De Morgan`s laws
... Both of these gates have 2 inputs and 1 output. A larger number of inputs are possible (see later). The NOT gate or inverter consists of a single input and the output is the opposite or complement of the input ...
... Both of these gates have 2 inputs and 1 output. A larger number of inputs are possible (see later). The NOT gate or inverter consists of a single input and the output is the opposite or complement of the input ...
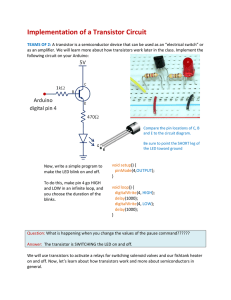
Implementation of a Transistor Circuit
... Implementation of a Transistor Circuit TEAMS OF 2: A transistor is a semiconductor device that can be used as an “electrical switch” or as an amplifier. We will learn more about how transistors work later in the class. Implement the following circuit on your Arduino: ...
... Implementation of a Transistor Circuit TEAMS OF 2: A transistor is a semiconductor device that can be used as an “electrical switch” or as an amplifier. We will learn more about how transistors work later in the class. Implement the following circuit on your Arduino: ...
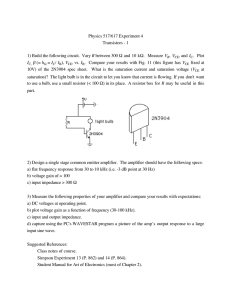
Physics 4700 HOMEWORK III Due Feb 23
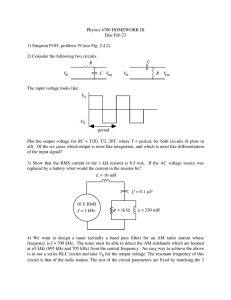
... Plot the output voltage for RC = T/20, T/2, 20T, where T = period, for both circuits (6 plots in all). Of the six cases which output is most like integration, and which is most like differentiation of the input signal? 3) Show that the RMS current in the 1 kΩ resistor is 6.5 mA. If the AC voltage so ...
... Plot the output voltage for RC = T/20, T/2, 20T, where T = period, for both circuits (6 plots in all). Of the six cases which output is most like integration, and which is most like differentiation of the input signal? 3) Show that the RMS current in the 1 kΩ resistor is 6.5 mA. If the AC voltage so ...
Circuit Timing
... Maximum: longest possible delay Typical: under near-ideal condition Minimum: smallest. Many manufactures don’t specify this values in most moderate-speed logic families (74LS,74S TTL). Set to zero or 1/4~1/3 of typical delay if not specified. ...
... Maximum: longest possible delay Typical: under near-ideal condition Minimum: smallest. Many manufactures don’t specify this values in most moderate-speed logic families (74LS,74S TTL). Set to zero or 1/4~1/3 of typical delay if not specified. ...
Astable multivibrator
... When T1 is on O1 is at 0.2 V and B1 is at 0.7 V T2 is off and O2 is at 6 V and B2 is at –5.3 V C1 charges up through R1 and C2 charges up through R4 As soon as B2 reaches 0.7 V T2 switches on Note that C1 charges slowly through the large resistor R1 while C2 charges more quickly through the small r ...
... When T1 is on O1 is at 0.2 V and B1 is at 0.7 V T2 is off and O2 is at 6 V and B2 is at –5.3 V C1 charges up through R1 and C2 charges up through R4 As soon as B2 reaches 0.7 V T2 switches on Note that C1 charges slowly through the large resistor R1 while C2 charges more quickly through the small r ...
Use the proportionality property of linear circuits to find the voltage Vx
... Find k by analysis of that circuit. We can then use k to find the output when given any input. So set Vx = 1 V and let the input be unknown. There is no current flowing through either the 22 Ω resistor or the 81 Ω resistor. This means that the voltage across each element is 0V. So we can replace the ...
... Find k by analysis of that circuit. We can then use k to find the output when given any input. So set Vx = 1 V and let the input be unknown. There is no current flowing through either the 22 Ω resistor or the 81 Ω resistor. This means that the voltage across each element is 0V. So we can replace the ...
NTE7142 - NTE Electronics Inc
... Lead Temperature (During Soldering, 10sec), TL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +300°C Note 1. Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the ...
... Lead Temperature (During Soldering, 10sec), TL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +300°C Note 1. Stresses beyond those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the ...
Lab Guide - inst.eecs.berkeley.edu - University of California, Berkeley
... c. What happens if you use a negative offset? d. What happens to the output if you make the input Vpp = 0.5V and you increase the offset = 0.5V. e. What happens if you lower the frequency of the function generator? f. What happens as you vary the resistance on the rheostat? g. Do different color LED ...
... c. What happens if you use a negative offset? d. What happens to the output if you make the input Vpp = 0.5V and you increase the offset = 0.5V. e. What happens if you lower the frequency of the function generator? f. What happens as you vary the resistance on the rheostat? g. Do different color LED ...
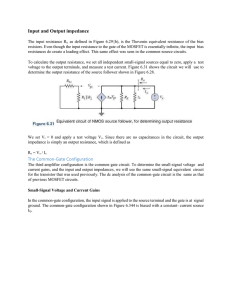
The Common-Gate Configuration
... The input resistance Ri, as defined in Figure 6.29{b), is the Thevenin equivalent resistance of the bias resistors. Even though the input resistance to the gate of the MOSFET is essentially infinite, the input bias resistances do create a loading effect. This same effect was seen in the common-sourc ...
... The input resistance Ri, as defined in Figure 6.29{b), is the Thevenin equivalent resistance of the bias resistors. Even though the input resistance to the gate of the MOSFET is essentially infinite, the input bias resistances do create a loading effect. This same effect was seen in the common-sourc ...
physics 202 - La Salle University
... low can also be interpreted as true and false, the circuits or parts of circuits performing these tasks are referred to as logic elements. Logic elements that do not require memory are called logic gates. Some input signals are fed into the logic gate, and an output signal results. The on-off nature ...
... low can also be interpreted as true and false, the circuits or parts of circuits performing these tasks are referred to as logic elements. Logic elements that do not require memory are called logic gates. Some input signals are fed into the logic gate, and an output signal results. The on-off nature ...
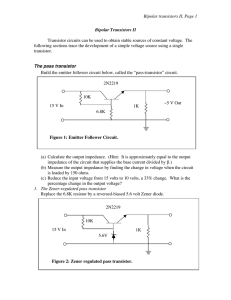
Bipolar transistors II, Page 1 Bipolar Transistors II
... “NC” means no connections to the center tap on the transformer. Plot I vs. V for this supply by loading it. Note: The zener-regulated pass transistor developed in this lab is an acceptable source of stable voltage to be used when circumstances are not demanding. Transistorized power supplies with tw ...
... “NC” means no connections to the center tap on the transformer. Plot I vs. V for this supply by loading it. Note: The zener-regulated pass transistor developed in this lab is an acceptable source of stable voltage to be used when circumstances are not demanding. Transistorized power supplies with tw ...
MOC211, MOC212 and MOC213 Small Outline
... Transistor Output These devices consist of a gallium arsenide infrared emitting diode optically coupled to a monolithic silicon phototransistor detector, in a surface mountable, small outline, plastic package. They are ideally suited for high density applications, and eliminate the need for through– ...
... Transistor Output These devices consist of a gallium arsenide infrared emitting diode optically coupled to a monolithic silicon phototransistor detector, in a surface mountable, small outline, plastic package. They are ideally suited for high density applications, and eliminate the need for through– ...
Transistor–transistor logic

Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a class of digital circuits built from bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and resistors. It is called transistor–transistor logic because both the logic gating function (e.g., AND) and the amplifying function are performed by transistors (contrast with RTL and DTL).TTL is notable for being a widespread integrated circuit (IC) family used in many applications such as computers, industrial controls, test equipment and instrumentation, consumer electronics, synthesizers, etc. The designation TTL is sometimes used to mean TTL-compatible logic levels, even when not associated directly with TTL integrated circuits, for example as a label on the inputs and outputs of electronic instruments.After their introduction in integrated circuit form in 1963 by Sylvania, TTL integrated circuits were manufactured by several semiconductor companies, with the 7400 series (also called 74xx) by Texas Instruments becoming particularly popular. TTL manufacturers offered a wide range of logic gate, flip-flops, counters, and other circuits. Several variations from the original bipolar TTL concept were developed, giving circuits with higher speed or lower power dissipation to allow optimization of a design. TTL circuits simplified design of systems compared to earlier logic families, offering superior speed to resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and easier design layout than emitter-coupled logic (ECL). The design of the input and outputs of TTL gates allowed many elements to be interconnected.TTL became the foundation of computers and other digital electronics. Even after much larger scale integrated circuits made multiple-circuit-board processors obsolete, TTL devices still found extensive use as the ""glue"" logic interfacing more densely integrated components. TTL devices were originally made in ceramic and plastic dual-in-line (DIP) packages, and flat-pack form. TTL chips are now also made in surface-mount packages. Successors to the original bipolar TTL logic often are interchangeable in function with the original circuits, but with improved speed or lower power dissipation.