2016 Q7 - Loreto Balbriggan
... A lot of the water will vaporise on falling In a heat pump, a fluid is used to transfer energy from a cold body to a warmer body. Describe the operation of a heat pump and explain how a heat pump can be used to reduce the temperature of a cold region, for example the interior of a refrigerator. Text ...
... A lot of the water will vaporise on falling In a heat pump, a fluid is used to transfer energy from a cold body to a warmer body. Describe the operation of a heat pump and explain how a heat pump can be used to reduce the temperature of a cold region, for example the interior of a refrigerator. Text ...
How Your Body Loses Heat
... Convection is simply heat loss caused by cooler air or water coming into contact with the skin. Just as you cool your cup of coffee by blowing on it, your body cools as the wind whips past. Minimizing exposed skin is the easiest way to prevent this. A better way is to ensure that your skin is covere ...
... Convection is simply heat loss caused by cooler air or water coming into contact with the skin. Just as you cool your cup of coffee by blowing on it, your body cools as the wind whips past. Minimizing exposed skin is the easiest way to prevent this. A better way is to ensure that your skin is covere ...
Cold Weather Heat Pump Operation Air to Air heat Pump Systems
... During the heating mode the unit extracts heat from the outside air and rejects it into the living space. During the cooling mode the unit extracts heat from the inside space and rejects it outside. As you can see from this operation the colder it gets the harder the machine has to work to extract h ...
... During the heating mode the unit extracts heat from the outside air and rejects it into the living space. During the cooling mode the unit extracts heat from the inside space and rejects it outside. As you can see from this operation the colder it gets the harder the machine has to work to extract h ...
The Specific Heat Capacity of Metals
... it to boil for about five minutes so that the metal reaches the temperature of the boiling water. Take the temperature of the water. Assume this is also the temperature of the metal. Record this temperature in the table. 3. Add 100 g of cold water to an insulated cup. Quickly remove the metal sample ...
... it to boil for about five minutes so that the metal reaches the temperature of the boiling water. Take the temperature of the water. Assume this is also the temperature of the metal. Record this temperature in the table. 3. Add 100 g of cold water to an insulated cup. Quickly remove the metal sample ...
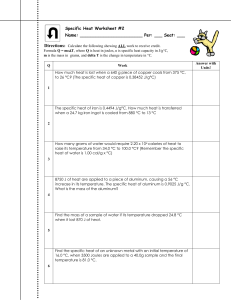
Specific Heat WS #2 - My Chemistry Class
... Directions: Calculate the following showing ALL work to receive credit. Formula Q = mcT, where Q is heat in joules, c is specific heat capacity in J/gC, m is the mass in grams, and delta T is the change in temperature in C. ...
... Directions: Calculate the following showing ALL work to receive credit. Formula Q = mcT, where Q is heat in joules, c is specific heat capacity in J/gC, m is the mass in grams, and delta T is the change in temperature in C. ...
09-TempControls
... • Daytime: cloud cover reflects sunlight = colder • Nighttime: cloud cover traps energy = warmer ...
... • Daytime: cloud cover reflects sunlight = colder • Nighttime: cloud cover traps energy = warmer ...
Hypothermia - CMA
... information of the receptors is processed and compared with the desired temperature. When needed, thermoregulation will take place from the hypothalamus to adjust the core temperature. The blood flow in the skin can be adjusted; by narrowing less blood flows through the vessels and less heat will be ...
... information of the receptors is processed and compared with the desired temperature. When needed, thermoregulation will take place from the hypothalamus to adjust the core temperature. The blood flow in the skin can be adjusted; by narrowing less blood flows through the vessels and less heat will be ...
Analysis of existing refrigeration plants onboard fishing
... used to obtain very high cooling power. To achieve compression ratios up to 1:20, oil cooling is necessary, so effective oil separators should be provided; it must be taken into account that this oil pressure reduces the system efficiency, increasing the compressor power requirements and reducing ca ...
... used to obtain very high cooling power. To achieve compression ratios up to 1:20, oil cooling is necessary, so effective oil separators should be provided; it must be taken into account that this oil pressure reduces the system efficiency, increasing the compressor power requirements and reducing ca ...
Problems
... Establish the direction of flow air in the duct. Assume air as and ideal gas having Cp= 1.005 & R=0.287kJ/kg. 3.6: What is the maximum useful work, which can be obtained when 100kJ is extracted from a heat reservoir at 675 K In an environment at 288 K? What is the loss of useful work or availability ...
... Establish the direction of flow air in the duct. Assume air as and ideal gas having Cp= 1.005 & R=0.287kJ/kg. 3.6: What is the maximum useful work, which can be obtained when 100kJ is extracted from a heat reservoir at 675 K In an environment at 288 K? What is the loss of useful work or availability ...
contents - UET Mechanical 09
... heat without exhibiting any increase in temperature. A heat sink temperature rise of 5 to 15°C above ambient (or cooling fluid) is typical for many thermoelectric applications. Heat sink performance:- Qs= (Ts-Ta)/Q ...
... heat without exhibiting any increase in temperature. A heat sink temperature rise of 5 to 15°C above ambient (or cooling fluid) is typical for many thermoelectric applications. Heat sink performance:- Qs= (Ts-Ta)/Q ...
Exercises – Chapter 8
... 15. Freezing and thawing cycles tend to damage road pavement during the winter, creating potholes. What provides the mechanical work that breaks up the pavement? E.15 Heat flowing into or out of the pavement during weather changes allows the pavement to do work as it tears itself apart. 16. The air ...
... 15. Freezing and thawing cycles tend to damage road pavement during the winter, creating potholes. What provides the mechanical work that breaks up the pavement? E.15 Heat flowing into or out of the pavement during weather changes allows the pavement to do work as it tears itself apart. 16. The air ...
Entropy - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... (5% later lost to air, tire friction) only 25% left for acceleration ...
... (5% later lost to air, tire friction) only 25% left for acceleration ...
HEAT ENERGY
... Gases, including air are poor conductors,e.g., wool feels warm because it traps a lot of air A fridge has insulation material round it to keep it cold – reduces amount of heat conducted to inside from the warmer room ...
... Gases, including air are poor conductors,e.g., wool feels warm because it traps a lot of air A fridge has insulation material round it to keep it cold – reduces amount of heat conducted to inside from the warmer room ...
Nernst`s postulate derived directly from the vanishing heat capacity
... It is worthwhile pointing out that when T is very small, so is −(∆T )S , whereas (∆yi )S need not be small. It may have a finite value which can be varied by controlling the exterior conditions, whether the temperature of the system is high or low [1,2]. In fact, this observation has been used extens ...
... It is worthwhile pointing out that when T is very small, so is −(∆T )S , whereas (∆yi )S need not be small. It may have a finite value which can be varied by controlling the exterior conditions, whether the temperature of the system is high or low [1,2]. In fact, this observation has been used extens ...
Process Heat Transfer Lab - University of Engineering and Technology
... provided, free and forced convective heat transfer coefficients may be determined for, a flat surface, an array of cylinders, and an array of fins. ...
... provided, free and forced convective heat transfer coefficients may be determined for, a flat surface, an array of cylinders, and an array of fins. ...
193008 - Thermal Hydraulics
... cooldown is in progress with steam release from the steam generator (SG) atmospheric steam relief valves (operated in manual control). If high point voiding interrupts natural circulation, which one of the following will occur? (Assume feedwater flow rate, SG relief valve position, and core decay he ...
... cooldown is in progress with steam release from the steam generator (SG) atmospheric steam relief valves (operated in manual control). If high point voiding interrupts natural circulation, which one of the following will occur? (Assume feedwater flow rate, SG relief valve position, and core decay he ...
Thermodynamics - Bowles Physics
... QH = remove from, absorbs = hot QC= exhausts to, expels = cold ...
... QH = remove from, absorbs = hot QC= exhausts to, expels = cold ...
Ch.19 (section 1 only)
... Device that uses heat to perform work Hot Reservoir (e.g. steam) Cool Reservoir (e.g. pool of water) Efficiency is work done per unit of input heat (e = W/QH) • Ex. A heat engine does 100J of work when given 300J from the hot reservoir. The efficiency is 100J/300J = 0.33 = ...
... Device that uses heat to perform work Hot Reservoir (e.g. steam) Cool Reservoir (e.g. pool of water) Efficiency is work done per unit of input heat (e = W/QH) • Ex. A heat engine does 100J of work when given 300J from the hot reservoir. The efficiency is 100J/300J = 0.33 = ...
Thermal Management of High Power in Small Spaces
... described as a change in the temperature of the air particles adjacent to the warm surface of the system dissipating heat. The temperature of these air particles is increased, thus changing their local density and causing these higher temperature fluid particles to become more buoyant in comparison ...
... described as a change in the temperature of the air particles adjacent to the warm surface of the system dissipating heat. The temperature of these air particles is increased, thus changing their local density and causing these higher temperature fluid particles to become more buoyant in comparison ...
module 6 humidification and air conditioning
... Thus, cooling is accomplished by sensible heat transfer from water to air and evaporation of a small portion of water. A generalized cooling tower system is shown in Figure 6.4. The hot water which is coming from heat exchanger is sprayed at the top of the cooling tower. Air enters through the louve ...
... Thus, cooling is accomplished by sensible heat transfer from water to air and evaporation of a small portion of water. A generalized cooling tower system is shown in Figure 6.4. The hot water which is coming from heat exchanger is sprayed at the top of the cooling tower. Air enters through the louve ...
PDF:31.9KB
... Generally, a flat-type device is pressed between cooling fins prior to use. In this process, the following points regarding the design should be considered carefully. If these points are not satisfied, the device may offer insufficient performance or become damaged. (1) Design a suitable stack whose ...
... Generally, a flat-type device is pressed between cooling fins prior to use. In this process, the following points regarding the design should be considered carefully. If these points are not satisfied, the device may offer insufficient performance or become damaged. (1) Design a suitable stack whose ...
Radiator (engine cooling)

Radiators are heat exchangers used for cooling internal combustion engines, mainly in automobiles but also in piston-engined aircraft, railway locomotives, motorcycles, stationary generating plant or any similar use of such an engine.Internal combustion engines are often cooled by circulating a liquid called engine coolant through the engine block, where it is heated, then through a radiator where it loses heat to the atmosphere, and then returned to the engine. Engine coolant is usually water-based, but may also be oil. It is common to employ a water pump to force the engine coolant to circulate, and also for an axial fan to force air through the radiator.