Classifying Animals Power Point
... • This is a silent thinking game • Choose a card and hold it up in front of you • Find a classmate that holds a animal card that is in the same classification group and subgroup as your animal • Think about what characteristics your animal has that makes it a fit in your group • Turn and Talk with y ...
... • This is a silent thinking game • Choose a card and hold it up in front of you • Find a classmate that holds a animal card that is in the same classification group and subgroup as your animal • Think about what characteristics your animal has that makes it a fit in your group • Turn and Talk with y ...
Animal Behaviors Power Point
... • Migrations is the instinctive movement of some animals during certain seasons • Hibernation is when reptiles and mammals phase into a sleeplike state during cold seasons • Estivation is when the body’s metabolism rate is reduced in order to maintain energy ...
... • Migrations is the instinctive movement of some animals during certain seasons • Hibernation is when reptiles and mammals phase into a sleeplike state during cold seasons • Estivation is when the body’s metabolism rate is reduced in order to maintain energy ...
CLINGFISH CARE SOP# = OSTE1 PURPOSE: To describe methods
... Search under rocks and logs for the Northern clingfish, then dislodge by sliding its body along the shelter at the same time you're pulling it free off the rock or log. Kelp clingfish can be dip-netted from in amongst algae. Fish must be kept well oxygenated during the trip back to the lab. Ensure t ...
... Search under rocks and logs for the Northern clingfish, then dislodge by sliding its body along the shelter at the same time you're pulling it free off the rock or log. Kelp clingfish can be dip-netted from in amongst algae. Fish must be kept well oxygenated during the trip back to the lab. Ensure t ...
Document
... sensory organs in the anterior end of an animal is called __________________. 20. Name a PHYLUM that does NOT show cephalization. ...
... sensory organs in the anterior end of an animal is called __________________. 20. Name a PHYLUM that does NOT show cephalization. ...
Introduction to Animals Notes
... –Detritivore = feed on decaying organic material –Filter Feeders = aquatic animals that strain food from water –Parasite = lives in or on another organism (symbiotic relationship) ...
... –Detritivore = feed on decaying organic material –Filter Feeders = aquatic animals that strain food from water –Parasite = lives in or on another organism (symbiotic relationship) ...
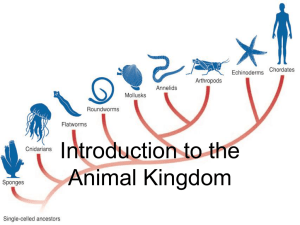
Introduction to the Animal Kingdom
... Introduction to the Animal Kingdom • Animals are multicellular eukaryotic heterotroph whose cells lack cell walls • Vertebrates: 5% of animal species with backbones • Invertebrates: 95% of animal species WITHOUT backbones • Cell specialization – special shape, physical structure, and chemical compo ...
... Introduction to the Animal Kingdom • Animals are multicellular eukaryotic heterotroph whose cells lack cell walls • Vertebrates: 5% of animal species with backbones • Invertebrates: 95% of animal species WITHOUT backbones • Cell specialization – special shape, physical structure, and chemical compo ...
Relationships in the Ecosystem
... for food. Prey = animal that is eaten by another. Predator / Prey populations will change in response to each other’s population. ...
... for food. Prey = animal that is eaten by another. Predator / Prey populations will change in response to each other’s population. ...
Animal Outline Notes - Darlington Middle School
... Some animals may look like another more poisonous or dangerous animal that give it protection Examples: o A “false” coral snake or hawk moth caterpillar that looks like a snake. o Certain moths have markings that look like eyes o Some flower flies resemble black and yellow wasps that have a powe ...
... Some animals may look like another more poisonous or dangerous animal that give it protection Examples: o A “false” coral snake or hawk moth caterpillar that looks like a snake. o Certain moths have markings that look like eyes o Some flower flies resemble black and yellow wasps that have a powe ...
The Red Data Book Species judged as threatened are listed by
... most cited of these list is the Red Data Book. It is a loose-leaf volume of information on the status of many kinds of species. This volume is continually updated and is issued by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (lUCN) located in Morges, Switzerland. "Red" of course is symbolic of ...
... most cited of these list is the Red Data Book. It is a loose-leaf volume of information on the status of many kinds of species. This volume is continually updated and is issued by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (lUCN) located in Morges, Switzerland. "Red" of course is symbolic of ...
4/20 & 4/21 - 7th Grade Agenda
... The balanced arrangement of a butterfly’s body is called ymmetry ilateral B_______ S________ • What are some characteristics of Bilateral Symmetry Animals? • Larger & More complex than radial symmetry animals • Moves more quickly • Sense organ in the front ...
... The balanced arrangement of a butterfly’s body is called ymmetry ilateral B_______ S________ • What are some characteristics of Bilateral Symmetry Animals? • Larger & More complex than radial symmetry animals • Moves more quickly • Sense organ in the front ...
Page 61
... Body Symmetry: bilateral with head end & tail end, left and right side Body Plan: long, narrow without legs – flat and soft as jelly Tissue/ organs/ organ systems: Respiratory & circulatory: not needed – body thin Nervous: interprets info and directs animals response Brain: knot of nerve tissue in h ...
... Body Symmetry: bilateral with head end & tail end, left and right side Body Plan: long, narrow without legs – flat and soft as jelly Tissue/ organs/ organ systems: Respiratory & circulatory: not needed – body thin Nervous: interprets info and directs animals response Brain: knot of nerve tissue in h ...
adaptation
... How do adaptations help animals survive in their environment? • An adaptation is a body part or behavior that helps an animal survive in a particular environment. • Adaptation can help an animal breathe, catch food, or hide. • All animals are adapted to live in certain habitats. • Animals that cann ...
... How do adaptations help animals survive in their environment? • An adaptation is a body part or behavior that helps an animal survive in a particular environment. • Adaptation can help an animal breathe, catch food, or hide. • All animals are adapted to live in certain habitats. • Animals that cann ...
Name
... -pod = foot (arthropoda: segmented coelomates with exoskeleton and jointed appendages) Arachn- = spider (arachnida: the arthropod group that includes scorpions, spiders, ticks, and mites) Brachio- = the arm (brachiopod: also called lamp shells, these animals superficially resemble clams and other bi ...
... -pod = foot (arthropoda: segmented coelomates with exoskeleton and jointed appendages) Arachn- = spider (arachnida: the arthropod group that includes scorpions, spiders, ticks, and mites) Brachio- = the arm (brachiopod: also called lamp shells, these animals superficially resemble clams and other bi ...
Kingdom Animalia
... Organisms can have a two, three or four chambered heart, or no heart at all. Reproduction in Animals Sexual reproduction – male (sperm) and female (egg) produce zygote (baby) Asexual reproduction - budding, regeneration Hermaphrodites – have both male and female sex parts (earthworms). Can breed wit ...
... Organisms can have a two, three or four chambered heart, or no heart at all. Reproduction in Animals Sexual reproduction – male (sperm) and female (egg) produce zygote (baby) Asexual reproduction - budding, regeneration Hermaphrodites – have both male and female sex parts (earthworms). Can breed wit ...
Nature Bowl GLOSSARY
... * Abiotic: a nonliving factor in an environment (e.g., light, water, temperature) ...
... * Abiotic: a nonliving factor in an environment (e.g., light, water, temperature) ...
*Reflects the NEW 2014 Standards Updates! 1 There are 35 phyla of
... Cold-blooded (ectothermic) animals- including fish, amphibians, and reptiles, which have an internal body temperature that changes with the temperature of the environment. They must gain heat to perform internal activities (for example digestion). If the environment is cold, ectothermic animals ...
... Cold-blooded (ectothermic) animals- including fish, amphibians, and reptiles, which have an internal body temperature that changes with the temperature of the environment. They must gain heat to perform internal activities (for example digestion). If the environment is cold, ectothermic animals ...
Evolutionary Trends in Animals
... hollow ball of cells called a(n) ____________________. 8. The ______________________ is the layer of cells in the blastula that gives rise to the outer layer of skin, the nervous system, and the sense organs. 9. The ______________________ is the layer of cells in the blastula that gives rise to the ...
... hollow ball of cells called a(n) ____________________. 8. The ______________________ is the layer of cells in the blastula that gives rise to the outer layer of skin, the nervous system, and the sense organs. 9. The ______________________ is the layer of cells in the blastula that gives rise to the ...
- ISpatula
... Concept 1: Animals are (multicellular, heterotrophic, eukaryotes). Nutrition: Animals can’t produce their food, instead they ingest organic molecules then use their Enzymes to digest them. Cell structure and specialization: animals do not have cell walls, instead they have proteins external to cell ...
... Concept 1: Animals are (multicellular, heterotrophic, eukaryotes). Nutrition: Animals can’t produce their food, instead they ingest organic molecules then use their Enzymes to digest them. Cell structure and specialization: animals do not have cell walls, instead they have proteins external to cell ...
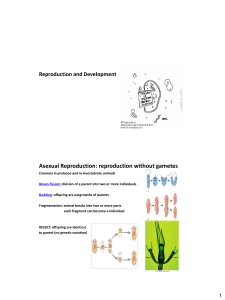
Reproduction and Development
... External fertilization: release of gametes into the surrounding environment Requirement: timing! ensure sperm encounters eggs Internal fertilization: Sperm is deposited in or near the female reproductive tract and fertilization occurs in it Requirement: cooperative behavior between male and female s ...
... External fertilization: release of gametes into the surrounding environment Requirement: timing! ensure sperm encounters eggs Internal fertilization: Sperm is deposited in or near the female reproductive tract and fertilization occurs in it Requirement: cooperative behavior between male and female s ...
final exam study guide intro to animal kingdom first semester
... Which of these scientists is credited with developing the system of grouping organisms that is still used today? What model is sometimes used to identify a group’s derived traits? The placing of information or objects into groups based on certain similarities is called ____________. When using binom ...
... Which of these scientists is credited with developing the system of grouping organisms that is still used today? What model is sometimes used to identify a group’s derived traits? The placing of information or objects into groups based on certain similarities is called ____________. When using binom ...
Animal coloration

Animal coloration is the general appearance of an animal resulting from the reflection or emission of light from its surfaces. Some animals are brightly coloured, while others are hard to see. In some species, such as the peacock, the male has strong patterns, conspicuous colours and is iridescent, while the female is far less visible.There are several separate reasons why animals have evolved colours. Camouflage enables an animal to remain hidden from view. Signalling enables an animal to communicate information such as warning of its ability to defend itself (aposematism). Animals also use colour in advertising, signalling services such as cleaning to animals of other species; to signal sexual status to other members of the same species; and in mimicry, taking advantage of another species' warning coloration. Some animals use colour to divert attacks by startle (deimatic behaviour), surprising a predator e.g. with eyespots or other flashes of colour, and possibly by motion dazzle, confusing a predator's attack by moving a bold pattern (such as zebra stripes) rapidly. Some animals are coloured for physical protection, such as having pigments in the skin to protect against sunburn, while some frogs can lighten or darken their skin for temperature regulation. Finally, animals can be coloured incidentally. For example, blood is red because the haem pigment needed to carry oxygen is red. Animals coloured in these ways can have striking natural patterns.Animals produce colour in different ways. Pigments are particles of coloured material. Chromatophores are cells containing pigment, which can change their size to make their colour more or less visible. Some animals, including many butterflies and birds, have microscopic structures in scales, bristles or feathers which give them brilliant iridescent colours. Other animals including squid and some deep-sea fish can produce light, sometimes of different colours. Animals often use two or more of these mechanisms together to produce the colours and effects they need.