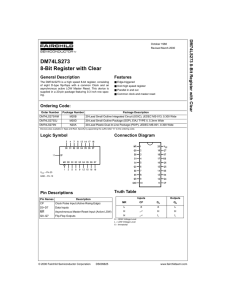
DM74LS273 8-Bit Register with Clear
... Functional Description The DM74LS273 is an 8-bit parallel register with a common Clock and common Master Reset. When the MR input is LOW, the Q outputs are LOW, independent of the other inputs. Information meeting the setup and hold time requirements of the D inputs is transferred to the Q outputs o ...
... Functional Description The DM74LS273 is an 8-bit parallel register with a common Clock and common Master Reset. When the MR input is LOW, the Q outputs are LOW, independent of the other inputs. Information meeting the setup and hold time requirements of the D inputs is transferred to the Q outputs o ...
Manual.
... features of the devices, hence on their operation characteristics. Parameters such as response speed, power – both output and consumption, functional characteristics, supply voltages, prices and many more, are all dependent on and influenced by the manufacturing technology. A rough classification di ...
... features of the devices, hence on their operation characteristics. Parameters such as response speed, power – both output and consumption, functional characteristics, supply voltages, prices and many more, are all dependent on and influenced by the manufacturing technology. A rough classification di ...
Ultrasonic Ranging Module HC
... The Timing diagram is shown below. You only need to supply a short 10uS pulse to the trigger input to start the ranging, and then the module will send out an 8 cycle burst of ultrasound at 40 kHz and raise its echo. The Echo is a distance object that is pulse width and the range in proportion .You c ...
... The Timing diagram is shown below. You only need to supply a short 10uS pulse to the trigger input to start the ranging, and then the module will send out an 8 cycle burst of ultrasound at 40 kHz and raise its echo. The Echo is a distance object that is pulse width and the range in proportion .You c ...
PHE-10
... 4. a) Calculate the value of load inductor and resistor in order to achieve a maximum power transfer from a source with 2 resistor and 50 F capacitor at 50 Hz frequency. (6) b) What is the function of grids in the vacuum valves? ...
... 4. a) Calculate the value of load inductor and resistor in order to achieve a maximum power transfer from a source with 2 resistor and 50 F capacitor at 50 Hz frequency. (6) b) What is the function of grids in the vacuum valves? ...
ETEE1123 Homework 4 - Personal Web Pages
... 4-42. If an electric motor having an efficiency of 87% and operating off a 220-V line delivers 3.6 hp, what input current does the motor draw? ...
... 4-42. If an electric motor having an efficiency of 87% and operating off a 220-V line delivers 3.6 hp, what input current does the motor draw? ...
PHYSICS 536 Experiment 9: Common Emitter Amplifier A. Introduction
... relatively small to minimize non-linearity. Monitor the input signal when the frequency is changed (refer to GIL section 4.3) For I c = 1mA , measure the midfrequency gain (vc / vb ) at 10kHz. Observe that the gain is constant in the midfrequency region by varying the signal frequency from 1kHz to 1 ...
... relatively small to minimize non-linearity. Monitor the input signal when the frequency is changed (refer to GIL section 4.3) For I c = 1mA , measure the midfrequency gain (vc / vb ) at 10kHz. Observe that the gain is constant in the midfrequency region by varying the signal frequency from 1kHz to 1 ...
PHYSICS 536 Experiment 9: Common Emitter Amplifier A. Introduction
... 1) Rs is the output resistance of signal source. 2) C2 is a “coupling capacitor” which passes AC signal from the source to amplifier input but blocks DC offsets from the source so that it does not affect the quiescent condition of the transistor. 3) C3 is a coupling capacitor, which passes the ampli ...
... 1) Rs is the output resistance of signal source. 2) C2 is a “coupling capacitor” which passes AC signal from the source to amplifier input but blocks DC offsets from the source so that it does not affect the quiescent condition of the transistor. 3) C3 is a coupling capacitor, which passes the ampli ...
CHAPTER 7 Internal structure of operational amplifiers
... Offset-setting is possible by an external potentiometer. Since R1 = R2 = 1 k, a potentiometer with the value of 10 kohm can be used. (According to the catalogue the offset voltage is: 1 … 10 mV.) Main amplifier (CE with Darlington pair of transistors): The T15 – T16 Darlington works in common emitte ...
... Offset-setting is possible by an external potentiometer. Since R1 = R2 = 1 k, a potentiometer with the value of 10 kohm can be used. (According to the catalogue the offset voltage is: 1 … 10 mV.) Main amplifier (CE with Darlington pair of transistors): The T15 – T16 Darlington works in common emitte ...
DM74LS14 Hex Inverter with Schmitt Trigger Inputs
... 14-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300 Wide Package Number N14A ...
... 14-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300 Wide Package Number N14A ...
Transistor–transistor logic

Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a class of digital circuits built from bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and resistors. It is called transistor–transistor logic because both the logic gating function (e.g., AND) and the amplifying function are performed by transistors (contrast with RTL and DTL).TTL is notable for being a widespread integrated circuit (IC) family used in many applications such as computers, industrial controls, test equipment and instrumentation, consumer electronics, synthesizers, etc. The designation TTL is sometimes used to mean TTL-compatible logic levels, even when not associated directly with TTL integrated circuits, for example as a label on the inputs and outputs of electronic instruments.After their introduction in integrated circuit form in 1963 by Sylvania, TTL integrated circuits were manufactured by several semiconductor companies, with the 7400 series (also called 74xx) by Texas Instruments becoming particularly popular. TTL manufacturers offered a wide range of logic gate, flip-flops, counters, and other circuits. Several variations from the original bipolar TTL concept were developed, giving circuits with higher speed or lower power dissipation to allow optimization of a design. TTL circuits simplified design of systems compared to earlier logic families, offering superior speed to resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and easier design layout than emitter-coupled logic (ECL). The design of the input and outputs of TTL gates allowed many elements to be interconnected.TTL became the foundation of computers and other digital electronics. Even after much larger scale integrated circuits made multiple-circuit-board processors obsolete, TTL devices still found extensive use as the ""glue"" logic interfacing more densely integrated components. TTL devices were originally made in ceramic and plastic dual-in-line (DIP) packages, and flat-pack form. TTL chips are now also made in surface-mount packages. Successors to the original bipolar TTL logic often are interchangeable in function with the original circuits, but with improved speed or lower power dissipation.