CONCLUSION
... computer operating systems into an unrelated market (for Internet browsers). Allowing Microsoft to incorporate such products into its operating system, the government argued, would deter new software companies such as Netscape from entering the market and offering new products. Microsoft responded b ...
... computer operating systems into an unrelated market (for Internet browsers). Allowing Microsoft to incorporate such products into its operating system, the government argued, would deter new software companies such as Netscape from entering the market and offering new products. Microsoft responded b ...
Krugman`s Chapter 11 PPT
... It says that an individual who consumes only a little bit of good A and a lot of good B will be willing to trade off a lot of B in return for one more unit of A; an individual who already consumes a lot of A and not much B will be less willing to make that tradeoff. 16 of 47 ...
... It says that an individual who consumes only a little bit of good A and a lot of good B will be willing to trade off a lot of B in return for one more unit of A; an individual who already consumes a lot of A and not much B will be less willing to make that tradeoff. 16 of 47 ...
The Consumer Theory
... all of our trade transactions, we might as well use it as our comparative measure of utility. (Note: This way of measuring utility is not much different from measuring utility in utils) • Jill could say: I am willing to pay $4 for a burger, $2 for a slice of pizza and $1 for a hotdog. Note: Even tho ...
... all of our trade transactions, we might as well use it as our comparative measure of utility. (Note: This way of measuring utility is not much different from measuring utility in utils) • Jill could say: I am willing to pay $4 for a burger, $2 for a slice of pizza and $1 for a hotdog. Note: Even tho ...
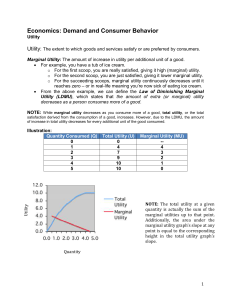
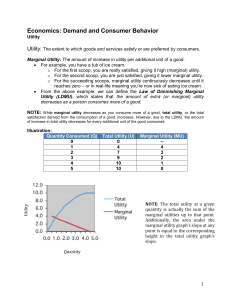
Economics: Demand and Consumer Behavior Utility Utility: The
... o On the other hand, since there are so few diamonds in the world, the marginal utility of the LAST diamond relative to that of the last glass of water is extremely high, since the amount of diamonds relative to water is extremely small; thus the water-diamond paradox.
...
... o On the other hand, since there are so few diamonds in the world, the marginal utility of the LAST diamond relative to that of the last glass of water is extremely high, since the amount of diamonds relative to water is extremely small; thus the water-diamond paradox.
Chapter 6: Household Behavior and Consumer Choice
... The Income Effect Price changes affect households in two ways. First, if we assume that households confine their choices to products that improve their well-being, then a decline in the price of any product, ceteris paribus, will make the household unequivocally better off. ...
... The Income Effect Price changes affect households in two ways. First, if we assume that households confine their choices to products that improve their well-being, then a decline in the price of any product, ceteris paribus, will make the household unequivocally better off. ...
Lecture 8 - people.vcu.edu
... divided into a “price box” and a “quantity box”. In the case of a price reduction, for example, the price box is the revenues lost from units that would have sold at the higher price (Dimension PQ). The quantity box denotes the extra revenues realized from lower the price (Dimension QP). The left ...
... divided into a “price box” and a “quantity box”. In the case of a price reduction, for example, the price box is the revenues lost from units that would have sold at the higher price (Dimension PQ). The quantity box denotes the extra revenues realized from lower the price (Dimension QP). The left ...
Notes 10: An Equation Based Model of the Macroeconomy
... Instead, I am doing it to formalize the intuition that we have already built. There is nothing new in what I am doing in this note. I am just putting simple functional forms on all the curves we already built. The math will just reinforce the intuition that we have already develope ...
... Instead, I am doing it to formalize the intuition that we have already built. There is nothing new in what I am doing in this note. I am just putting simple functional forms on all the curves we already built. The math will just reinforce the intuition that we have already develope ...
The Economic Way of Thinking 10e ©Prentice Hall 2003
... Marginal Opportunity Cost All opportunity cost are marginal cost and all marginal cost are opportunity cost. Opportunity cost calls attention to the value of the opportunity forgone by an action. Marginal cost calls attention to the change in the existing situation that the action entails. The full ...
... Marginal Opportunity Cost All opportunity cost are marginal cost and all marginal cost are opportunity cost. Opportunity cost calls attention to the value of the opportunity forgone by an action. Marginal cost calls attention to the change in the existing situation that the action entails. The full ...
Economics for Today 2005
... complementary explanations for the law of demand. When the price changes, these effects work in combination to change in the quantity demanded in the opposite directions. ...
... complementary explanations for the law of demand. When the price changes, these effects work in combination to change in the quantity demanded in the opposite directions. ...
Middle-class squeeze

The middle-class squeeze is the situation where increases in wages fail to keep up with inflation for middle-income earners, while at the same time, the phenomenon fails to have a similar impact on the top wage earners. Persons belonging to the middle class find that inflation in consumer goods and the housing market prevent them from maintaining a middle-class lifestyle, making downward mobility a threat to aspirations of upward mobility. In the United States for example, middle-class income is declining while many goods and services are increasing in price, such as education, housing, child care and healthcare.