The Milky Way - University of North Texas
... b. Objects below this mass can only form in HI clouds. c. Objects below this mass are not hot enough to fuse normal hydrogen. d. They form too slowly and hot stars nearby clear the gas and dust quickly. e. Our telescopes do not have enough light gathering power to detect dim objects. ...
... b. Objects below this mass can only form in HI clouds. c. Objects below this mass are not hot enough to fuse normal hydrogen. d. They form too slowly and hot stars nearby clear the gas and dust quickly. e. Our telescopes do not have enough light gathering power to detect dim objects. ...
Lecture 6: Continuum Opacity and Stellar Atmospheres
... The HI atom can also be ionized from any excited state, as well, in which case less energy is required. For example, an HI atom in the n=2 state is already at a level of over 10.x ev above ground so it only requires an additional 3.x ev to ionize it. This requires a photon of 3646 angstroms or short ...
... The HI atom can also be ionized from any excited state, as well, in which case less energy is required. For example, an HI atom in the n=2 state is already at a level of over 10.x ev above ground so it only requires an additional 3.x ev to ionize it. This requires a photon of 3646 angstroms or short ...
death_low_mass
... forming. O,B,A,F,G,K,M • Spiral arms barely move, but gas clouds and stars orbit around the galaxy moving in and out of spiral arms • From the HR diagram, by far the most luminous stars are the O-type stars. Their luminosity can be 100,000 times the Sun’s. • Why is the spiral structure in galaxies s ...
... forming. O,B,A,F,G,K,M • Spiral arms barely move, but gas clouds and stars orbit around the galaxy moving in and out of spiral arms • From the HR diagram, by far the most luminous stars are the O-type stars. Their luminosity can be 100,000 times the Sun’s. • Why is the spiral structure in galaxies s ...
NGC 3370 Spiral Galaxy
... forming. O,B,A,F,G,K,M • Spiral arms barely move, but gas clouds and stars orbit around the galaxy moving in and out of spiral arms • From the HR diagram, by far the most luminous stars are the O-type stars. Their luminosity can be 100,000 times the Sun’s. • Why is the spiral structure in galaxies s ...
... forming. O,B,A,F,G,K,M • Spiral arms barely move, but gas clouds and stars orbit around the galaxy moving in and out of spiral arms • From the HR diagram, by far the most luminous stars are the O-type stars. Their luminosity can be 100,000 times the Sun’s. • Why is the spiral structure in galaxies s ...
Document
... Other theories imagine that one can amass knowledge and become enlightened. For us again it is much more simple. In Romans chapter 10 we read, “Consequently, faith comes from hearing the message, and the message is heard through the word of Christ.” Before we talk about how stars shine it is fascina ...
... Other theories imagine that one can amass knowledge and become enlightened. For us again it is much more simple. In Romans chapter 10 we read, “Consequently, faith comes from hearing the message, and the message is heard through the word of Christ.” Before we talk about how stars shine it is fascina ...
What is the biggest star? - University of Central Lancashire
... There are about 100-400 billion stars in our Milky Way alone, it’s hard to know an exact number as we can’t see through the centre of the Galaxy to know what is on the other side. Also, we think there are around 100 billion galaxies in the Universe so that is a lot of stars! What colours can the sta ...
... There are about 100-400 billion stars in our Milky Way alone, it’s hard to know an exact number as we can’t see through the centre of the Galaxy to know what is on the other side. Also, we think there are around 100 billion galaxies in the Universe so that is a lot of stars! What colours can the sta ...
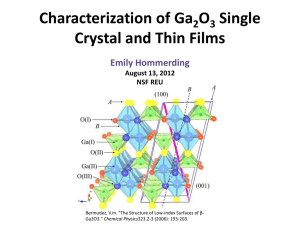
Characterization of Ga 2 0 3 Single Crystal and Thin Films
... Elliptically Polarized Light Leaves Sample "Light & Materials - Part I." Spectroscopic Ellipsometry Tutorial Light and Materials I. J.A. WOOLLAM CO. INC, n.d. Web. 31 July 2012..
...
... Elliptically Polarized Light Leaves Sample "Light & Materials - Part I." Spectroscopic Ellipsometry Tutorial Light and Materials I. J.A. WOOLLAM CO. INC, n.d. Web. 31 July 2012.
Gemini IFU Observations of Feedback from Radio
... "extended emission line regions" (~50 kpc) RQ quasars don't have them photoionized by nucleus galaxy-scale winds driven by radiation? But only ~10% quasars are radio-loud... ...
... "extended emission line regions" (~50 kpc) RQ quasars don't have them photoionized by nucleus galaxy-scale winds driven by radiation? But only ~10% quasars are radio-loud... ...
Stars and Constellations
... 2) Have students construct simple astrolabes using drinking straws, washers, string and protractors (see drawing and instructions below). Ask them to practice using their astrolabe to measure the declination of objects in the room. 3) Distribute star charts to students and allow them to examine them ...
... 2) Have students construct simple astrolabes using drinking straws, washers, string and protractors (see drawing and instructions below). Ask them to practice using their astrolabe to measure the declination of objects in the room. 3) Distribute star charts to students and allow them to examine them ...
The Planck blackbody spectral distribution
... There are two aspects of the solar radiation that can be easily measured: the spectral distribution and the light intensity. Both of these can be used to estimate the solar surface temperature. To perform the required measurements, you will need all the same equipment used for calibration but withou ...
... There are two aspects of the solar radiation that can be easily measured: the spectral distribution and the light intensity. Both of these can be used to estimate the solar surface temperature. To perform the required measurements, you will need all the same equipment used for calibration but withou ...
The Dynamic Earth and Space Geodesy, SC/EATS 1010
... when the core becomes dense enough; later will become the Sun. 3. Dust grains stick to each other and sweep their paths, forming larger particles (Planetesimals). 4. Orbital paths are cleared. 5. The Sun and its planets all spin in the same direction. ...
... when the core becomes dense enough; later will become the Sun. 3. Dust grains stick to each other and sweep their paths, forming larger particles (Planetesimals). 4. Orbital paths are cleared. 5. The Sun and its planets all spin in the same direction. ...
The VLT LEGA-C Spectroscopic Survey: The Physics of Galaxies at
... typically well over 5 Gyr and it is difficult to resolve star formation histories from integrated spectra. Now LEGA-C is obtaining spectra of similar quality for ∼3200 K-band selected galaxies in the redshift range 0.6 < z < 1.0, at a look-back time of 6 − 8 Gyr. LEGA-C is a 4-year, 128-night Public ...
... typically well over 5 Gyr and it is difficult to resolve star formation histories from integrated spectra. Now LEGA-C is obtaining spectra of similar quality for ∼3200 K-band selected galaxies in the redshift range 0.6 < z < 1.0, at a look-back time of 6 − 8 Gyr. LEGA-C is a 4-year, 128-night Public ...
Document
... photoelectrons are emitted. The most energetic of these are stopped by a potential difference of 0.46 volts. Use this information to calculate the work function of aluminum in electron volts. Exercise 3-7: The threshold wavelength of potassium is 558 nm. What is the work function for potassium? What ...
... photoelectrons are emitted. The most energetic of these are stopped by a potential difference of 0.46 volts. Use this information to calculate the work function of aluminum in electron volts. Exercise 3-7: The threshold wavelength of potassium is 558 nm. What is the work function for potassium? What ...
Document
... • Molecular Gas Mass as traced by CO emission and the star formation rate in spiral galaxies, LIRGS, ULIRGs and high z molecular galaxies (Early Molecular Galaxies, EMGs) • Dense molecular Gas as traced by HCN emission is a star formation rate indicator. The mass of dense molecular gas is the key to ...
... • Molecular Gas Mass as traced by CO emission and the star formation rate in spiral galaxies, LIRGS, ULIRGs and high z molecular galaxies (Early Molecular Galaxies, EMGs) • Dense molecular Gas as traced by HCN emission is a star formation rate indicator. The mass of dense molecular gas is the key to ...
Final Exam Review – December 2015
... 27. According to the H–R diagram, which type of stars have the highest surface temperature? ______________________________ 28. According to the H–R diagram, which type of stars are in spectral class B and have low luminosity? ______________________________ 29. According to the H–R diagram, which typ ...
... 27. According to the H–R diagram, which type of stars have the highest surface temperature? ______________________________ 28. According to the H–R diagram, which type of stars are in spectral class B and have low luminosity? ______________________________ 29. According to the H–R diagram, which typ ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... The Universe is believed to have been formed from a very dense fireball _____________ of years ago. As the fireball expanded and cooled stars and galaxies formed. The fireball explosion is often called the ___ ________. The explosion threw all the material outwards; that is why scientists believe th ...
... The Universe is believed to have been formed from a very dense fireball _____________ of years ago. As the fireball expanded and cooled stars and galaxies formed. The fireball explosion is often called the ___ ________. The explosion threw all the material outwards; that is why scientists believe th ...
Introduction to Acousto Optics
... Figure 1. The NIR spectra of two common organic materials, glucose and glycole. The key to interpreting NIR spectra is on-line data processing and chemometrics, which has become possible with the advent of spectroscopic systems with intelligence in the form of dedicated, or in some cases, built-in m ...
... Figure 1. The NIR spectra of two common organic materials, glucose and glycole. The key to interpreting NIR spectra is on-line data processing and chemometrics, which has become possible with the advent of spectroscopic systems with intelligence in the form of dedicated, or in some cases, built-in m ...
Lasers Essay Research Paper The light from
... This configuration is unstable. The electron wants to return to its regular orbit, the ground state. As the excited (stimulated) atoms in the gas relax back to the ground state, some of the energy that excited the electron(s) is emitted (released) in the form of random photons of light This is calle ...
... This configuration is unstable. The electron wants to return to its regular orbit, the ground state. As the excited (stimulated) atoms in the gas relax back to the ground state, some of the energy that excited the electron(s) is emitted (released) in the form of random photons of light This is calle ...
Word doc - UC-HiPACC - University of California, Santa Cruz
... A simulation run on the GreenPlanet supercomputer cluster at the University of California, Irvine suggests its spiral structure may have been triggered by an act of cosmic violence: a series of collisions with a dwarf galaxy. Dwarf galaxy, big impact Since 1994, it’s been known that the Sagittarius ...
... A simulation run on the GreenPlanet supercomputer cluster at the University of California, Irvine suggests its spiral structure may have been triggered by an act of cosmic violence: a series of collisions with a dwarf galaxy. Dwarf galaxy, big impact Since 1994, it’s been known that the Sagittarius ...
The Magnitude Scale
... filtered band intended to be close to visual) is around 550 nm; CCDs tend to peak around 700 nm. The examples are given for integer values are not "exact", in that celestial objects are often measured to a precision or 0.1 or 0.01 magnitude; for example, Sirius shines at V = -1.47 (Yale Bright Star ...
... filtered band intended to be close to visual) is around 550 nm; CCDs tend to peak around 700 nm. The examples are given for integer values are not "exact", in that celestial objects are often measured to a precision or 0.1 or 0.01 magnitude; for example, Sirius shines at V = -1.47 (Yale Bright Star ...
High Mass Stars
... The end result of the CNO cycle is the same as for the proton-proton chain - 4 protons produce 1 helium atom and release energy - but the steps are different. Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen act as catalysts that speed up the reaction. They aid the reaction without being consumed. Discovering Astronomy ...
... The end result of the CNO cycle is the same as for the proton-proton chain - 4 protons produce 1 helium atom and release energy - but the steps are different. Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen act as catalysts that speed up the reaction. They aid the reaction without being consumed. Discovering Astronomy ...
Apparent size (apparent diameter)
... 1. The changing angle of insolation completes one full cycle per year. a. Intensity of insolation (maximum at solar noon): i. Solar noon insolation in the northern hemisphere increases from December 21st through June 21st. This is opposite in the southern hemisphere. ii. Solar noon insolation in the ...
... 1. The changing angle of insolation completes one full cycle per year. a. Intensity of insolation (maximum at solar noon): i. Solar noon insolation in the northern hemisphere increases from December 21st through June 21st. This is opposite in the southern hemisphere. ii. Solar noon insolation in the ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.