a more dense medium at some angle other than 90 degrees, the wave will slow down and change directions. It will also speed up again and change directions again when it leaves the new medium. This change in direction is called Refraction. ...
Supernovae Gamma-Ray Bursts and and some of their uses
... layers of the star • The star may collapse directly into a black hole: these are called hypernovae or collapsars • Hypernova may or may not produce a supernova explosion, it can emit jets of gamma rays • Mergers of neutron stars should occur occassionally but not enough to produce the number of GRBs ...
... layers of the star • The star may collapse directly into a black hole: these are called hypernovae or collapsars • Hypernova may or may not produce a supernova explosion, it can emit jets of gamma rays • Mergers of neutron stars should occur occassionally but not enough to produce the number of GRBs ...
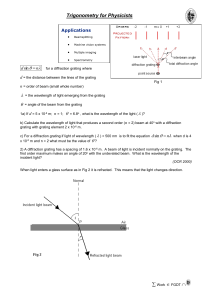
trigonometry
... b) If light arrives at an angle of 15o to the normal at an air-to-glass boundary for which the refractive index is 1.5, what is the expected angle of refraction? 4) The Refractive Index for an air-to-diamond boundary is about 2.42. If light arrives at an angle of 60o to the normal at an air-to-diamo ...
... b) If light arrives at an angle of 15o to the normal at an air-to-glass boundary for which the refractive index is 1.5, what is the expected angle of refraction? 4) The Refractive Index for an air-to-diamond boundary is about 2.42. If light arrives at an angle of 60o to the normal at an air-to-diamo ...
(a) Because the core of heavy-mass star never reaches high enough
... 17. Which one of the following is correct? (a) Right after the big bang, the most abundant element in the universe was helium (b) The first generation stars tend to be more massive than today’s stars (c) High mass stars tend to have red color (d) Large and high luminosity stars tend to live longer t ...
... 17. Which one of the following is correct? (a) Right after the big bang, the most abundant element in the universe was helium (b) The first generation stars tend to be more massive than today’s stars (c) High mass stars tend to have red color (d) Large and high luminosity stars tend to live longer t ...
q 1 - Helios
... For polarized light incident on a sheet of Polaroid, the resultant intensity depends on the angle q between the original direction of polarization and the sheet The new electric field becomes: Since I depends on E2 it becomes: I = I0 cos2 q ...
... For polarized light incident on a sheet of Polaroid, the resultant intensity depends on the angle q between the original direction of polarization and the sheet The new electric field becomes: Since I depends on E2 it becomes: I = I0 cos2 q ...
Introduction to Basic Stargazing Part II - Naples Free-Net
... astronomical unit (au) – one au is defined as the average distance from Earth to the Sun. There are two reasons for this; 1. It greatly improves computational ease of raw data. 2. It improves comprehension of relative distances. For example, the astronomical unit is measured at 92,956,000 miles. If ...
... astronomical unit (au) – one au is defined as the average distance from Earth to the Sun. There are two reasons for this; 1. It greatly improves computational ease of raw data. 2. It improves comprehension of relative distances. For example, the astronomical unit is measured at 92,956,000 miles. If ...
Counter-rotating Stellar Components in Simulated Disk Galaxies
... NGC 7331 Prada et al (1996) found that the line-of-sight velocity distribution has two distinct peaks and can be decomposed into a fast-rotating component with v/σ ~ 3, and a slower rotating, retrograde component with v/σ ~1–1.5. The radial surface brightness profile of the counter-rotating compone ...
... NGC 7331 Prada et al (1996) found that the line-of-sight velocity distribution has two distinct peaks and can be decomposed into a fast-rotating component with v/σ ~ 3, and a slower rotating, retrograde component with v/σ ~1–1.5. The radial surface brightness profile of the counter-rotating compone ...
Basics about stars
... There are different types of variables appearing in the HRD. Basically, whenever the ”instability strip” overlaps with an actual stellar population variable stars are found. • δ-Cepheids : Luminosities range from 300−3000L and periods between 1-50 days. Brightness variation during 1 period can be u ...
... There are different types of variables appearing in the HRD. Basically, whenever the ”instability strip” overlaps with an actual stellar population variable stars are found. • δ-Cepheids : Luminosities range from 300−3000L and periods between 1-50 days. Brightness variation during 1 period can be u ...
Theoretical Problem 3
... the ratio of mass M to radius R is the same and depends only on physical constants. Find the equation for the ratio M / R for stars fusing hydrogen. ...
... the ratio of mass M to radius R is the same and depends only on physical constants. Find the equation for the ratio M / R for stars fusing hydrogen. ...
Non-Thermal Radio Emission from Binary Systems
... be expressed in terms of the Rayleigh-Jeans approximation to the BB formula k: Boltzmann’s constant TB: brightness temperature ΩS: solid angle subtended by the star ...
... be expressed in terms of the Rayleigh-Jeans approximation to the BB formula k: Boltzmann’s constant TB: brightness temperature ΩS: solid angle subtended by the star ...
get ready for rtmc may 26-28th!
... burning. Theory said that both members of such a binary pair would have formed at the same time, and the smaller one would have (continued on page 8) ...
... burning. Theory said that both members of such a binary pair would have formed at the same time, and the smaller one would have (continued on page 8) ...
Revolutionary Times: Copernicus and Tycho Brahe
... 1. Raise or lower the movable stick to point it at each star in turn as it passes through the meridian. Differences in this ‘up-down’ sense tells you which stars are farther North or South in the sky. 2. Use a clock. If Star A passes through the meridian before Star B, then Star A is to the West of ...
... 1. Raise or lower the movable stick to point it at each star in turn as it passes through the meridian. Differences in this ‘up-down’ sense tells you which stars are farther North or South in the sky. 2. Use a clock. If Star A passes through the meridian before Star B, then Star A is to the West of ...
Chapter 2 Knowing the Heavens
... apparent path around the celestial sphere over the course of a year. ...
... apparent path around the celestial sphere over the course of a year. ...
Distance measurement in astronomy
... Of course the period of a variable star in distant galaxies is really difficult to measure and so yet another method was needed to push back the limits of cosmic distance measurement. ...
... Of course the period of a variable star in distant galaxies is really difficult to measure and so yet another method was needed to push back the limits of cosmic distance measurement. ...
Expanding Universe
... Dark energy is stronger at large distances, and now, because of two reasons. At distance, gravity is weaker because of the laws of inverse squares. Dark energy appears to be a property of space itself, and as the universe expands, there will be more and more space. ...
... Dark energy is stronger at large distances, and now, because of two reasons. At distance, gravity is weaker because of the laws of inverse squares. Dark energy appears to be a property of space itself, and as the universe expands, there will be more and more space. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... (b) Derive the condition for the combination of two thin prisms to produces mean deviation without net dispersion. Also obtain an expression for the net mean ...
... (b) Derive the condition for the combination of two thin prisms to produces mean deviation without net dispersion. Also obtain an expression for the net mean ...
Milky Way is bigger - Intranet Sint
... it came to the major galaxies in Earth's cosmic neighborhood, our Milky Way was a weak sister to the larger Andromeda. Not anymore. The Milky Way is considerably larger, bulkier and spinning faster than astronomers once thought, Andromeda's equal. Scientists mapped the Milky Way in a more detailed, ...
... it came to the major galaxies in Earth's cosmic neighborhood, our Milky Way was a weak sister to the larger Andromeda. Not anymore. The Milky Way is considerably larger, bulkier and spinning faster than astronomers once thought, Andromeda's equal. Scientists mapped the Milky Way in a more detailed, ...
Time Trek brochure
... The local group of galaxies consists of the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies as well as 50 smaller galaxies. The closest galaxy cluster is the Virgo cluster, of which the central galaxy is M87. The Virgo cluster has about 2000 known galaxies. 11010: The Universe is full of active galaxies, quasars. ...
... The local group of galaxies consists of the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxies as well as 50 smaller galaxies. The closest galaxy cluster is the Virgo cluster, of which the central galaxy is M87. The Virgo cluster has about 2000 known galaxies. 11010: The Universe is full of active galaxies, quasars. ...
Across the Universe
... The Earth is the third planet from the sun, and the fifth-largest of the eight planets in our solar system. The solar system was formed over 4 billion years ago. Our solar system consists of the sun, Earth, as well as Uranus, Neptune, Saturn, Mars, Jupiter, Mercury, and Venus. Each planet moves in a ...
... The Earth is the third planet from the sun, and the fifth-largest of the eight planets in our solar system. The solar system was formed over 4 billion years ago. Our solar system consists of the sun, Earth, as well as Uranus, Neptune, Saturn, Mars, Jupiter, Mercury, and Venus. Each planet moves in a ...
TOWARD A MODEL FOR THE Be BINARY SYSTEM PER 1
... immediately seen that it is probably non-Keplerian and shows the influence of gaseous motion within the system. The points plotted are the means of individual observational points and in this process of forming the normal points, the quite considerable scatter for such sharp features is masked. The ...
... immediately seen that it is probably non-Keplerian and shows the influence of gaseous motion within the system. The points plotted are the means of individual observational points and in this process of forming the normal points, the quite considerable scatter for such sharp features is masked. The ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.