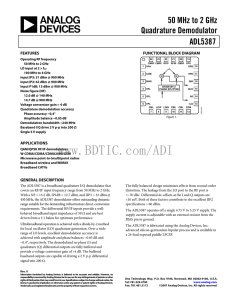
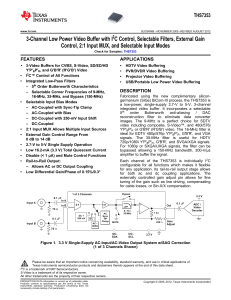
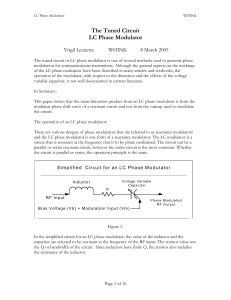
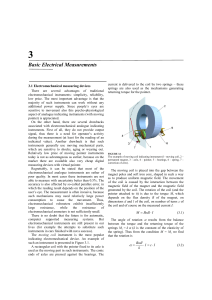
$doc.title
... † Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not implied. Exposure to ...
... † Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not implied. Exposure to ...
3 Basic Electrical Measurements
... low price. The most important advantage is that the majority of such instruments can work without any additional power supply. Since people’s eyes are sensitive to movement also this psycho-physiological aspect of analogue indicating instruments (with moving pointer) is appreciated. On the other han ...
... low price. The most important advantage is that the majority of such instruments can work without any additional power supply. Since people’s eyes are sensitive to movement also this psycho-physiological aspect of analogue indicating instruments (with moving pointer) is appreciated. On the other han ...
F81 User Guide - Funktion-One
... loudspeakers so that their high frequency units are approximately 2/3rds up the screen and then tilt them so that they aim approximately 2/3rds across the audience area. ...
... loudspeakers so that their high frequency units are approximately 2/3rds up the screen and then tilt them so that they aim approximately 2/3rds across the audience area. ...
ELEC 7770: Advanced VLSI Design Spring 2010 Radio Frequency (RF) Testing
... THD(%) = [(P2 + P3 + · · · ) / Pfundamental ] × 100% Or THD(%) = [(V22 + V32 + · · · ) / V2fundamental ] × 100% Where P2, P3, . . . , are the power in watts of second, third, . . . , harmonics, respectively, and Pfundamental is the fundamental signal power, And V2, V3, . . . , are voltage amplit ...
... THD(%) = [(P2 + P3 + · · · ) / Pfundamental ] × 100% Or THD(%) = [(V22 + V32 + · · · ) / V2fundamental ] × 100% Where P2, P3, . . . , are the power in watts of second, third, . . . , harmonics, respectively, and Pfundamental is the fundamental signal power, And V2, V3, . . . , are voltage amplit ...
Oscilloscopes and their Calibration
... attenuation ratios (i.e., Volts/Div settings) until the upper limit of the UUT is reached. The steps are repeated on any additional available vertical inputs. This process may be a throwback to earlier designs, where the lowest range commonly bypassed the vertical attenuator networks, delivering the ...
... attenuation ratios (i.e., Volts/Div settings) until the upper limit of the UUT is reached. The steps are repeated on any additional available vertical inputs. This process may be a throwback to earlier designs, where the lowest range commonly bypassed the vertical attenuator networks, delivering the ...
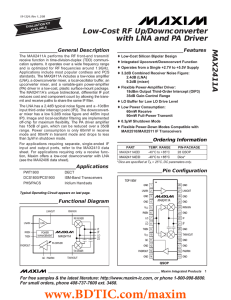
MAX2411A Low-Cost RF Up/Downconverter with LNA and PA Driver ________________General Description
... input third-order intercept point (IP3). The downconverter mixer has a low 9.2dB noise figure and 4dBm input IP3. Image and local-oscillator filtering are implemented off-chip for maximum flexibility. The PA driver amplifier has 15dB of gain, which can be reduced over a 35dB range. Power consumption ...
... input third-order intercept point (IP3). The downconverter mixer has a low 9.2dB noise figure and 4dBm input IP3. Image and local-oscillator filtering are implemented off-chip for maximum flexibility. The PA driver amplifier has 15dB of gain, which can be reduced over a 35dB range. Power consumption ...
Audio crossover

Audio crossovers are a class of electronic filter used in audio applications. Most individual loudspeaker drivers are incapable of covering the entire audio spectrum from low frequencies to high frequencies with acceptable relative volume and absence of distortion so most hi-fi speaker systems use a combination of multiple loudspeaker drivers, each catering to a different frequency band. Crossovers split the audio signal into separate frequency bands that can be separately routed to loudspeakers optimized for those bands.Active crossovers are distinguished from passive crossovers in that they divide the audio signal prior to amplification. Active crossovers come in both digital and analog varieties. Digital active crossovers often include additional signal processing, such as limiting, delay, and equalization.Signal crossovers allow the audio signal to be split into bands that are processed separately before they are mixed together again. Some examples are: multiband dynamics (compression, limiting, de-essing), multiband distortion, bass enhancement, high frequency exciters, and noise reduction such as Dolby A noise reduction.