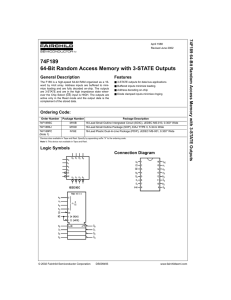
Evaluates: MAX6469–MAX6476 MAX6470 Evaluation Kit General Description Features
... The MAX6470 PC board accommodates the MAX6469–MAX6476 ICs in both a 6-pin SOT23 package and an 8-pin QFN package. The MAX6470 board layout features the dual circuitry in parallel. The SOT23 circuit is populated and fully functional. The QFN circuit is left unpopulated of all components. The two PC b ...
... The MAX6470 PC board accommodates the MAX6469–MAX6476 ICs in both a 6-pin SOT23 package and an 8-pin QFN package. The MAX6470 board layout features the dual circuitry in parallel. The SOT23 circuit is populated and fully functional. The QFN circuit is left unpopulated of all components. The two PC b ...
ADM208 数据手册DataSheet 下载
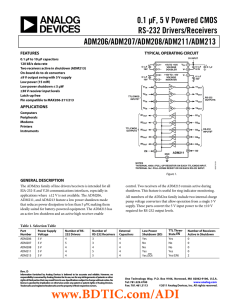
... specifications while using a single digital 5 V supply. The EIA232-E standard requires transmitters that will deliver ±5 V minimum on the transmission channel and receivers that can accept signal levels down to ±3 V. The ADM2xx meet these requirements by integrating step-up voltage converters and le ...
... specifications while using a single digital 5 V supply. The EIA232-E standard requires transmitters that will deliver ±5 V minimum on the transmission channel and receivers that can accept signal levels down to ±3 V. The ADM2xx meet these requirements by integrating step-up voltage converters and le ...
Application Note AN-3010 Using the QVE00033 Surface Mount Phototransistor Optical Interrupter Switch
... schematic shows, the logic output is high or “1” when the path is blocked. This is because the blocked phototransistor is conducting very little current, and the 68K load resistor pulls the input of Fairchild TinyLogic™ buffer high. As the shield is pulled out of the interrupter’s throat, the 0.4 mm ...
... schematic shows, the logic output is high or “1” when the path is blocked. This is because the blocked phototransistor is conducting very little current, and the 68K load resistor pulls the input of Fairchild TinyLogic™ buffer high. As the shield is pulled out of the interrupter’s throat, the 0.4 mm ...
Document
... power systems. Proposed system: A dual-phase-shift controlled soft-switching DC/DC converter for high-efficiency, wide voltage range and galvanic isolation application is proposed. With optimized control scheme, soft switching is achieved for all MOSFETs and diodes within a wide load range. Leakage ...
... power systems. Proposed system: A dual-phase-shift controlled soft-switching DC/DC converter for high-efficiency, wide voltage range and galvanic isolation application is proposed. With optimized control scheme, soft switching is achieved for all MOSFETs and diodes within a wide load range. Leakage ...
SP4633 1GHz 64 NON SELF OSCILLATING PRESCALER
... ■ Low Supply Current ■ Low Radiation ■ Input Wideband Amplifier ■ High Input Sensitivity ■ High Input Impedance ■ Balanced ECL Outputs ■ Electrostatic Protection † ...
... ■ Low Supply Current ■ Low Radiation ■ Input Wideband Amplifier ■ High Input Sensitivity ■ High Input Impedance ■ Balanced ECL Outputs ■ Electrostatic Protection † ...
Transistor–transistor logic

Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a class of digital circuits built from bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and resistors. It is called transistor–transistor logic because both the logic gating function (e.g., AND) and the amplifying function are performed by transistors (contrast with RTL and DTL).TTL is notable for being a widespread integrated circuit (IC) family used in many applications such as computers, industrial controls, test equipment and instrumentation, consumer electronics, synthesizers, etc. The designation TTL is sometimes used to mean TTL-compatible logic levels, even when not associated directly with TTL integrated circuits, for example as a label on the inputs and outputs of electronic instruments.After their introduction in integrated circuit form in 1963 by Sylvania, TTL integrated circuits were manufactured by several semiconductor companies, with the 7400 series (also called 74xx) by Texas Instruments becoming particularly popular. TTL manufacturers offered a wide range of logic gate, flip-flops, counters, and other circuits. Several variations from the original bipolar TTL concept were developed, giving circuits with higher speed or lower power dissipation to allow optimization of a design. TTL circuits simplified design of systems compared to earlier logic families, offering superior speed to resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and easier design layout than emitter-coupled logic (ECL). The design of the input and outputs of TTL gates allowed many elements to be interconnected.TTL became the foundation of computers and other digital electronics. Even after much larger scale integrated circuits made multiple-circuit-board processors obsolete, TTL devices still found extensive use as the ""glue"" logic interfacing more densely integrated components. TTL devices were originally made in ceramic and plastic dual-in-line (DIP) packages, and flat-pack form. TTL chips are now also made in surface-mount packages. Successors to the original bipolar TTL logic often are interchangeable in function with the original circuits, but with improved speed or lower power dissipation.