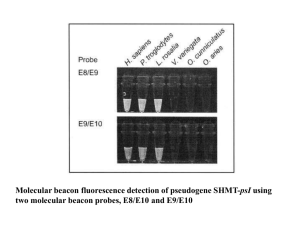
Ppt
... C: striated only one nuclei per cell; branching cells join at junctions called intercalated discs; involuntary F: intercalated disc enable to heart to beat as one unit. Cardiac muscle contracts together and relaxes together. L: walls of heart ...
... C: striated only one nuclei per cell; branching cells join at junctions called intercalated discs; involuntary F: intercalated disc enable to heart to beat as one unit. Cardiac muscle contracts together and relaxes together. L: walls of heart ...
- Google Sites
... Skeletal muscle: Where is it found? In muscles that are attached to bone Its cells are long and so are called muscle _fibers_. They may have several ___nuclei_. The cells appear striped and are said to be __striated__. Is it usually voluntary or involuntary? Usually voluntary Smooth muscle ...
... Skeletal muscle: Where is it found? In muscles that are attached to bone Its cells are long and so are called muscle _fibers_. They may have several ___nuclei_. The cells appear striped and are said to be __striated__. Is it usually voluntary or involuntary? Usually voluntary Smooth muscle ...
page 1 of 5 LECTURE OUTLINE: CTP
... Most water is hydrated to GAGS. Different connective tissues differ in their ground substance composition. Result: different functional characteristics. Protein Fibers Collagen Basic Structure: 3 polypeptide chains tropocollagen Linked tropocollagen molecules collagen fibril Collagen fibrils c ...
... Most water is hydrated to GAGS. Different connective tissues differ in their ground substance composition. Result: different functional characteristics. Protein Fibers Collagen Basic Structure: 3 polypeptide chains tropocollagen Linked tropocollagen molecules collagen fibril Collagen fibrils c ...
Histology Review Guide
... Dense regular – found in ligaments and tendons consists mainly of regular, wavy rows of collagen and very little matrix. Dense regular can stretch, but resists twisting. Elastic connective tissue proper is widely distributed in arteries and lungs and allows them to expand and contract. Cartilage Ava ...
... Dense regular – found in ligaments and tendons consists mainly of regular, wavy rows of collagen and very little matrix. Dense regular can stretch, but resists twisting. Elastic connective tissue proper is widely distributed in arteries and lungs and allows them to expand and contract. Cartilage Ava ...
Neurodegenerative Diseases Stem Cell
... of disease. The current modalities are only symptomatic treatment with no cure in horizon. Therefore, therapeutic interventions for neurodegenerative diseases remain the most daunting task today. The emerging new technology like stem cells based therapeutics can offer some respite and is becoming an ...
... of disease. The current modalities are only symptomatic treatment with no cure in horizon. Therefore, therapeutic interventions for neurodegenerative diseases remain the most daunting task today. The emerging new technology like stem cells based therapeutics can offer some respite and is becoming an ...
Chapter 5 Tissue Notes File
... 2) Elastic fibers – composed of elastin (protein that has elasticity + extensibility) 3) Reticular fibers – composed of reticulin (thin, branching protein that resists physical stress); not abundant Connective tissue is vascular – blood vessels pass though intercellular material (allows tissue to gr ...
... 2) Elastic fibers – composed of elastin (protein that has elasticity + extensibility) 3) Reticular fibers – composed of reticulin (thin, branching protein that resists physical stress); not abundant Connective tissue is vascular – blood vessels pass though intercellular material (allows tissue to gr ...
Chap05 ed11
... Dense Connective Tissue (Fig. 5.15) a. This tissue consists of densely packed collagenous fibers and is very strong but lacks a good blood supply. b. It is found as part of tendons and ligaments. ...
... Dense Connective Tissue (Fig. 5.15) a. This tissue consists of densely packed collagenous fibers and is very strong but lacks a good blood supply. b. It is found as part of tendons and ligaments. ...
No Slide Title
... the sole of the foot • Layers of epithelium covered with compact, ______ squamous cells (no nuclei) packed with protein keratin • Retards water loss, prevents entrance of organisms • Forms epidermal layer of skin (esp. soles and palms) ...
... the sole of the foot • Layers of epithelium covered with compact, ______ squamous cells (no nuclei) packed with protein keratin • Retards water loss, prevents entrance of organisms • Forms epidermal layer of skin (esp. soles and palms) ...
Connective Tissue
... Elongated, cylindrical cells that lie adjacent to each other, striated in appearance, multinucleate ...
... Elongated, cylindrical cells that lie adjacent to each other, striated in appearance, multinucleate ...
ex vivo bioengineering of lung - HELENA
... Engineering Approach to Restoring Lung Function • Minimum requirements: • Gas exchange (oxygen in, carbon dioxide out) • Filters (prevent particles and pathogens from entering the ...
... Engineering Approach to Restoring Lung Function • Minimum requirements: • Gas exchange (oxygen in, carbon dioxide out) • Filters (prevent particles and pathogens from entering the ...
epithelial tissue - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... 3) Mast cells: usually near blood vessels; release heparin and histamine ...
... 3) Mast cells: usually near blood vessels; release heparin and histamine ...
Stem cells – no magic bullet
... heart failure, the infinite potential of stem cells should not be dismissed. For example, the National University Hospital (NUH) is conducting a clinical trial on using stem cell therapy to treat early osteoarthritis. Dr Prem Pillay, a consultant neurosurgeon at Singapore Brain-Spine-Nerves Centre a ...
... heart failure, the infinite potential of stem cells should not be dismissed. For example, the National University Hospital (NUH) is conducting a clinical trial on using stem cell therapy to treat early osteoarthritis. Dr Prem Pillay, a consultant neurosurgeon at Singapore Brain-Spine-Nerves Centre a ...
Animal Cloning repro and non
... commonplace and use one of two methods: – Artificial embryo splitting – Somatic cell nuclear transfer ...
... commonplace and use one of two methods: – Artificial embryo splitting – Somatic cell nuclear transfer ...
C. Organ Level
... Scientists are increasingly turning to bioengineering in their search for ways to repair or replace damaged tissues and organs One of the most successful tissue-engineering advances has come in the form of artificial, a type of human-engineered tissue designed for everyone from burn victims to diab ...
... Scientists are increasingly turning to bioengineering in their search for ways to repair or replace damaged tissues and organs One of the most successful tissue-engineering advances has come in the form of artificial, a type of human-engineered tissue designed for everyone from burn victims to diab ...
Bob Caruthers, CST, PLD - Association of Surgical Technologists
... stomach, liver, gall bladder, spleen, pancreas and small intesvisceral afferent fibers. A lateral portion is found along the lateral edge of the solitary fasciculus. Cells from the medial portion extend rostrally and join the corresponding cell col- ...
... stomach, liver, gall bladder, spleen, pancreas and small intesvisceral afferent fibers. A lateral portion is found along the lateral edge of the solitary fasciculus. Cells from the medial portion extend rostrally and join the corresponding cell col- ...
Cell culture models for study of differentiated adipose cells
... Clynes Stem Cell Research & Therapy 2014, 5:137 http://stemcellres.com/content/5/6/137 ...
... Clynes Stem Cell Research & Therapy 2014, 5:137 http://stemcellres.com/content/5/6/137 ...
****Note this copy has the ones I told you to skip deleted so yours
... 30. The type of muscle tissue that can be controlled voluntarily is called __________ muscle. SKELETAL 31. The type of tissue consisting of cells embedded in an extracellular matrix is __________ tissue. CONNECTIVE 32. The type of connective tissue that contains fat stored in adipocytes is called __ ...
... 30. The type of muscle tissue that can be controlled voluntarily is called __________ muscle. SKELETAL 31. The type of tissue consisting of cells embedded in an extracellular matrix is __________ tissue. CONNECTIVE 32. The type of connective tissue that contains fat stored in adipocytes is called __ ...
tissues
... produces blood cells, and stores fat. • matrix material is the material that fills the cell. It is a semifluid or solid. • Different types of fibers float in matrix ...
... produces blood cells, and stores fat. • matrix material is the material that fills the cell. It is a semifluid or solid. • Different types of fibers float in matrix ...
cholera haiti
... thought kept running through her mind that the earthquake wasn’t over—it was just wreaking havoc in cells instead of buildings now. Bedeline had severe diarrhea and was producing watery stools at a rate of nearly 1L/hour. Her skin appeared shriveled, and when a fold of skin was pinched, it remained ...
... thought kept running through her mind that the earthquake wasn’t over—it was just wreaking havoc in cells instead of buildings now. Bedeline had severe diarrhea and was producing watery stools at a rate of nearly 1L/hour. Her skin appeared shriveled, and when a fold of skin was pinched, it remained ...
Controlled Drug Release from Silk-Based
... Departments of Biomedical Engineering and Chemical and Biological Engineering, Tufts University School of Engineering ...
... Departments of Biomedical Engineering and Chemical and Biological Engineering, Tufts University School of Engineering ...
File
... Angiotensin II exerts as a powerful effect on blood pressure, causing increased pressure through ___ and retention of___ Vasoconstriction; salt, water The neural communication between the cerebrum and the cerebellum goes through the: pons Which is responsible for the synthesis of fatty acids: cortis ...
... Angiotensin II exerts as a powerful effect on blood pressure, causing increased pressure through ___ and retention of___ Vasoconstriction; salt, water The neural communication between the cerebrum and the cerebellum goes through the: pons Which is responsible for the synthesis of fatty acids: cortis ...
Chapter 3-2
... aponeuroses and fascia. Has a wavy appearance on slides. Forms tendons to attach muscles to bone and ligaments to attach bones to bones. ...
... aponeuroses and fascia. Has a wavy appearance on slides. Forms tendons to attach muscles to bone and ligaments to attach bones to bones. ...