1 The (Aggregate) Demand for State Lottery Tickets: What Have We
... commonly used to estimate cross-price elasticities for different lottery games implicitly assumes that there are no cross-price effects across lottery games, i.e. lottery games are neither substitutes or complements. To summarize thus far, it has been shown that only under the assumption that consu ...
... commonly used to estimate cross-price elasticities for different lottery games implicitly assumes that there are no cross-price effects across lottery games, i.e. lottery games are neither substitutes or complements. To summarize thus far, it has been shown that only under the assumption that consu ...
CHAPTER 6 CONSUMPTION AND THE COST OF LIVING I. Socially
... The socially necessary level of consumption is also constrained by the institutional structure of society. Quite apart from the technology of consumption, the institutional structure of society sets boundaries to the type of consumption workers are obligated to undertake. For example, firms expect t ...
... The socially necessary level of consumption is also constrained by the institutional structure of society. Quite apart from the technology of consumption, the institutional structure of society sets boundaries to the type of consumption workers are obligated to undertake. For example, firms expect t ...
Microeconomics, 4e (Perloff)
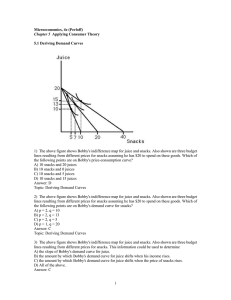
... 8) As the price of a good rises, the consumer will experience A) a desire to consume a different bundle. B) a decrease in utility. C) a southwesterly movement on the indifference map. D) All of the above. Answer: D Topic: Deriving Demand Curves 9) An increase in the price of a good causes A) a chang ...
... 8) As the price of a good rises, the consumer will experience A) a desire to consume a different bundle. B) a decrease in utility. C) a southwesterly movement on the indifference map. D) All of the above. Answer: D Topic: Deriving Demand Curves 9) An increase in the price of a good causes A) a chang ...
x 2
... rare cases of extreme incomeinferiority, the income effect may be larger in size than the substitution effect, causing quantity demanded to fall as own-price rises. Such goods are Giffen goods. ...
... rare cases of extreme incomeinferiority, the income effect may be larger in size than the substitution effect, causing quantity demanded to fall as own-price rises. Such goods are Giffen goods. ...
Lecture 3
... substitute towards oranges. The CPI overcompensates people for in‡ation by ignoring the fact that substitution towards cheaper goods occurs. ...
... substitute towards oranges. The CPI overcompensates people for in‡ation by ignoring the fact that substitution towards cheaper goods occurs. ...
ELASTICITY
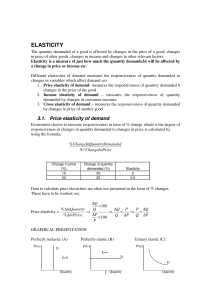
... 1. Income inelastic → EY < 1 (Dd rises by a smaller proportion as Y) 2. Unit income elasticity → EY = 1 (Dd rises by exactly the same proportion as Y) 3. Income elastic → EY > 1 (Dd rises by a greater proportion than Y) In the short run, people often save increases in income, so most goods except im ...
... 1. Income inelastic → EY < 1 (Dd rises by a smaller proportion as Y) 2. Unit income elasticity → EY = 1 (Dd rises by exactly the same proportion as Y) 3. Income elastic → EY > 1 (Dd rises by a greater proportion than Y) In the short run, people often save increases in income, so most goods except im ...
The Initial Incidence of a Carbon Tax across Income Groups
... of Maryland, bResources for the Future, cNational Bureau of Economic Research, dUniversity of Calgary. We thank the Center for Climate and Electricity Policy at Resources for the Future for support and Peter Wilcoxen for comments. The authors appreciate the excellent assistance of Samuel Grausz and ...
... of Maryland, bResources for the Future, cNational Bureau of Economic Research, dUniversity of Calgary. We thank the Center for Climate and Electricity Policy at Resources for the Future for support and Peter Wilcoxen for comments. The authors appreciate the excellent assistance of Samuel Grausz and ...
PDF
... theoretical basis (Deaton and Muellbauer 1980b), has a weighting scheme that may not reflect that in the original or chain indexes. The weighting schemes of the different price indexes are, of course, important for measuring real income in empirical analysis. For example if all prices were doubled, ...
... theoretical basis (Deaton and Muellbauer 1980b), has a weighting scheme that may not reflect that in the original or chain indexes. The weighting schemes of the different price indexes are, of course, important for measuring real income in empirical analysis. For example if all prices were doubled, ...
inferior goods - Gore High School
... Complements are good that are consumed together. Coffee and muffins are complements, When the price of coffee falls from P to P1 the quantity demanded of coffee increases from Q to Q1 cups a week and, Alexi will demand more muffins to go with the coffee. The increase in demand for muffins is shown a ...
... Complements are good that are consumed together. Coffee and muffins are complements, When the price of coffee falls from P to P1 the quantity demanded of coffee increases from Q to Q1 cups a week and, Alexi will demand more muffins to go with the coffee. The increase in demand for muffins is shown a ...
Answer on Question #54472, Economics / Economics of Enterprise
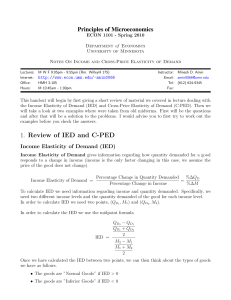
... We apply the formula noted above in order to determine the income elasticity of demand. Income Elasticity of Demand = ...
... We apply the formula noted above in order to determine the income elasticity of demand. Income Elasticity of Demand = ...
Lec 5
... When income elasticity is positive, the good is considered a “normal good.” An increase in income is correlated with an increase in the demand function. A decrease in income is associated with a decrease in the demand function. For both increases The greater the value of ey, the more responsive buy ...
... When income elasticity is positive, the good is considered a “normal good.” An increase in income is correlated with an increase in the demand function. A decrease in income is associated with a decrease in the demand function. For both increases The greater the value of ey, the more responsive buy ...
The Law of Demand: The Slutsky Equation
... Slutsky’s Effects for Normal Goods • Since both the substitution and income effects increase demand when own-price falls, a normal good’s ordinary demand curve slopes down. • The Law of Downward-Sloping Demand therefore always applies to normal goods. ...
... Slutsky’s Effects for Normal Goods • Since both the substitution and income effects increase demand when own-price falls, a normal good’s ordinary demand curve slopes down. • The Law of Downward-Sloping Demand therefore always applies to normal goods. ...
Lecture 5: Consumer Theory (cont`d)
... The income effect is the change in an item’s consumption brought about by the increase in purchasing power, with the price of the item held constant. When a person’s income increases, the quantity demanded for the product may increase or decrease. Even with inferior goods, the income effect is rarel ...
... The income effect is the change in an item’s consumption brought about by the increase in purchasing power, with the price of the item held constant. When a person’s income increases, the quantity demanded for the product may increase or decrease. Even with inferior goods, the income effect is rarel ...