Structural Abnormalities of the Central Auditory Pathway in Infants
... brain stem–evoked response (ABR) hearing threshold acquisition with click stimuli. Thirty-three infants with active middle ear disease (diagnosed otitis media or abnormal tympanograms in one or both ears) or with a history of recurrent (three times within 6 months or four or more episodes within 1 y ...
... brain stem–evoked response (ABR) hearing threshold acquisition with click stimuli. Thirty-three infants with active middle ear disease (diagnosed otitis media or abnormal tympanograms in one or both ears) or with a history of recurrent (three times within 6 months or four or more episodes within 1 y ...
Implantable microcoils for intracortical magnetic
... Downloaded from http://advances.sciencemag.org/ on June 11, 2017 Fig. 1. Micrometer-sized microcoils generate suprathreshold fields. (A) Surface (middle) plot of the electric field gradients in the x direction (dEx/dx) arising from the 500-mm square coil on the left (red). Note that the horizontally ...
... Downloaded from http://advances.sciencemag.org/ on June 11, 2017 Fig. 1. Micrometer-sized microcoils generate suprathreshold fields. (A) Surface (middle) plot of the electric field gradients in the x direction (dEx/dx) arising from the 500-mm square coil on the left (red). Note that the horizontally ...
Brain Stimulation for Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders
... without a defined epileptic focus amenable to surgical removal. This significant population of several million patients could potentially benefit from DBS therapy (Fig. 2). Initial attempts to use brain stimulation to treat epileptic patients started in the 1970s. Because the cerebellum has abundant ...
... without a defined epileptic focus amenable to surgical removal. This significant population of several million patients could potentially benefit from DBS therapy (Fig. 2). Initial attempts to use brain stimulation to treat epileptic patients started in the 1970s. Because the cerebellum has abundant ...
A Symmetric Approach Elucidates Multisensory Information Integration
... “unimodal multisensory neurons” [17], have been demonstrated. In addition, multisensory interactions have been reported at system levels traditionally classified as strictly unimodal: both primary and secondary sensory areas receive substantial inputs from sources that carry information about events ...
... “unimodal multisensory neurons” [17], have been demonstrated. In addition, multisensory interactions have been reported at system levels traditionally classified as strictly unimodal: both primary and secondary sensory areas receive substantial inputs from sources that carry information about events ...
Parkinson`s Disease Rigidity Quantification Kylen Bares1, Eddie
... activities. They include tremor or trembling in the hands, arms, legs, jaw, and face as well as rigidity or stiffness of the limbs and trunk [8]. Other examples of symptoms are slowness of motor movements and reduction in rate at which one can blink his or her eyes. As one’s muscles also control one ...
... activities. They include tremor or trembling in the hands, arms, legs, jaw, and face as well as rigidity or stiffness of the limbs and trunk [8]. Other examples of symptoms are slowness of motor movements and reduction in rate at which one can blink his or her eyes. As one’s muscles also control one ...
Somatotopic mapping of natural upper- and lower
... four patients, and observed values in the same range as for upper extremities (analyzed in six patients). Speech-related responses in the three investigated patients, however, exhibited only a very low sensitivity. The present findings indicate that localization of not only upper- but also lower-extr ...
... four patients, and observed values in the same range as for upper extremities (analyzed in six patients). Speech-related responses in the three investigated patients, however, exhibited only a very low sensitivity. The present findings indicate that localization of not only upper- but also lower-extr ...
Neuroscience, Fifth Edition
... How Information from the Cochlea Reaches Targets in the Brainstem 293 Integrating Information from the Two Ears 294 Monaural Pathways from the Cochlear Nucleus to the Nuclei of the Lateral Lemniscus 297 Integration in the Inferior Colliculus 297 The Auditory Thalamus 297 The Auditory Cortex 298 BOX ...
... How Information from the Cochlea Reaches Targets in the Brainstem 293 Integrating Information from the Two Ears 294 Monaural Pathways from the Cochlear Nucleus to the Nuclei of the Lateral Lemniscus 297 Integration in the Inferior Colliculus 297 The Auditory Thalamus 297 The Auditory Cortex 298 BOX ...
pdf
... humans (19) and has been found to be associated with auditory attention (1, 20, 41) resulting in top-down modulation of auditory processing (25). This finding was further confirmed by electrophysiological data indicating that tinnitus might occur as the result of a dysfunction in the top-down inhibito ...
... humans (19) and has been found to be associated with auditory attention (1, 20, 41) resulting in top-down modulation of auditory processing (25). This finding was further confirmed by electrophysiological data indicating that tinnitus might occur as the result of a dysfunction in the top-down inhibito ...
Neurochemical excitation of propriospinal neurons facilitates
... abolish brain stem-evoked locomotor activity, baseline rhythmic activity in the absence of drug application was first established. The selected antagonist was then applied using a range of concentrations as needed, using the baseline brain stem stimulation parameters. If locomotor-like activity was ...
... abolish brain stem-evoked locomotor activity, baseline rhythmic activity in the absence of drug application was first established. The selected antagonist was then applied using a range of concentrations as needed, using the baseline brain stem stimulation parameters. If locomotor-like activity was ...
Not all brains are created equal: The relevance of
... Given the large number of options available in the selection of tES parameters, the effects on the individual subject’s cortical excitability and tissue may be very specific and extremely variable across a whole sample. For instance, there are sharp contrasts in outcomes observed using different cur ...
... Given the large number of options available in the selection of tES parameters, the effects on the individual subject’s cortical excitability and tissue may be very specific and extremely variable across a whole sample. For instance, there are sharp contrasts in outcomes observed using different cur ...
Technology Insight: noninvasive brain stimulation in neurology
... investigated in the late 19th century.10 It was not until the mid-1980s, however, that Barker and colleagues introduced transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS),11 having solved the technical challenges involved in bridging the scalp and skull with a magnetic field pulse of sufficient strength and ra ...
... investigated in the late 19th century.10 It was not until the mid-1980s, however, that Barker and colleagues introduced transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS),11 having solved the technical challenges involved in bridging the scalp and skull with a magnetic field pulse of sufficient strength and ra ...
Chronic multiunit recordings in behaving animals: advantages and
... function. By the use of multiunit recording, it becomes much easier to detect relatively weak interactions between neurons at different cortical locations. ...
... function. By the use of multiunit recording, it becomes much easier to detect relatively weak interactions between neurons at different cortical locations. ...
Deep Brain Stimulation Does Not Silence Neurons in Subthalamic
... al. 2001; Walter and Vitek 2004). Electrical stimulation was thus inferred to mimic a lesion by suppressing output from the STN. The functional lesion hypothesis received support from studies in humans and in a primate model of Parkinson’s disease in which high-frequency stimulation in the STN was s ...
... al. 2001; Walter and Vitek 2004). Electrical stimulation was thus inferred to mimic a lesion by suppressing output from the STN. The functional lesion hypothesis received support from studies in humans and in a primate model of Parkinson’s disease in which high-frequency stimulation in the STN was s ...
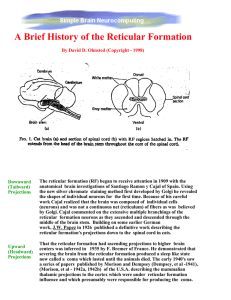
A Brief History of the Reticular Formation
... states that whenever the motivation is the same, a defined set of stimuli will always release a specific motor response. Lorentz was the first to propose this concept in a 1935 German paper but not until 1948 and 1951 did Tinbergen introduce this concept to the English speaking world. The region of ...
... states that whenever the motivation is the same, a defined set of stimuli will always release a specific motor response. Lorentz was the first to propose this concept in a 1935 German paper but not until 1948 and 1951 did Tinbergen introduce this concept to the English speaking world. The region of ...
PDF
... were mainly restricted to the dorsal CN (DCN) and only relatively low frequency pulse trains were tested (up to 400 pps). Meanwhile, it has been demonstrated that significant improvement in speech recognition and a more natural pattern of activity in AN fibers can be achieved using high-rate pulsati ...
... were mainly restricted to the dorsal CN (DCN) and only relatively low frequency pulse trains were tested (up to 400 pps). Meanwhile, it has been demonstrated that significant improvement in speech recognition and a more natural pattern of activity in AN fibers can be achieved using high-rate pulsati ...
Lecture VIII. Spinal Cord
... Segmental Nerves Spinal or Posterior (dorsal) Root, Ganglion Cells & Sensory Nerves (axons in from posterior (dorsal) root ganglia) ...
... Segmental Nerves Spinal or Posterior (dorsal) Root, Ganglion Cells & Sensory Nerves (axons in from posterior (dorsal) root ganglia) ...
Visuomotor development
... Coordinate system transformation and the inverse kinematics problem The concepts of reference frames and coordinate systems are used widely in the study of eye and limb movements. A reference frame is invoked when an experimental result is described: for example, describing the position of eyes rela ...
... Coordinate system transformation and the inverse kinematics problem The concepts of reference frames and coordinate systems are used widely in the study of eye and limb movements. A reference frame is invoked when an experimental result is described: for example, describing the position of eyes rela ...
Lecture VIII. Spinal Cord
... Segmental Nerves Spinal or Posterior (dorsal) Root, Ganglion Cells & Sensory Nerves (axons in from posterior (dorsal) root ganglia) ...
... Segmental Nerves Spinal or Posterior (dorsal) Root, Ganglion Cells & Sensory Nerves (axons in from posterior (dorsal) root ganglia) ...
Modulation of brain activity by electrical stimulation and external
... effective to ameliorate parkinsonian symptoms, and remains the most common treatment method to this day. But because its positive effects decline over time and it can cause some serious side effect, some patients need to resort to other treatment methods. High frequency electrical stimulation of com ...
... effective to ameliorate parkinsonian symptoms, and remains the most common treatment method to this day. But because its positive effects decline over time and it can cause some serious side effect, some patients need to resort to other treatment methods. High frequency electrical stimulation of com ...
Current BCI Platforms
... · Implant must be reliable and durable in its ability to acquire signals(DBS, cortical stimulators, grid electrodes) · Affected by device design · Patients responds - Duration problems · Cause removal and replacement ...
... · Implant must be reliable and durable in its ability to acquire signals(DBS, cortical stimulators, grid electrodes) · Affected by device design · Patients responds - Duration problems · Cause removal and replacement ...
Neurophysiological investigation of the basis of the fMRI signal
... slow-varying ®eld potentials. An ideal combination is functional imaging in experimental animals with microelectrode recordings of such potentials, including single-spike responses and ®eld potentials, whereby the latter relate well not only to spike activity but also to subthreshold integrative pro ...
... slow-varying ®eld potentials. An ideal combination is functional imaging in experimental animals with microelectrode recordings of such potentials, including single-spike responses and ®eld potentials, whereby the latter relate well not only to spike activity but also to subthreshold integrative pro ...
CONTROL OF FUNCTIONAL ELECTRICAL STIMULATION FOR
... Emeritus Professor, Aalborg University, Aalborg, Denmark Abstract. An injury or disease of the central nervous system (CNS) results in significant limitations in the communication with the environment (e.g., mobility, reaching and grasping). Functional electrical stimulation (FES) externally activat ...
... Emeritus Professor, Aalborg University, Aalborg, Denmark Abstract. An injury or disease of the central nervous system (CNS) results in significant limitations in the communication with the environment (e.g., mobility, reaching and grasping). Functional electrical stimulation (FES) externally activat ...
CHAPTER 12: THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM MODULE 12.1
... Diencephalon – deep underneath cerebral hemispheres; central core of brain Consists of four distinct structural and functional parts Responsible for processing, integrating, and relaying information to different parts of brain, homeostatic functions, regulation of movement, and biological ...
... Diencephalon – deep underneath cerebral hemispheres; central core of brain Consists of four distinct structural and functional parts Responsible for processing, integrating, and relaying information to different parts of brain, homeostatic functions, regulation of movement, and biological ...
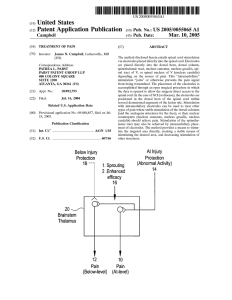
18 "1: 1_ Sprouting (Abnormiall1 Actrvlty)
... for SCI-related central pain: operative intramedullary elec trophysiological guidance and clinical outcome). Cells in the thalamus that have lost inputs from distal regions (as a result of the SCI) recruit inputs from the abnormal dorsal horn cells near the SCI. Thus, the inputs from this spinal cor ...
... for SCI-related central pain: operative intramedullary elec trophysiological guidance and clinical outcome). Cells in the thalamus that have lost inputs from distal regions (as a result of the SCI) recruit inputs from the abnormal dorsal horn cells near the SCI. Thus, the inputs from this spinal cor ...