The Specific Heat Capacity of Metals
... lower temperature is equal to the heat lost by the object at the higher temperature. ...
... lower temperature is equal to the heat lost by the object at the higher temperature. ...
Heat Transfer
... When the energy of the sun hits an object, some of the sun’s energy is transferred to the object’s molecules, heating them. When heat is transferred by invisible waves is this is called radiation. When a person touches that warmed object then some of the energy in the object’s molecules is transfer ...
... When the energy of the sun hits an object, some of the sun’s energy is transferred to the object’s molecules, heating them. When heat is transferred by invisible waves is this is called radiation. When a person touches that warmed object then some of the energy in the object’s molecules is transfer ...
Specific Heat Equation Practice Worksheet
... c. Determine the heat capacity of a substance using mass, specific heat, and temperature. You have probably noticed that a metal spoon heats up quickly when placed in a cup of soap while a plastic spoon heats more slowly. The difference between the final temperatures of the two spoons depends on whe ...
... c. Determine the heat capacity of a substance using mass, specific heat, and temperature. You have probably noticed that a metal spoon heats up quickly when placed in a cup of soap while a plastic spoon heats more slowly. The difference between the final temperatures of the two spoons depends on whe ...
~therm= heat,temperature
... • An organism that has adapted to living in very high temperatures or heat, such as bacteria or algae ...
... • An organism that has adapted to living in very high temperatures or heat, such as bacteria or algae ...
1-14 The filament of a 150 W incandescent lamp is 5 cm long and
... 1-105 A 1000-W iron is left on the iron board with its base exposed to the air at 20°C. The temperature of the base of the iron is to be determined in steady operation. Assumptions 1 Steady operating conditions exist. 2 The thermal properties of the iron base and the convection heat transfer coeffi ...
... 1-105 A 1000-W iron is left on the iron board with its base exposed to the air at 20°C. The temperature of the base of the iron is to be determined in steady operation. Assumptions 1 Steady operating conditions exist. 2 The thermal properties of the iron base and the convection heat transfer coeffi ...
Thermodynamics lesson 1 Tempersture
... ΔL = k L ΔT So? Well the amount something expands when heated depends on how long it was in the first place (L), the amount it’s temperature changes (ΔT) and something to do with the material (k) called the coefficient of thermal expansion. ...
... ΔL = k L ΔT So? Well the amount something expands when heated depends on how long it was in the first place (L), the amount it’s temperature changes (ΔT) and something to do with the material (k) called the coefficient of thermal expansion. ...
Name Date Class THE FLOW OF ENERGY—HEAT AND WORK
... Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 9. The joule is the SI unit of force. 10. Endothermic processes absorb heat from the surroundings. ...
... Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 9. The joule is the SI unit of force. 10. Endothermic processes absorb heat from the surroundings. ...
Specific Heat and Calorimeters
... 5) How much heat energy is needed to raise the temperature of a 425 g aluminum baking sheet from room temperature, 25 OC, to a baking temperature of 200 OC (the specific heat of aluminum is 0.897 J/g •OC)? ...
... 5) How much heat energy is needed to raise the temperature of a 425 g aluminum baking sheet from room temperature, 25 OC, to a baking temperature of 200 OC (the specific heat of aluminum is 0.897 J/g •OC)? ...
Chapter 11 Notes - Net Start Class
... • calorie - the amount of heat it takes to raise one gram of water by one degree celsius • (note: this is different from a food Calorie, which is actually 1 kilocalorie) • Joules: 4.184 Joules = 1 calorie ...
... • calorie - the amount of heat it takes to raise one gram of water by one degree celsius • (note: this is different from a food Calorie, which is actually 1 kilocalorie) • Joules: 4.184 Joules = 1 calorie ...
AA2 FALL 2005
... Conduction is the process through which heat is diffused to cooler materials as radiation is absorbed. Land surfaces heat quickly, while water bodies can mix and have higher heat capacity. Solids (land) are better conductors than gases (atmosphere). Convection is physical mixing with a strong vertic ...
... Conduction is the process through which heat is diffused to cooler materials as radiation is absorbed. Land surfaces heat quickly, while water bodies can mix and have higher heat capacity. Solids (land) are better conductors than gases (atmosphere). Convection is physical mixing with a strong vertic ...
Chapter 11 1. While checking the temperature of an IC. chip the
... with an inside temperature of 4500F sitting in a room of temperature 720F. What is the heat flow out of the oven in BTU? 7. A power transistor bank is mounted on a 1kg aluminum heat sink. The transistors dissapates 500W and all this heat flows into the sink. What is the change in temperature of the ...
... with an inside temperature of 4500F sitting in a room of temperature 720F. What is the heat flow out of the oven in BTU? 7. A power transistor bank is mounted on a 1kg aluminum heat sink. The transistors dissapates 500W and all this heat flows into the sink. What is the change in temperature of the ...
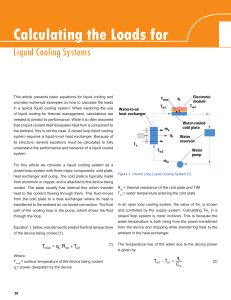
Calculating the Loads for Liquid cooling Systems
... This article presents basic equations for liquid cooling and provides numerical examples on how to calculate the loads in a typical liquid cooling system. When exploring the use of liquid cooling for thermal management, calculations are needed to predict its performance. While it is often assumed th ...
... This article presents basic equations for liquid cooling and provides numerical examples on how to calculate the loads in a typical liquid cooling system. When exploring the use of liquid cooling for thermal management, calculations are needed to predict its performance. While it is often assumed th ...
Cold Weather Heat Pump Operation Air to Air heat Pump Systems
... Air to Air heat Pump Systems (Different for Water to Air Systems) The basic theory behind the operation of a heat pump system is as follows. During the heating mode the unit extracts heat from the outside air and rejects it into the living space. During the cooling mode the unit extracts heat from t ...
... Air to Air heat Pump Systems (Different for Water to Air Systems) The basic theory behind the operation of a heat pump system is as follows. During the heating mode the unit extracts heat from the outside air and rejects it into the living space. During the cooling mode the unit extracts heat from t ...
21.3 Administering Heat/Cold Applications
... Usually a patient sits on a pan of warm water over a toilet and tubing irrigates the effected area ...
... Usually a patient sits on a pan of warm water over a toilet and tubing irrigates the effected area ...
Heat, Enthalpy, Temperature
... o Food is burned to release energy (like burning wood for fire) o The energy is absorbed by water o Using specific heat of water and temperature change of known mass of water the heat can be calculated. o This amount of heat is the amount of energy that is available for your body. It is what determi ...
... o Food is burned to release energy (like burning wood for fire) o The energy is absorbed by water o Using specific heat of water and temperature change of known mass of water the heat can be calculated. o This amount of heat is the amount of energy that is available for your body. It is what determi ...
Title - Iowa State University
... 9: If 20.0 g of solid NaOH are added to 1000 mL of a solution containing 0.500 moles of HCl, the temperature of the solution rises 6.9oC. Assuming that the total solution mass is 1000 g and the specific heat of the solution is 4.184 J/goC, calculate the heat released by this reaction. Then calculate ...
... 9: If 20.0 g of solid NaOH are added to 1000 mL of a solution containing 0.500 moles of HCl, the temperature of the solution rises 6.9oC. Assuming that the total solution mass is 1000 g and the specific heat of the solution is 4.184 J/goC, calculate the heat released by this reaction. Then calculate ...
Heat exchanger

A heat exchanger is a device used to transfer heat between one or more fluids. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contact. They are widely used in space heating, refrigeration, air conditioning, power stations, chemical plants, petrochemical plants, petroleum refineries, natural-gas processing, and sewage treatment. The classic example of a heat exchanger is found in an internal combustion engine in which a circulating fluid known as engine coolant flows through radiator coils and air flows past the coils, which cools the coolant and heats the incoming air.